What is the minidisc, How the minidisc got so small, Premastered mds – Sony MDS-101 User Manual
Page 5: Recordable mds, Recording mechanism, Parts making up a minidisc, How quick random access and the toc systems work
Attention! The text in this document has been recognized automatically. To view the original document, you can use the "Original mode".
What Is the MiniDisc?
How MiniDiscs work
How the MiniDisc got so small
MiniDiscs (MD) come in two types: premastered
(prerecorded) and recordable (blank). Premastered MOs,
recorded at music studios, can be played back almost
endlessly. However, they can’t be recorded on or over like
cassette tapes. To record, you use a ‘‘recordable MD”.
Premastered MDs
Premastered MDs are recorded and played like regular CDs.
A laser beam focuses on the pits in the surface of the MD
and reflects the data back to the lens in the recorder. The
recorder then decodes the signals and plays them back as
music.
Recordable MDs
Recordable MDs, which use magneto-optical (MO)
technology, can be recorded again and again. The laser
inside the recorder applies heat to the MD, demagnetizing
the magnetic layer of the MD. (See illustration below.) The
recorder then applies a magnetic field to the layer. This
magnetic field corresponds exactly to the audio signals
generated by the connected source. (The north and south
polarities equate to digital “1" and “0”.) The demagnetized
MD adopts the polarity of the magnetic field, resulting in a
recorded MD.
■ Recording Mechanism
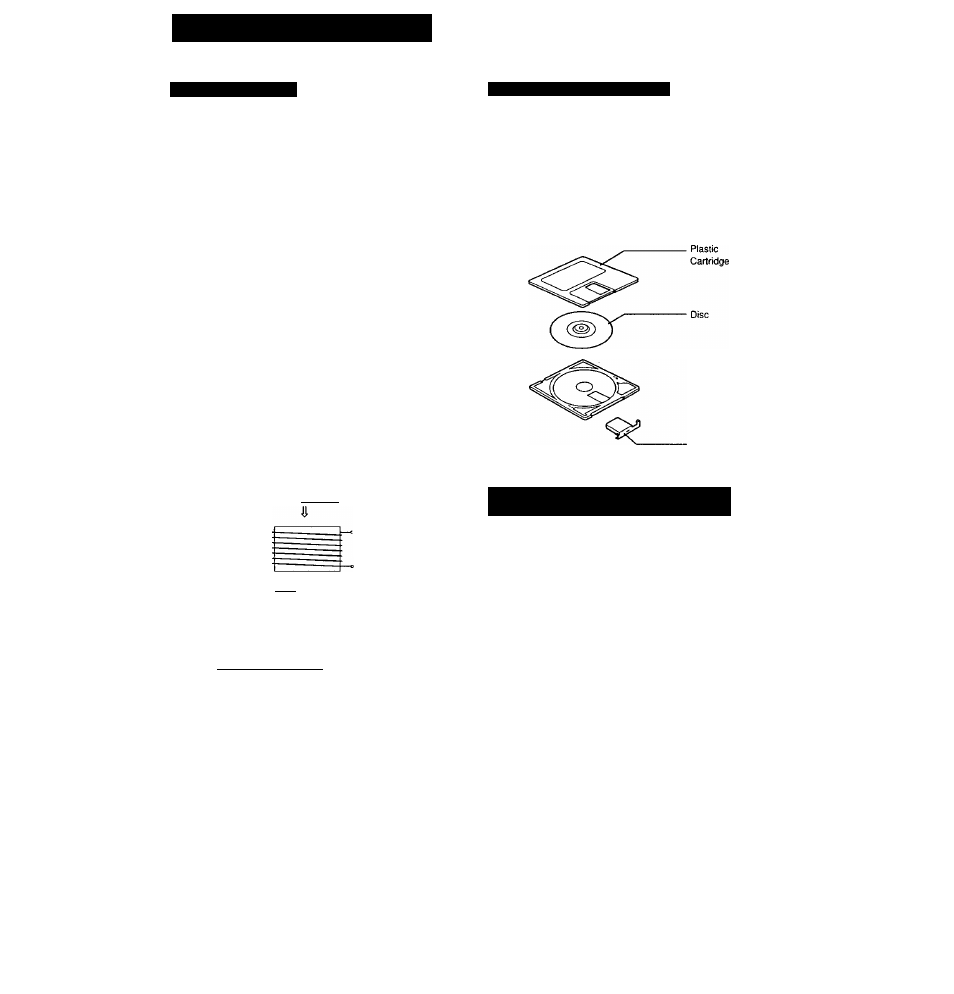
The 2.5-inch MiniDisc, encased in a plastic cartridge that
looks like a 3.5-inch diskette (see Illustration below), uses a
new digital audio compression technology called ATRAC
(Adaptive TRansform Acoustic Coding). To store more sound
In less space, ATRAC extracts and encodes only those
frequency components actually audible to the human ear.
■ Parts Making Up a MiniDisc
Shutter
Head Drive Signal
ih П П
Recording Head
tTttttttttttt
Magnetic
Field
О I-
Cross-Sectional
View
Recorded Pattern
ЕЕЕПЗЕХНН:
Laser Beam
M ove direction New
Old
n
(
s
( N (
S~~T^S~(
n
(
Recorded Pattern
How Quick Random Access and the TOC
systems work
Like CDs, MDs offer instantaneous random access to the
beginning of any music track. Premastered MDs are
recorded with location addresses corresponding to each
music selection. Recordable MDs are manufactured with a
"User TOC* Area” to contain the order of the music. The
TOC system is similar to the “directory management system"
of floppy disks. In other words, starting and ending
addresses for all music tracks recorded on the disc are
stored in this area. This lets you randomly access the
beginning of any track as soon as you enter the track
number (AMS), as well as label the location with a track
name as you would a file on a diskette.
* TOC is the acronym for Table of Contents.
