Configuration by eeprom, 1 pin descriptions, 2 eeprom hardware interface – Cirrus Logic CS5378 User Manual
Page 25: 3 eeprom organization, Pin descriptions, Eeprom hardware interface, Eeprom organization, Figure 14. eeprom configuration block diagram, Cs5378, Sck - pin 24
CS5378
DS639F3
25
8. CONFIGURATION BY EEPROM
After reset, the CS5378 reads the state of the
GPIO7:BOOT pin to determine a source for con-
figuration commands. If BOOT is high, the
CS5378 initiates serial transactions to read config-
uration information from an external EEPROM.
8.1 Pin Descriptions
Pins required for EEPROM boot are listed here,
other serial pins are inactive.
SCK - Pin 24
Serial clock output, nominally 1.024 MHz.
MISO - Pin 25
Serial data input pin. Valid on rising edge of SCK,
transition on falling edge.
MOSI - Pin 26
Serial data output pin. Valid on rising edge of
SCK, transition on falling edge.
SS:EECS - Pin 27
EEPROM chip select output, active low.
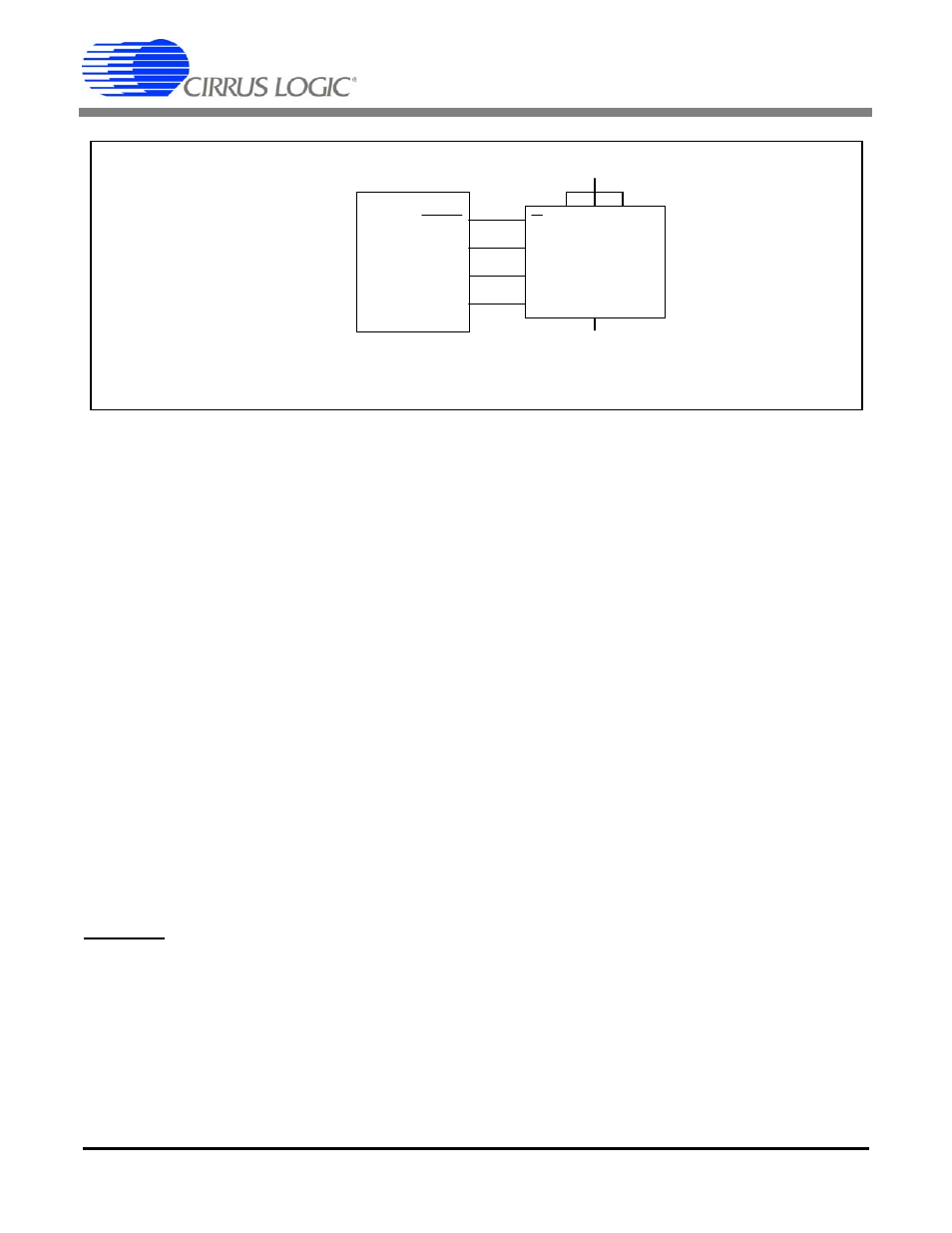
8.2 EEPROM Hardware Interface
When booting from EEPROM the CS5378 actively
performs serial transactions, as shown in Figure 15,
to read configuration commands and data. 8-bit
SPI opcodes and 16-bit addresses are combined to
read back 8-bit configuration commands and 24-bit
configuration data.
System design should include a connection to the
configuration EEPROM for in-circuit reprogram-
ming. The CS5378 serial pins tri-state when inac-
tive to support external connections to the serial
bus.
8.3 EEPROM Organization
The boot EEPROM holds the 8-bit commands and
24-bit data required to initialize the CS5378 into an
operational state. Configuration information starts
at memory location 0x10, with addresses 0x00 to
0x0F free for use as manufacturing header informa-
tion.
The first serial transaction reads a 1-byte command
from memory location 0x10 and then, depending
on the command type, reads multiple 3-byte data
words to complete the command. Command and
data reads continue until the ‘Filter Start’ command
is recognized.
SS:EECS
SCK
MISO
MOSI
CS5378
AT25640
CS
SCK
SI
SO
27
24
25
26
1
6
2
5
VD
GND
WP
VCC HOLD
3
8
7
4
Figure 14. EEPROM Configuration Block Diagram
