When the threshold for invalid data is exceeded, When the – HP Matrix Operating Environment Software User Manual
Page 175
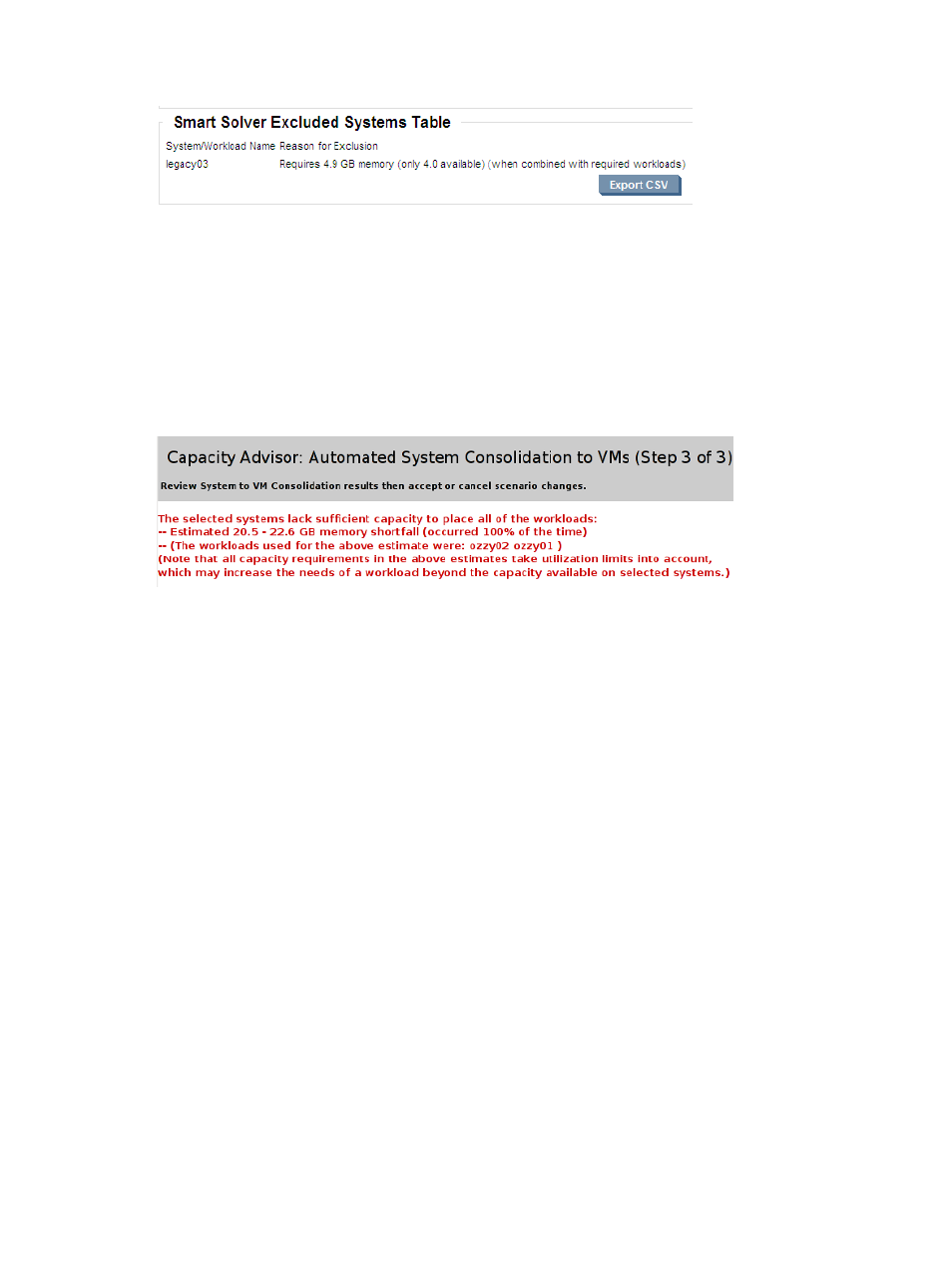
Figure G-1 Example of Smart Solver Excluded Systems table, part of the a Smart Solver Results
screen
Remember that the Smart Solver includes utilization limits set for the workload, system, or
scenario-wide when calculating desired capacity for the solution. Therefore, one way to correct
the resource insufficiency could be to raise the utilization limits for the specified metrics. Another
way is to select or add additional systems having at least the minimum required capacity.
In
, the Smart Solver is unable to arrange the workloads such that they can all
be placed on available systems, even though the systems have sufficient resources to place at
least one workload per system.
Figure G-2 Solver error messages when too few systems are available for the calculated required
capacity needed
Here every workload can be placed on at least one system. However, the Smart Solver has
concluded that there is simply insufficient total capacity across all systems to place all the
workloads.
In this case, the Smart Solver cannot derive a singular estimate of additional required capacity
for a resource because an estimate depends on whether the remaining workloads will all be
placed on a single system (thereby using the most restrictive utilization limits), or spread across
multiple systems.
As a result, a range of estimates is displayed: the first value specifies the total aggregate demand
if all workloads were placed together, while the second value is the summed demand for each
workload if it were placed separately. The workload(s) used in the estimation are named.
It is possible that different combinations of the same workloads and systems can result in failures
on different metrics. The Smart Solver results might state that the failure to arrive at a solution
is due to memory shortfalls, which occurred 100% of the time. Given the same workloads and
systems but an alternate solution, the Smart Solver may identify that 80% of the failures were
due to CPU overages while 20% were due to memory shortfalls.
When the threshold for invalid data is exceeded
The Smart Solver tracks placement attempts that were abandoned because the attempted
aggregation of workloads would have exceeded the percentage of invalid data allowed for each
system. (The invalid data threshold for each system is currently configured to be equal to the
invalid data threshold specified by users for each workload.)
In this situation, you would see a message similar to this:
Some placement attempts failed because workloads exceeded the 16% per-system invalid data threshold
-Per-attribute exceedances: 15% CPU, 0% memory, 0% disk I/O, 0% network I/O
The above message indicates that, while trying to place workloads, 15% of the placement attempts
failed because the resulting set of workloads would have exceeded the invalid data threshold
for CPU allowed for each system. As a result, the returned solution was less than ideal because
the Smart Solver had to rearrange workloads to keep those having significant invalid data in
HP Smart Solver error messages
175
