Troubleshooting, Table 6 troubleshooting – Outback Power Systems GS4048A Operators Manual User Manual
Page 54
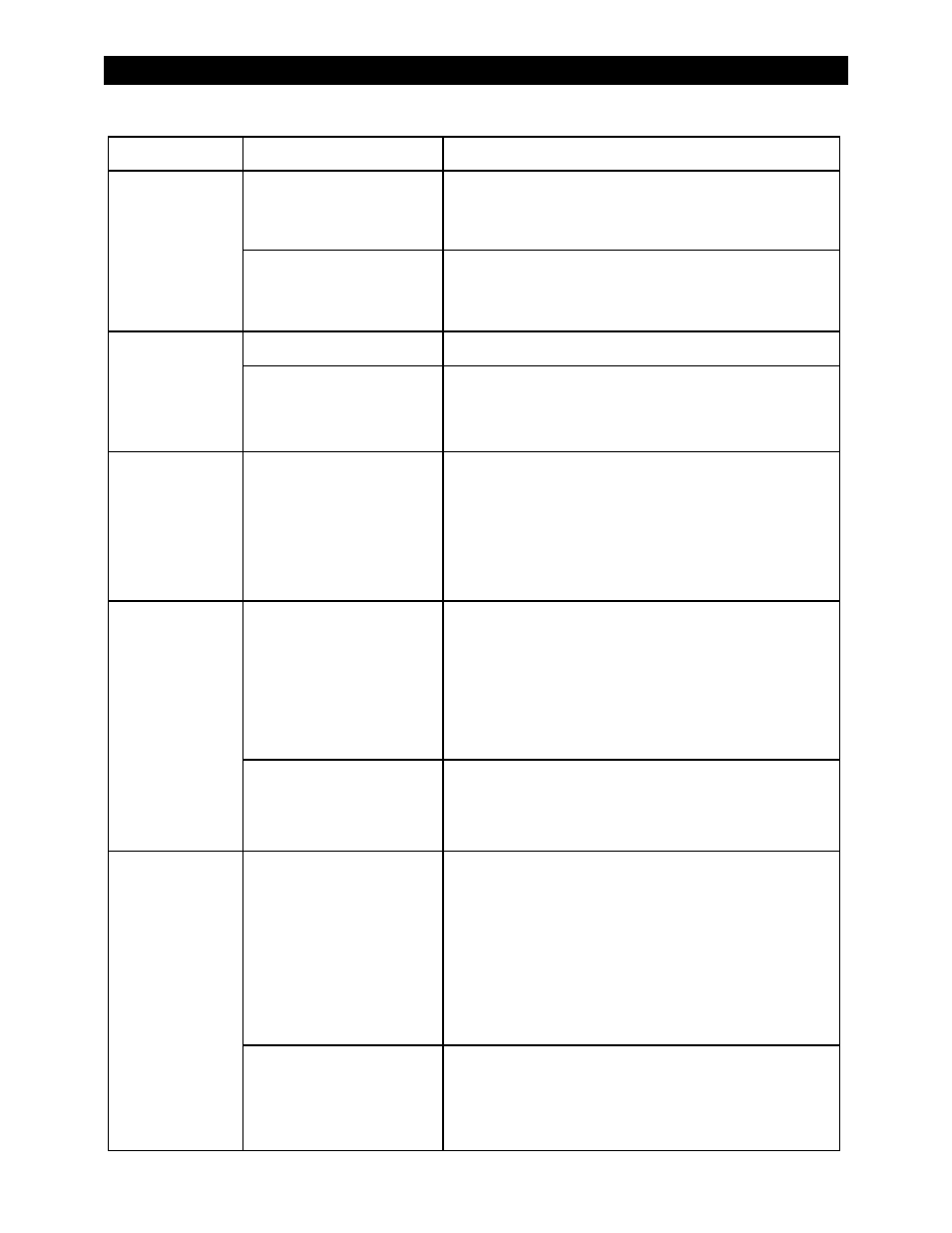
Troubleshooting
52
Table 6
Troubleshooting
Symptom
Possible Cause
Possible Remedy
Reduced power sold
to the utility grid.
AC source voltage is driven high
when the inverter sells large
amounts of power.
When the inverter senses a rise in grid voltage while selling, it
reduces the sell current, to avoid forcing the voltage to
unacceptable levels. Check AC input voltage while selling. The
inverter may be operating correctly.
High temperature.
The inverter will reduce the current rate for selling and other
activities if the internal temperature exceeds a certain level.
Check temperature readings and allow the inverter to cool if
necessary. (See page 57.) External cooling may also be applied.
Inverter does not
perform the Offset
function when
expected.
Incorrect input mode.
Offset does not function in
Generator, UPS, and Backup modes.
Specific mode only offsets
under particular conditions.
Support mode will perform the Support function based on load.
This may appear as Offset without reaching the reference voltage.
Grid Zero mode will perform Offset based on the DoD Volts
setting. Other reference voltages are not used.
Unusual voltage on
hot or neutral
output line.
System neutral and ground may
not be bonded.
Test
L1 OUT, L2 OUT, and N OUT test points with AC voltmeter.
(See page 49.) These measurements should give full voltage. Test
neutral and ground connections. This measurement should read
zero volts. Any other result means neutral and ground are not
bonded correctly. If this is the case, the hot line often reads 60
to75 Vdc and the neutral reads 45 to 60 Vdc with respect to
ground. (If bonding is not required or is prohibited by national or
local codes, then no action may be required.)
Unusual and
different voltages
on AC hot input
lines.
Input neutral is not connected
correctly. The inverter also may
not connect to the AC source.
Test L1 input and neutral connections with AC voltmeter.
Test L2 input and neutral connections with AC voltmeter.
(This can be on
Grid or Gen input, depending on where the
symptoms appear.) Test L1 to L2 input. From hot to neutral
should be approximately 120 Vac unless the output has been
adjusted. L1 to L2 should be approximately 240 Vac. If the two
outputs are different voltages but still add up to 240 Vac, the
neutral is not connected to the inverter.
Inverter has not synchronized
with input source.
MATE3 system display only: The
AC In reading accessed by the
Inverter soft key may be erratic or inaccurate after initial
connection until the inverter has synchronized with the AC
source. This may require a short time.
Loads drop out or
crash during
transfer.
Erratic AC source voltage.
Check AC voltage on the inverter’s input test points. (See
page 49.) If not consistent, the problem is external.
MATE3 system display only: AC source voltage may have dipped or
hovered at a low enough point to crash a sensitive load before
the inverter could take over. This can happen if the inverter’s
Grid
AC Input Voltage Limits or Gen AC Input Voltage Limits were
turned down to accommodate a problematic AC source. To make
the inverter respond sooner, raise the lower limit setting in the
appropriate menu. (If this setting was intentional, then no action
is required.)
Inverter set to
Search (Search
mode).
The unit will take a moment to come out of Search mode after
transferring.
MATE3 system display only: If constant power is required, set
to
ON with the INVERTER hot key. (If this setting was
intentional, then no action is required.)
