Banner Safe Speed Monitoring Modules User Manual
Page 5
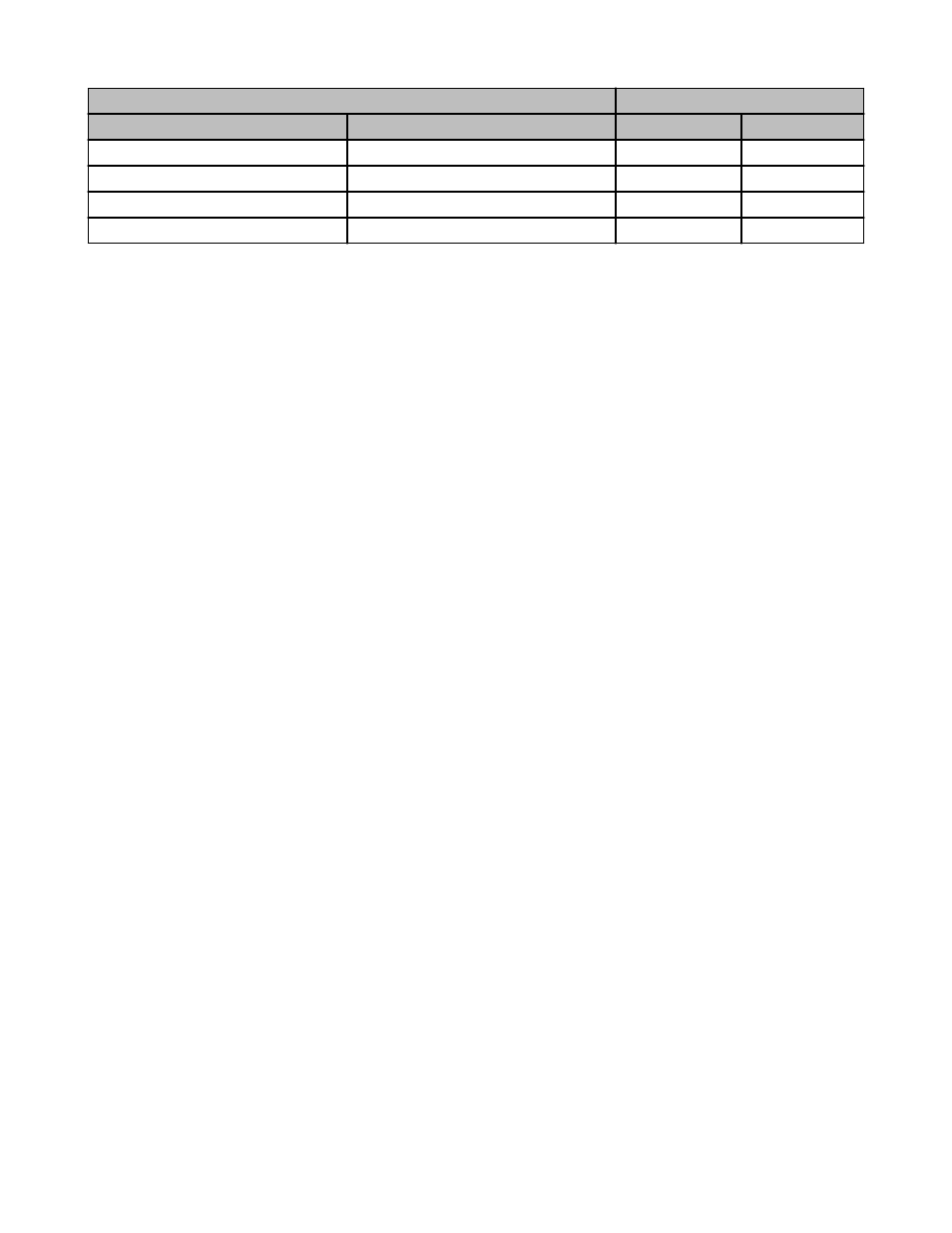
Range Settings
DIP Switch Banks A and B
Model SSM-…10
Model SSM-…20
1
2
5–40 ipm
10–80 ipm
OFF
OFF
1,200–10,500
2,400–20,000
OFF
ON
300–2,700
600–5,300
ON
OFF
35–340 ipm
80–650 ipm
ON
ON
Adjusting the Switch Point Value
The Module's four impulse-per-minute (ipm) ranges are selected via redundant pairs of DIP switches, as shown in the table. To access the DIP switches, insert a small flat-
blade screwdriver in the slot behind the Module's front panel, and pry the front panel off.
To adjust the switch point to any value, first select the range via the DIP switches. Then select the value within that range via the fine-tuning potentiometer, using either of
two methods.
Approximate Method
The mechanical range of the potentiometer is 270°. Because the potentiometer is linear, set the approximate values as in the following example:
• Desired switching point: 1,400 ipm
• Selected range: 300 to 2,700 ipm
• Potentiometer range delta: 2,700 ipm minus 300 ipm = 2,400 ipm
With the potentiometer dial all the way to the left (counterclockwise), the switch point is at 300 ipm. To increase the setting to 1,400 ipm, 1,100 ipm (1,400 minus 300 =
1,100 ipm) must be added:
[270 degrees ÷ 2,400 ipm (total range)] x 1,100 ipm = 123.75 degrees
Starting from the left, turn the potentiometer dial 123.75° clockwise. The middle position of the potentiometer is 135° (or 1,200 ipm), so the setting is just a few degrees
right from the middle position. This method provides only an approximate value.
More Precise Method
Measure the motor speed, including the speeds to be detected as over-speed, under-speed or zero speed (standstill), using an rpm meter.
Adjusting Simultaneity
The input channels are factory pre-adjusted; use the simultaneity potentiometer (behind the Module's front cover) to further synchronize the input channel timing.
1. Start the motor.
The safety output contacts and indicators should turn OFF (safety contacts open), as soon as the motor speed passes the switch point.
2. Stop the motor.
After the motor speed drops below the switch point value and after the selected delay time, the safety output contacts and indicators should turn ON.
3. If only one of the two channels detects the low-speed condition, restart the motor and turn the simultaneity potentiometer a few degrees clockwise (or counterclock-
wise, depending on which of the two channels switched first) to adjust the simultaneity. Repeat this procedure until both channels detect standstill and turn OFF both
internal relays simultaneously.
Configuring for Under-speed Detection
Under-speed detection is detecting a low speed anywhere within the set range of the Module. For this example, we are using 500 ipm.
1. Turn OFF power to the Module.
2. Using a small flat-blade screwdriver, pry open the Module's front plate.
3. Using the four DIP switches, select a switching range of 300-2,700 or 80-650, depending on the model.
4. Turn the fine-tune potentiometer counterclockwise to the 1 setting.
5. Set the simultaneity potentiometer to the middle position (0).
6. If sensors are not yet installed, install them now so that they can detect the rotation of the motor.
7. Connect the sensors to the Module.
8. Disconnect the wires from the Module safety output contacts 13-14 and 23-24.
9. Connect power to the Module; the Motor should still be OFF.
The Module's Power LED must come ON immediately. The safety output contacts (13-14 and 23-24) and indicators should come ON after no more than a 3-second
time delay, indicating a standstill condition.
10. Start the motor and run it at the speed you want to detect as under-speed (for this example, 500 ipm).
11. The N.C. safety output contacts and indicators must turn OFF.
SSM-FM-11A... Safe Speed Monitoring Modules
P/N 140782 rev. C
www.bannerengineering.com - tel: 763-544-3164
5
