Medical basis, 1 bioelectric impedance analysis (bia), Classic analysis of body composition – Seca 515 User Manual
Page 44
44 •
8. MEDICAL BASIS
This section briefly describes the basis for bioelectric impedance analysis,
as well as the contents and medical goals of the evaluation modules that
have been pre-set in this device. The references on which the evaluations
rest will also be presented.
For additional information, we refer to the appropriate professional
literature.
8.1
Bioelectric impedance analysis (BIA)
Classic analysis of body
composition
The current "gold standard" for analyzing body composition involves a
combination of methods for calculating individual parameters, some of
which are technically complex and all of which are time-consuming. The
parameters are considered in combination with the weight and body size
of the patient. This way, the nutritional condition and health risk of the
patient can be individually assessed. The following table offers an
overview of the gold standard parameters and the corresponding
calculation methods.
In order to determine the fat mass, a high degree of technical complexity is
required. The following tables serves as an overview in this regard:
The high technical and financial input, combined with considerable time
and space requirements, means that the “gold standard” is unsuitable for
day-to-day operations in clinics and doctor’s practices.
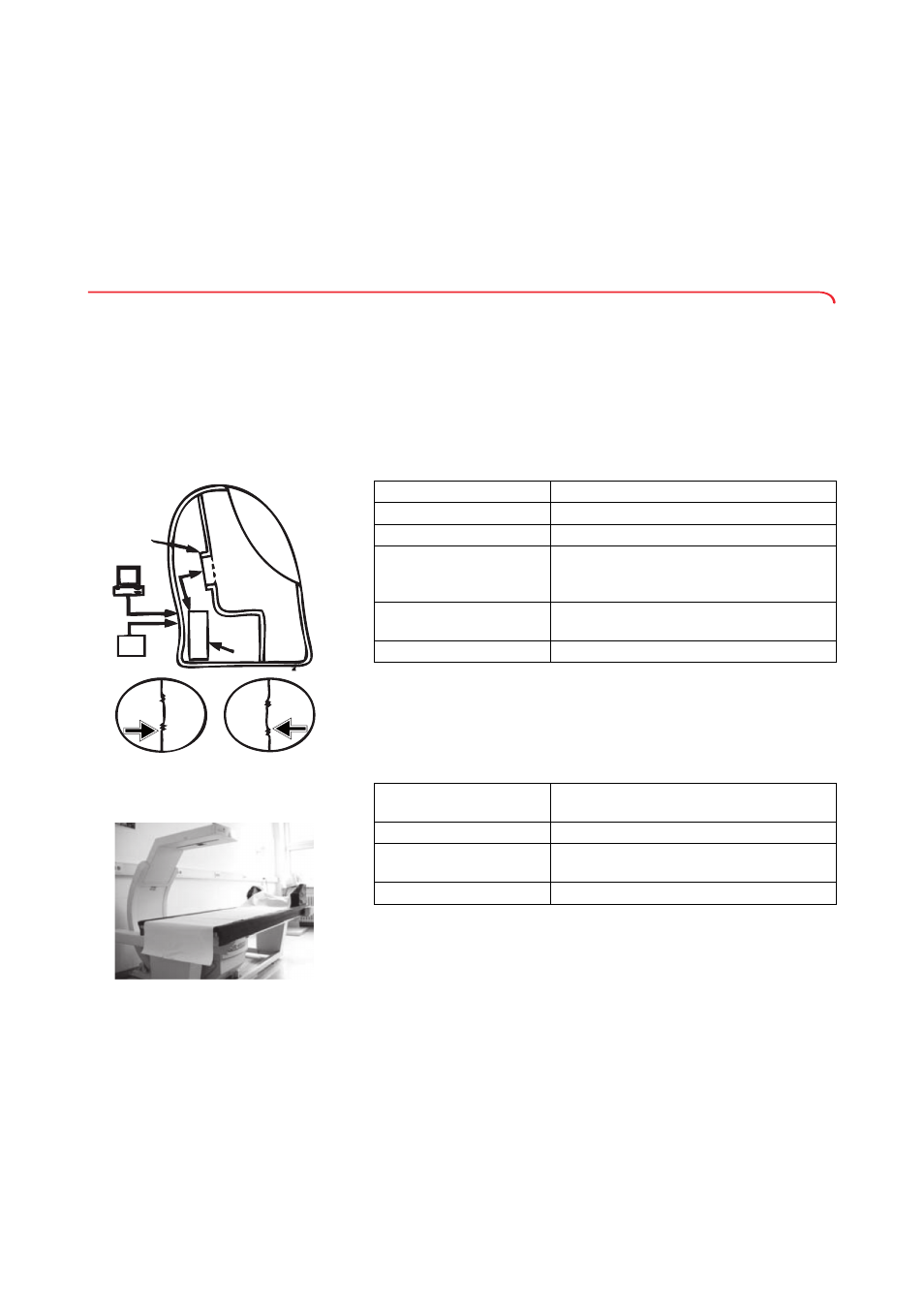
Diaphragm
Computer
Window
Test chamber
Reference
chamber
Electronics
Low
pressure
High
pressure
High
pressure
Moving diaphragm produces
complementary pressure changes in the chambers
Low
pressure
Scale
Air Displacement Plethysmography (ADP)
Dual Energy X-ray Absorbtiometry (DEXA)
Parameters
Method
Total body water (TBW)
Dilatation method, tracer: Deuterium
Extracellular water (ECW)
Dilatation method, tracer: Sodium bromide
Fat mass (FM)
Calculation based on the four component
model
a
of the quantities: body volume,
bone minerals, weight, and total body water.
a.Fuller NJ, Jebb SA, Laskey MA, Coward WA, Elia M. Four-component
model for the assessment of body composition in humans: comparison
with alternative methods, and evaluation of the density and hydration of
fat-free mass. Clin Sci 1992; 82: 687-693.
Fat-free mass (FFM)
Difference between weight and fat-free
mass
Lean soft tissue (LST)
Dual Energy X-ray Absorbtiometry (DEXA)
Height for calculating the
FM
Method
Total body water (TBW)
Dilatation method, tracer: Deuterium
Body volume
Densitometry e.g. Air Displacement
Plethysmography (ADP)
Bone minerals
Dual Energy X-ray Absorbtiometry (DEXA)
