Programs of ramp and soak, Link of programs, Event – NOVUS Controller N1100 User Manual
Page 9: Determination of pid parameters, Maintenance, Problems with the controller
N1100 Controller
NOVUS AUTOMATION
9/11
The master password is made up by the last three digits of the serial
number of the controller added to the number 9000.
As an example, for the equipment with serial number 07154321, the
master password is 9 3 2 1.
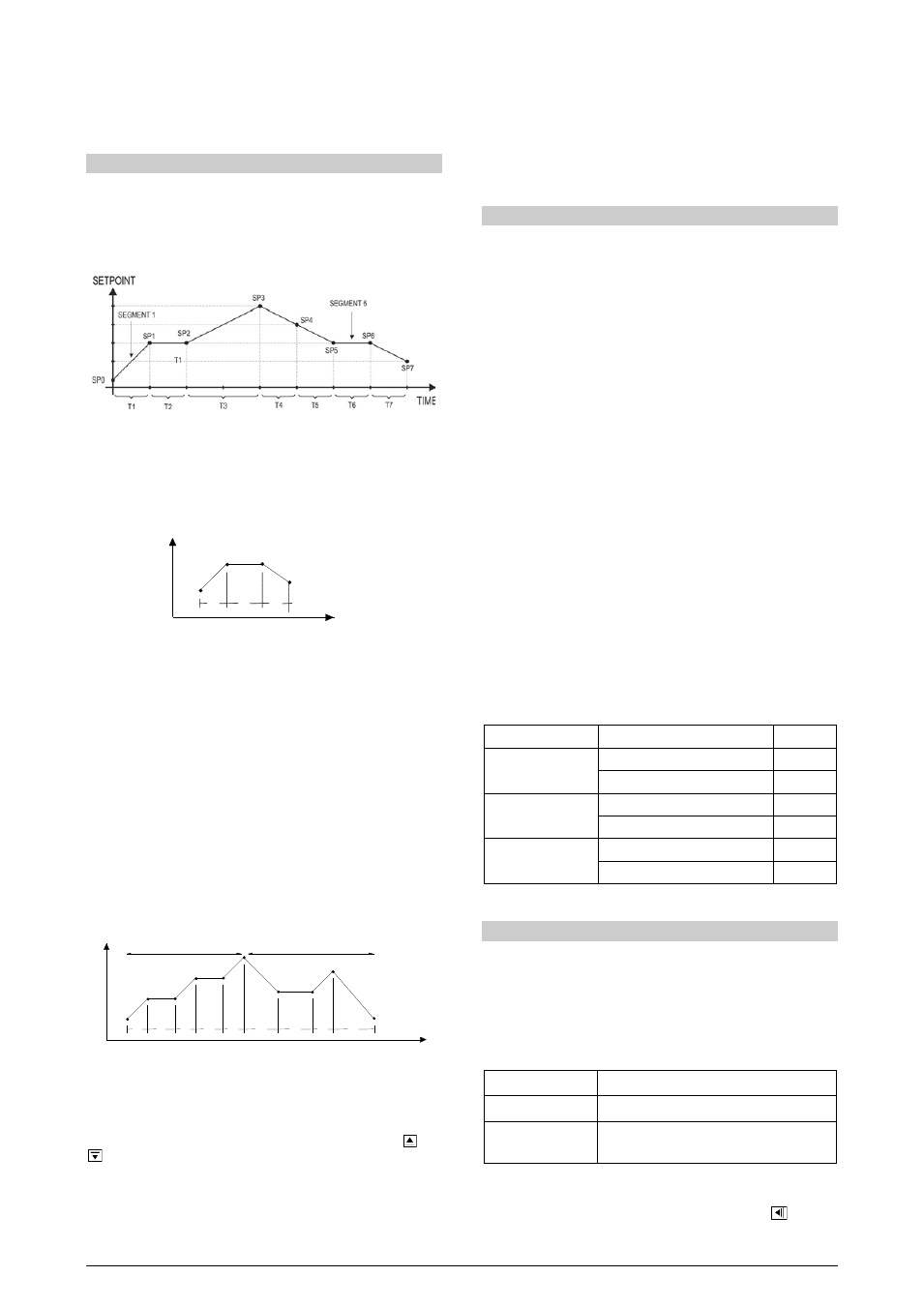
PROGRAMS OF RAMP AND SOAK
This feature allows the creation of Ramp and Soak Setpoint Profiles
(Programs). Up to 7 different profiles with 7 segments each can be
programmed. Longer profiles of up to 49 segments can be created by
linking 2 or more profiles together.
The figure below displays a profile model:
Figure 8 - Example of a Ramp and Soak program
Once a profile is defined and selected for execution, the controller
starts to generate the SP profile automatically in accordance with the
elaborated program.
To execute a profile with fewer segments just program 0 (zero) for
the time intervals that follow the last segment to be executed.
SV
Time
T1
T2
T3
SP0
SP1
SP2
SP3
T4=0
Figure 9 - Program example with few segments
The program tolerance “ptol” defines the maximum deviation
between PV and SP for the execution of the profile. If this deviation is
exceeded, the program will be halted until the deviation falls to within
the tolerance band.
Programming 0 (zero) in the “Ptol” parameter disables the program
tolerance and the profile execution will continue regardless of the PV
value (time priority as opposed to SP priority).
LINK OF PROGRAMS
It is possible to create a more complex program (up to 49 segments),
joining two or more programs. This way, at the end of a program
execution the controller immediately starts to run the next one, as
indicated in the parameter “LP".
To force the controller to run a given program or many programs
continuously, it is only necessary to link a program to itself or the last
program to the first.
SV
time
T1
T2
T3
T4
T5
T1
T2
T3
T4
SP0
SP1
SP2
SP3
SP4
SP5 / SP0
SP1 SP2
SP3
SP4
Program 1
Program 2
Figure 10 – Example of interlinked programs
EVENT
The Event Alarm function associates the alarms to specific segments
of a program. The information of which alarms are to be activated or
deactivated is given in parameters “ PE1“ to “ PE7. Press the and
keys until the desired alarm numbers are displayed.
The Event Alarm requires that the Alarm function be configured as
“rS “.
Notes:
1. If PtoL is different than zero, the controller will wait for the PV to
reach the first program set point SP0 in order to start the
program execution. Otherwise, it will start promptly.
2. Should any power failure occur, the controller resumes the
program execution at the beginning of the segment where it was
interrupted.
DETERMINATION OF PID PARAMETERS
During the automatic tuning the process is controlled in ON / OFF
mode in the programmed SP. Depending on the process behavior,
oscillations may occur above or below the Setpoint. The automatic
tuning may take many minutes to the concluded, particularly in slow
processes.
When the parameter ATUN is altered to YES, the automatic tuning
is immediately initiated by the controller (provided RUN=YES,
otherwise it will wait until this condition becomes true).
Some recommendations for the automatic tuning process are:
•
avto
= YES: make sure the controller is set for automatic control
mode.
•
Disable Ramp & Soak programs configuring Pr n = 0. (the
automatic tuning algorithm expects a stable Setpoint value)
•
Select a Setpoint that is close or equal to the desired process
Setpoint.
•
Enable the automatic tuning (atvn = YES).
•
Enable outputs if not yet enabled (rvn = YES).
The “TUNE” indicator on the display stays lit until the completion of
the automatic tuning process.
For control output types relay or pulse, the automatic tuning
calculates the longest suitable period (cycle time (t) for the PWM
output. The cycle time period may be reduced if the process
experiences some oscillation. When driving a SSR, it’s
recommended to set (t = 1 s.
If the automatic tuning does not result in a satisfactory control, refer
to Table 7 for guidelines on how to correct the behavior of the
process.
PARAMETER
VERIFIED PROBLEM
SOLUTION
Proportional Band
Slow answer
Decrease
Great oscillation
Increase
Rate of Integration
Slow answer
Increase
Great oscillation
Decrease
Derivative Time
Slow answer or instability
Decrease
Great oscillation
Increase
Table 7 - Guidance for manual adjustment of the PID parameters
MAINTENANCE
PROBLEMS WITH THE CONTROLLER
Connection errors and inadequate programming are the most
common errors found during the controller operation. A final revision
may avoid loss of time and damages.
The controller displays some messages to help the user identify
problems.
MENSSAGE
DESCRIPTION OF THE PROBLEM
----
Open input. No sensor or signal.
Err1
Err6
Connection and/or configuration errors.
Check the wiring and the configuration.
Other error messages may indicate hardware problems requiring
maintenance service. When contacting the manufacturer, inform the
instrument serial number, obtained by pressing the key
for more
than 3 seconds.
