Horner APG SmartMod HE359RTD100 User Manual
Page 2
MAN0840-04-EN
Specifications / Installation
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5/11/2009 Page 2 of 2 ECN #
950
3
Init Default Setup
Communication parameters will be set to INIT default after performing the
procedure:
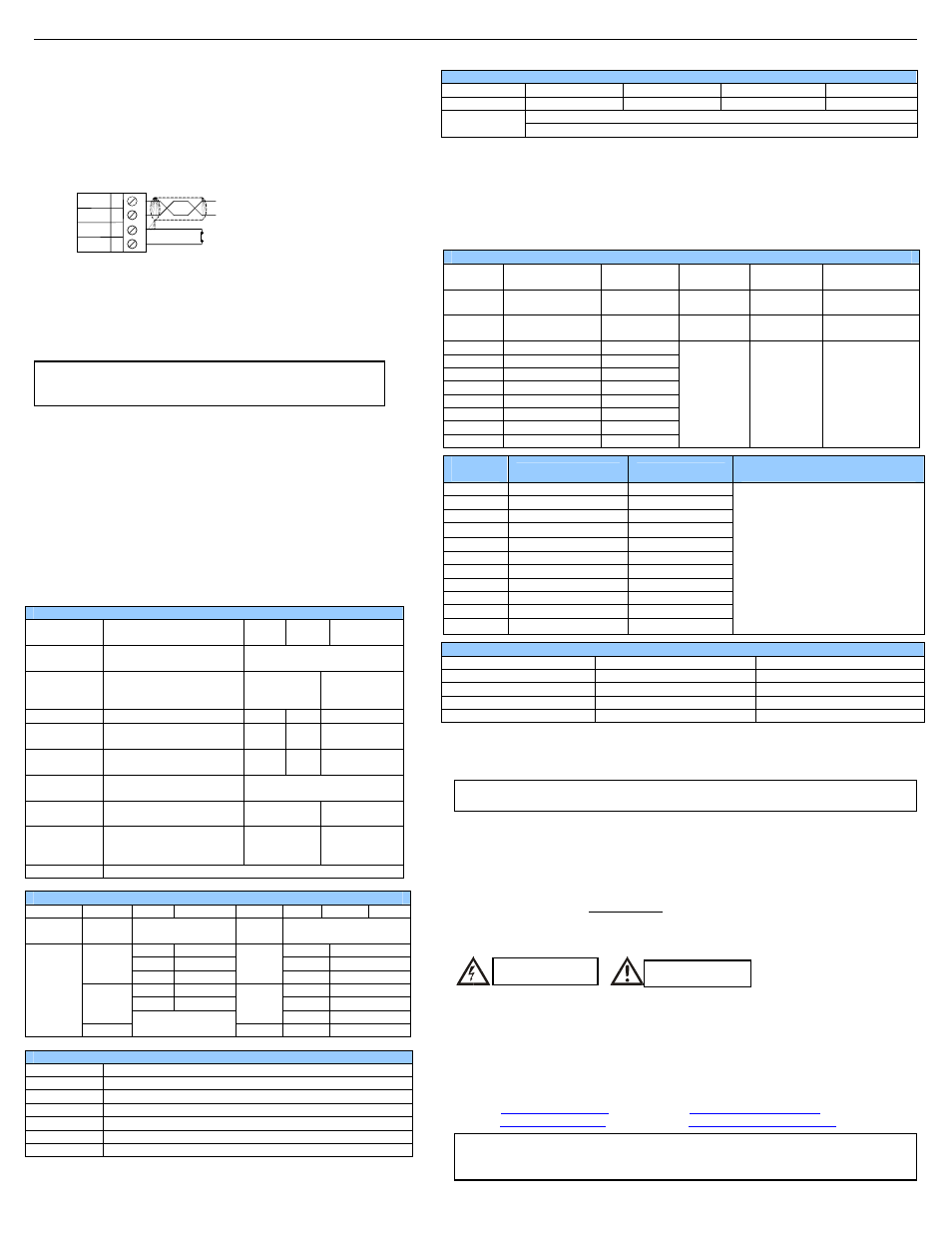
1. Install jumper between INIT and GND terminals of the RS-485 port.
2. Apply power to Smartmod unit.
3. Read parameter words to see current parameters.
4. Write changes if necessary.
The INIT Default RS485 Settings Are:
Modbus ID = 1
Baud rate = 9600
Parity = None
Stop Bits = 1
Data Bits = 8
No handshake
4
Configuration DATA
SmartMod Configuration settings are mapped into Modbus Register space.
This configuration data may be modified with any Modbus/RTU Master device.
For convenience, Horner APG has developed a variety of Cscape application
files which allow an OCS (Xle, NX, LX, QX) to act as a SmartMod configurator.
Initial configuration of SmartMod module should be done on an individual
basis, since all modules come from the factory with a default Modbus ID of 1.
Once each module on the network has its own unique Modbus ID, further
configuration adjustments can be made with the entire network powered.
All configuration parameters listed below (except 40012 Channel Enable) are
stored in EPROM. That means they should not be constantly rewritten.
Configuration Parameters – Registers 40001 through 40013
Modbus
Register
Description
Min
Max
Default
40001-
40005
Reserved
40006
Communications
Parameters
See Table
38.4kbaud,
N, 8, 1, RTU
Mode
40007
Modbus ID
1
255
1
40008
Rx/Tx Delay (in 2mS
steps)
0
255
0mS
40009
Watchdog Timer (in 0.5s
steps)
0
255
10 (5s)
40010
Modbus Coil Data
Not Configuration Data – See
I/O Data
40011
Input Type
See Table
23 (RTD Pt-
100 Type)
40012
Channel Enable
See Table
255 (All
Channels
enabled)
40013
Reserved
Register 40006 (Communications Parameters) Bit Definition
Bits 7-15
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
Unused
Mode
Parity
Data
Bits
Baud Rate
Value
Meaning
Value
Meaning
0
Mark
0
1200 baud
0 =
ASCII
Mode
1
Even
0 = 7
Data
Bits
1
2400 baud
2
Odd
2
4800 baud
3
Space
3
9600 baud
1 =
RTU
Mode
1 = 8
Data
Bits
4
19200 baud
5-7
38400 baud
Register 40011 (Input Type) Value Definition
Value
Input Type
7
0-2000ohm Resistance
8
0-500ohm Resistance
23
RTD Pt-100 Type
24
RTD Ni-100 Type
25
RTD Pt-1000 Type
26
RTD Ni-1000 Type
Register 40012 (Channel Enable) Bit Definition
Bit 4-15
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
Unused
Input 3
Input 2
Input 1
Input 0
0 = Disable Input
1 = Enable Input
5
Input/Output DATA
SmartMod Analog I/O utilizes both Modbus Registers (40001-40030) and Coils (1-11). It is possible
to access all data using Registers only, because the Coils can be accessed through Register 40010.
The following tables lists all Modbus I/O data available.
I/O Register Data (Registers 40014-40022)
Modbus
Register
Description
Access
Minimum
Maximum
Units
40010
Mirror of Coil
Data
Read/Write
n/a
n/a
n/a
40014
Cold Junction
Temperature
Read-only
-1000
6000
0.01 degrees C
40015
Input 0
Read-only
40016
Input 1
Read-only
40017
Input 2
Read-only
40018
Input 3
Read-only
40019
Input 4
Read-only
40020
Input 5
Read-only
40021
Input 6
Read-only
40022
Input 7
Read-only
Depends
on Input
Type
Depends
on Input
Type
0.1C or 0.1 ohm
Modbus
Coil
Description
Access
Watchdog Event & Power-up
Event Operation
00001
Open Detect Input 0
Read/Write
00002
Open Detect Input 1
Read/Write
00003
Open Detect Input 2
Read/Write
00004
Open Detect Input 3
Read/Write
00005
Open Detect Input 4
Read/Write
00006
Open Detect Input 5
Read/Write
00007
Open Detect Input 6
Read/Write
00008
Open Detect Input 7
Read/Write
00009
Watchdog Enabled
Read/Write
00010
Watchdog Event
Read/Write
00011
Power-up Event
Read/Write
If Coil 9 (Watchdog Enabled) is set,
Coil 10 (Watchdog Event) will set if the
Watchdog Timeout value is exceeded.
The Watchdog Timeout value is set in
Register 40009. When set, Coil 10
can be reset by the controller when
normal communications resumes.
The Power-up Event (Coil 11) is set
every time the power is applied. It can
be cleared by the controller if desired.
RTD Sensor Temperature Ranges
RTD Sensor Type
Minimum Temperature
Maximum Temperature
Pt-100
-200 degrees C
+850 degrees C
Ni-100
-80 degrees C
+180 degrees C
Pt-1000
-200 degrees C
+200 degrees C
Ni-1000
-60 degrees C
+150 degrees C
6
Installation / safety
a. All applicable codes and standards should be followed in the installation of this product.
b. Shielded, twisted-pair wiring should be used for best performance.
c. Shields may be terminated at the module terminal strip.
d. In severe applications, shields should be tied directly to the ground block within the panel.
e. Use the following wire type or equivalent: Belden 8441.
For detailed installation and a handy checklist that covers panel box layout requirements and
minimum clearances, refer to the hardware manual of the controller you are using.
When found on the product, the following symbols specify:
7
Technical Support
Technical Support at the following locations:
North America:
Tel: 317 916-4274
Fax: 317 639-4279
Web:
http://www.heapg.com
Email:
Europe:
Tel: +353-21-4321266
Fax: +353-21-4321826
Web:
http://www.horner-apg.com
Email:
No part of this publication may be reproduced without the prior agreement and written
permission of Horner APG, Inc. Information in this document is subject to change without
notice.
INIT
D-
D+
GND
A
B
C
D
Warning: Remove power from the OCS controller, CAN port, and any peripheral equipment
connected to this local system before adding or replacing this or any module.
Warning: Consult
user documentation.
Warning: Electrical
Shock Hazard.
Note: There are 2 types of default settings possible:
1. Factory default as described in section 1 (Specifications)
2. Default after INIT as described in section 3 (INIT Default Setup)
