Custom data block (cdb), Chapter 3 – Rockwell Automation 1771-SPI,D17716.5.122 SPI PROTOCOL INTERFACE User Manual
Page 30
Defining Command and Status Blocks
Chapter 3
3-8
Custom data blocks (CDBs) are used with custom configuration blocks
(CCBs) blocks to communicate with devices on the SPI network via the
SPI module. For a specified device on the SPI network, the custom
configuration block (CCB) tells the SPI module:
the type of data in each word, specified by SPI command-code pairs
the location of data, specified by word number
the order in which it will store the data
Custom data blocks must obey the “specs” of custom configuration blocks.
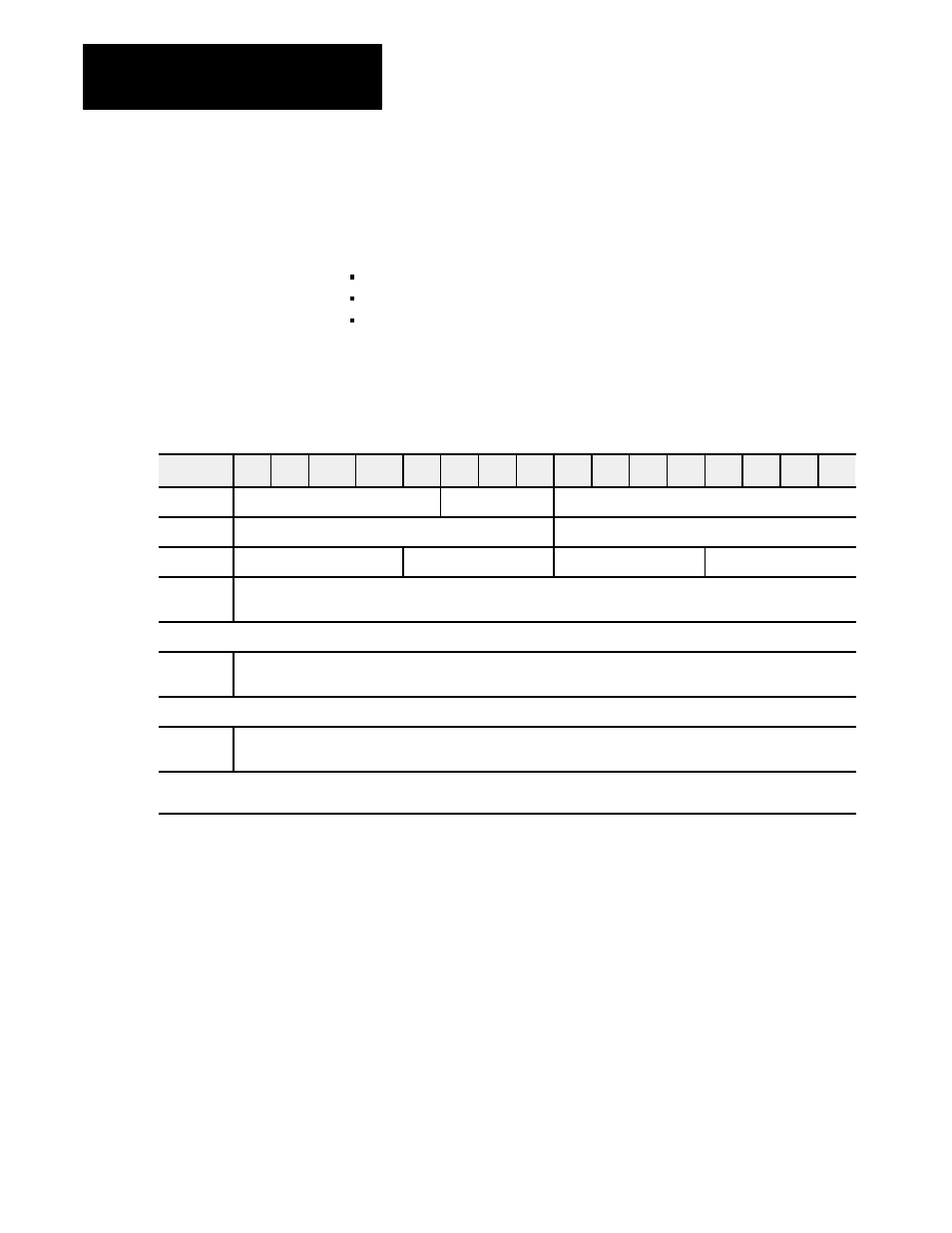
Table 3.G
Word/Bit Map of the Custom Data Block (CDB)
Word
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
1
0
DC
SPIĆspecified Device ID
2
Zone Address (for temperature control devices, only)
Device Address
3 and 4
0
0
0
0
starting at
5
Load bitĆcommand words for BTW to the SPI module whose code(s) you specified in the CCB block.
[ 1 ]
(If you specified none in the CCB block, start loading numeric setpoints here.)
:
:
:
:
:
:
two words Load numeric presets for BTW to the SPI module whose code(s) you specified in the CCB block.
[ 1 ]
(Numeric setpoints are 32Ćbit words, equivalent to 2 PLC words)
:
:
:
:
:
:
two words Load ASCII strings for BTW to the SPI module whose code(s) you specified in the CCB block.
[ 1 ]
(ASCII strings are 32Ćbit words, equivalent to 2 PLC words)
[ 1 ]:
Command words that you load in this CDB must match the SPI command codes that you loaded in the CCB.
They must match in type, quantity and order. Otherwise, the SPI module declares a fault.
Custom Data Block (CDB)
