1 measuring principle, Technical data – KROHNE OPTISYS TUR 1050 EN User Manual
Page 55
TECHNICAL DATA
7
55
OPTISYS TUR 1050
www.krohne.com
11/2012 - 4002444301 MA OPTISYS TUR 1050 R02 en
7.1 Measuring principle
According to the US EPA definition, turbidity is the cloudy appearance of water caused by the
presence of suspended and colloidal matter. In the waterworks field, a turbidity measurement is
used to indicate the clarity of water. Technically, turbidity is an optical property of the water
based on the amount of light reflected by suspended particles and colloidal matter.
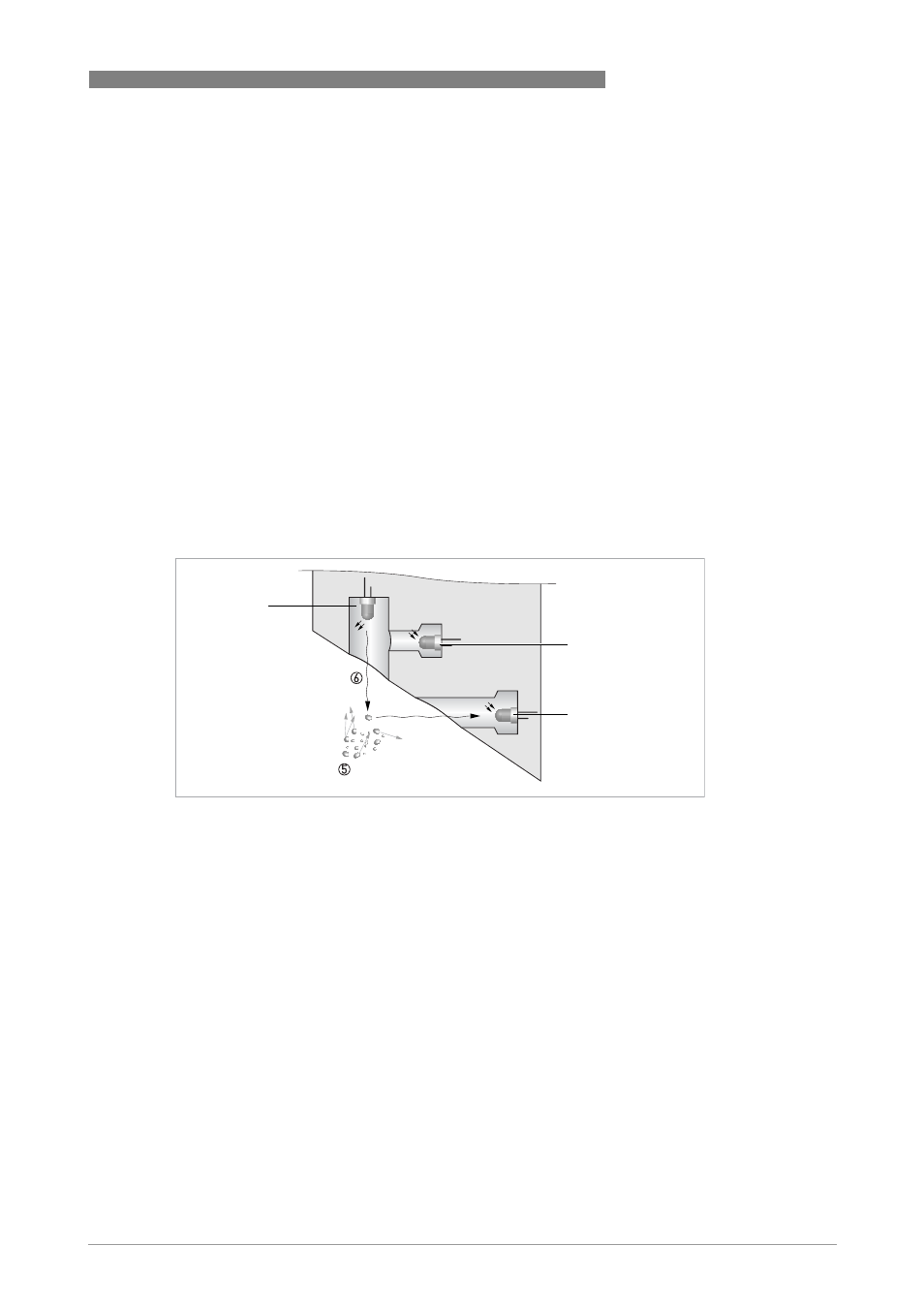
According to ISO 7027 turbidity values below < 40 NTU are measured with the 90° scattered light
method. Light source and receiver are positioned in a 90° angle to each other. The light
transmitted from the source is directed in equal strength to the reference receiver and into the
medium. The light is reflected from the particles and fractions of the scattered light are received
by the detector, which is positioned in a 90° angle. The meter compares the light from reference
and scattered light receiver and calculates the turbidity value.
The measuring units for the turbidity are:
• NTU (Nephelometric Turbidity Unit)
• FNU (Formazin Nephelometric Unit)
Figure 7-1: Measuring principle for turbidity measurement
1 Light source
2 Reference sensor
3 Sensor
4 Reflected light beam
5 Particles
6 Emitted light beam
4
1
2
3
