Array data structures, Array – Rockwell Automation 1756-XXXX ControlLogix Digital I/O Modules User Manual
Page 211
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-UM058G-EN-P - November 2012
211
Tag Definitions
Appendix B
Array Data Structures
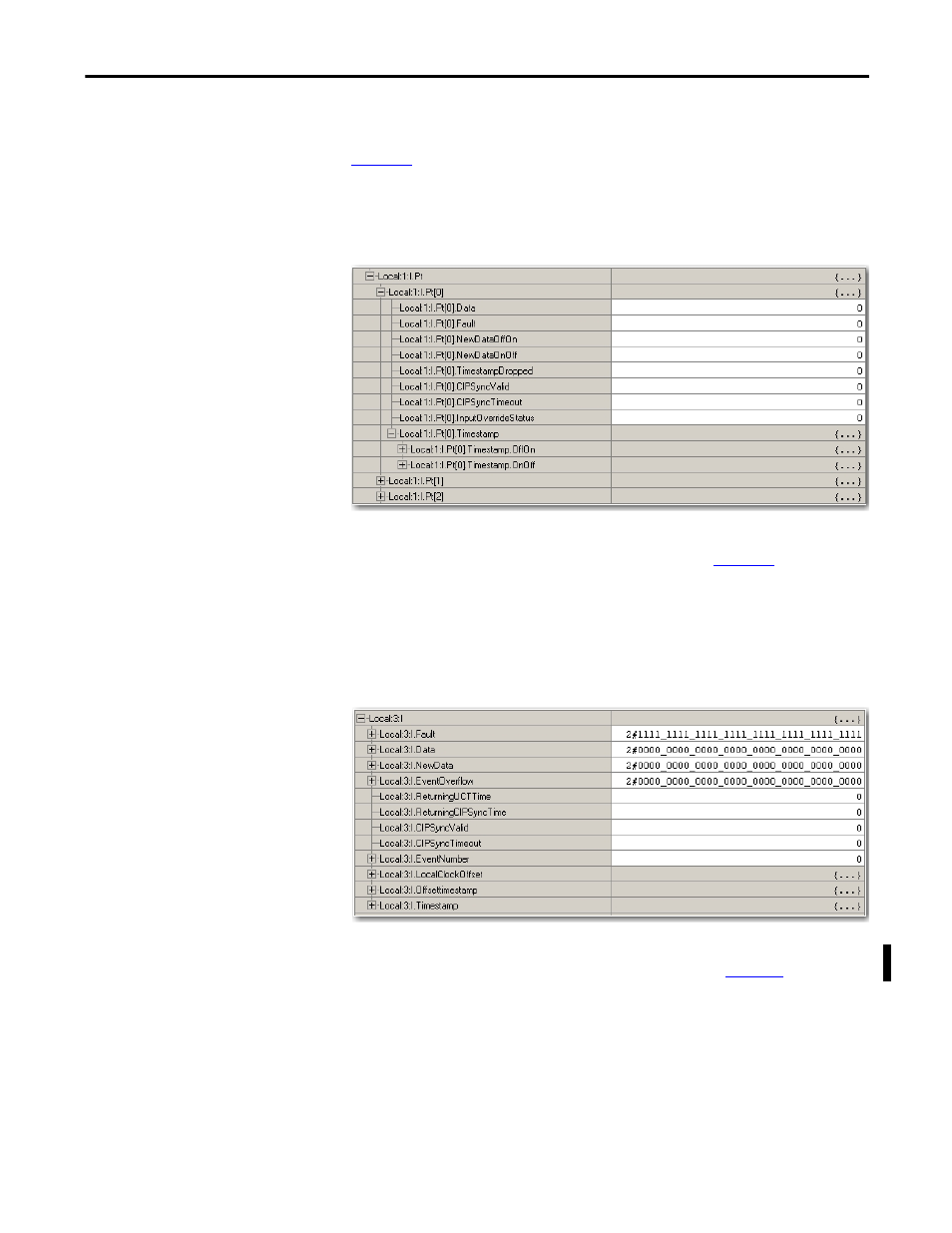
Fast digital I/O modules use an array data structure. In this type of structure, all
the tags for a particular point are organized under that point. For example, in
, all of the tags that appear under point 0 also appear under points 1…15
for the input module in slot 1. With this structure, you can copy or access all of
the data for a particular point by simply referencing or copying the point or alias
for the point, such as Pt[3] or PressureValveTank3.
Figure 26 - Array Data Structure
Other digital I/O modules use a flat data structure. In this type of structure, only
one instance of a tag exists for a module. For example, in
Figure 27
, only one
instance of each tag appears under the input module in slot 3. To reference or
copy data for an individual point, you specify the tag name followed by a bit
number, such as Data.0 or EventOverflow.3. Unlike an array structure where all
the data for a point can be accessed via a single tag reference, a flat structure
requires multiple tag references to access all the data for a point.
Figure 27 - Flat Data Structure
The 1756-OB16IEFS module uses either type of data structure depending on
how you configure the module. For more information, see
