Warning messages, E 56, E 56) b – Outback Power Systems GS4048A Operators Manual User Manual
Page 58: Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
56
Warning Messages
A warning message is caused by a non-critical fault. When this occurs, the unit will not shut down, but
the
MATE3 system display will show an event and a specific warning message. This screen is viewed
using the MATE3 Home screen’s soft keys. (See the MATE3 manual for more instructions.) One or
more messages will display
Y (yes). If a message says N (no), it is not the cause of the warning.
NOTE: The Radian series has no external indicators and requires the MATE3 system display to identify
a warning.
Some warnings can become errors if left unattended. Frequency and voltage warnings are meant to
warn of a problematic AC source. Often the inverter will disconnect from the source. This will occur if
the condition lasts longer than the inverter’s transfer delay settings. If the inverter disconnects, the
warning will display as long as the source is present, accompanied by a disconnect message. (See
page 58.)
Warning screens can only display warnings; they cannot clear them. The way to correct the fault may
be obvious from the message.
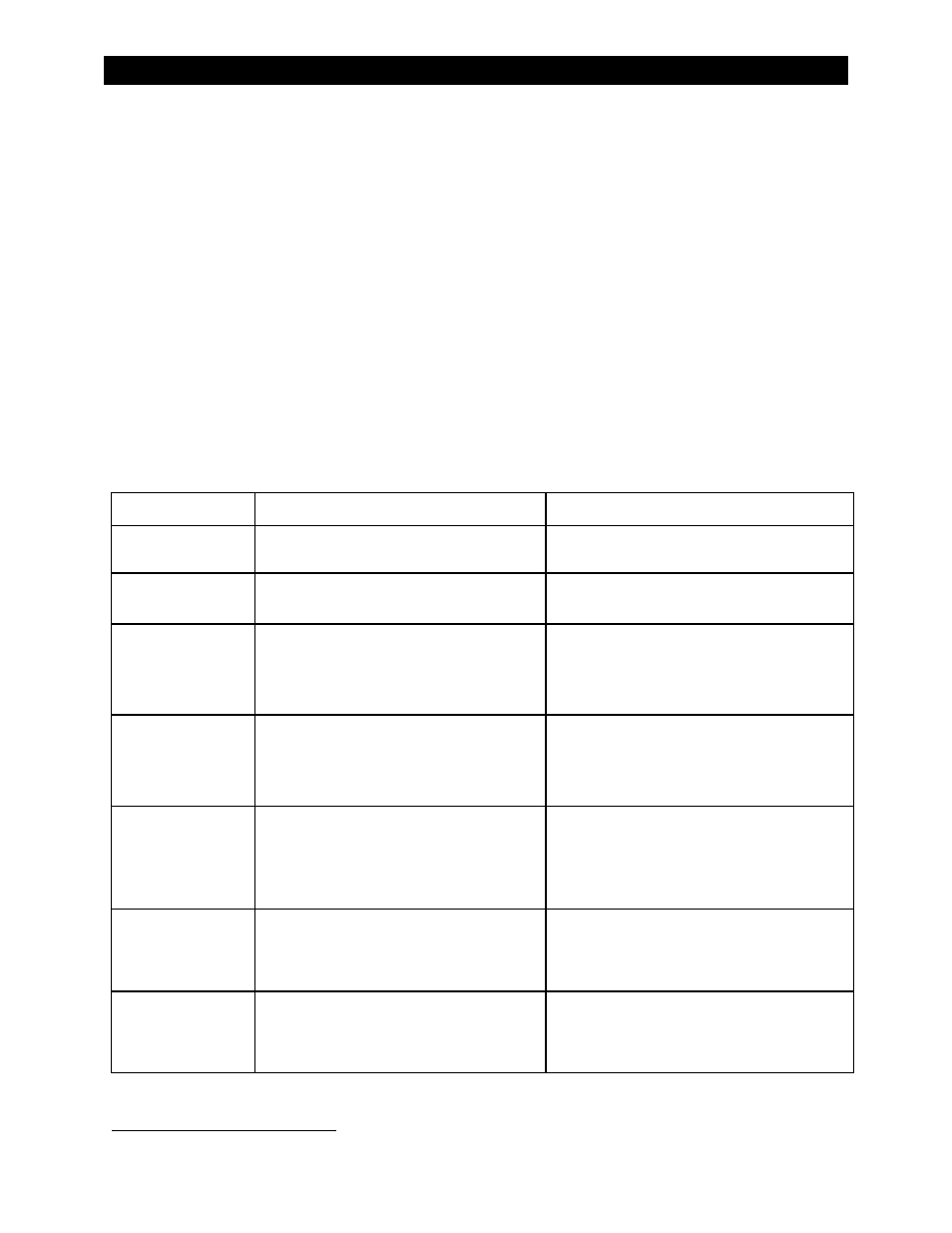
Table 8
Warning Troubleshooting
Message
Definition
Possible Remedy
AC Freq Too High
The AC source is above the upper acceptable
frequency limit and prevents connection.
Check the AC source. If it is a generator, reduce
its speed.
AC Freq Too Low
The AC source is below the lower acceptable
frequency limit and prevents connection.
Check the AC source. If it is a generator, increase
its speed.
Voltage Too High
The AC source is above the upper acceptable
voltage limit and prevents connection.
Check the AC source. The inverter’s acceptance
range is adjustable.
NOTE: Adjusting the range may accommodate a
problematic AC source, but it will not fix it.
Voltage Too Low
The AC source is below the lower acceptable
voltage limit and prevents connection.
Check the AC source. Check the AC wiring. The
inverter’s acceptance range is adjustable.
NOTE: Adjusting the range may accommodate a
problematic AC source, but it will not fix it.
Input Amps > Max
AC loads are drawing more current from the
AC source than allowed by the input setting.
Check the loads. Oversized loads can open circuit
breakers. If they exceed the inverter’s transfer
relay size, the relay can be damaged.
This issue is usually the result of a poorly-sized
load, as opposed to a wiring problem.
Temp Sensor Bad
An internal inverter temperature sensor may
be malfunctioning. One of the three internal
sensor meters may give an unusual reading.
In the MATE3, the three readings are
labeled
Transformer, Output FETs, and
Capacitors. These values are given in degrees
Celsius. See next page.
Phase Loss
A slave was ordered to transfer to an AC source
by the master, but the AC source is the wrong
phase or no AC source is present.
Check the AC voltage on the inverter input
terminals. If AC voltage is not present, problem is
external. If AC voltage is present, the unit may be
damaged. Contact OutBack Technical Support.
9
See inside front cover of this manual.
