1 - ethernet ip overview, 0 industrial ethernet protocol, 1 common industral protocol – Yokogawa Standalone MW100 User Manual
Page 4
1 - EtherNet IP Overview
1.0 Industrial Ethernet Protocol
The Industrial Ethernet Protocol (Ethernet IP) was originally developed by Rockwell Automation and is now managed by
the Open DeviceNet Vendors Association (ODVA). It is a well-established Industrial Ethernet communication system with
Real-Time capabilities. EtherNet IP has a strong presence in America and Asia and has been selected by many major
manufacturers as a plant wide communication system for factories worldwide. EtherNet IP is standardized in the
International standard IEC 61158 and EtherNet IP devices are certified by ODVA for interoperability and conformance.
EtherNet IP extends commercial off-the-shelf Ethernet to the Common Industrial Protocol (CIP) — the same upper-layer
protocol and object model found in DeviceNet and ControlNet. CIP allows EtherNet IP and DeviceNet system integrators
and users to apply the same objects and profiles for plug-and-play interoperability among devices from multiple vendors
and in multiple sub-nets. Combined, DeviceNet, ControlNet and EtherNet IP promote transparency from sensors to the
enterprise software.
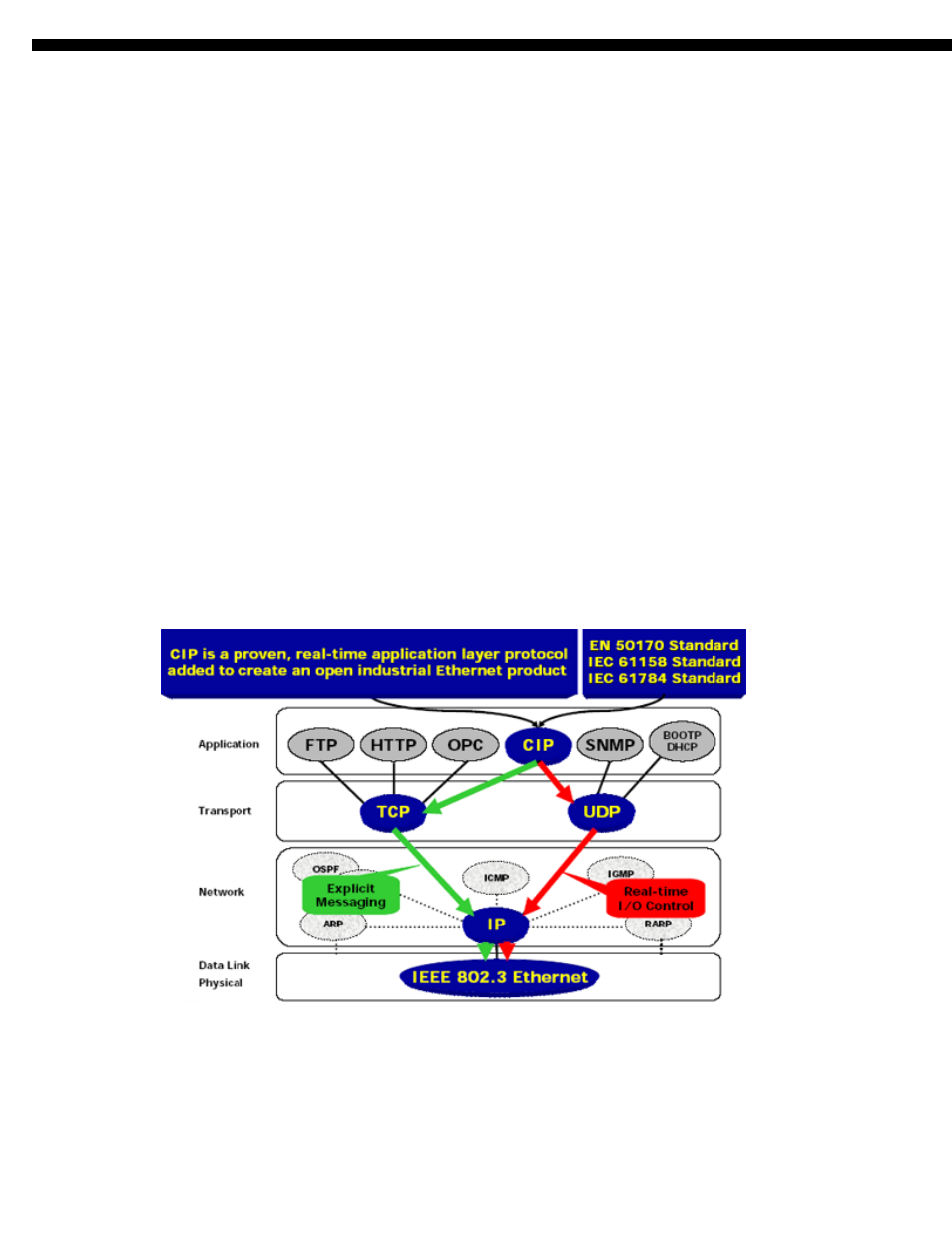
1.1 Common Industrial Protocol (CIP)
CIP provides a wide range of standard objects and services for access to data and for control of network devices via so-
called "implicit" and "explicit" messages. The CIP data packets are encapsulated before they will be send with standard
TCP or UDP telegrams on the Ethernet.
EtherNet IP uses all the transport and control protocols of standard Ethernet including the Transport Control Protocol
TCP), the User Datagram Protocol (UDP), the Internet Protocol (IP) and the media access and signaling technologies
found in off-the-shelf Ethernet technology. Building on these standard communication technologies means that EtherNet
IP works transparently with all the standard Ethernet devices found in today's market place. It also means that EtherNet IP
automatically benefits from all further technology enhancements such as Gigabit Ethernet and Wireless technologies.
1
