9 - eccentricity measurement (optional) – CEMB USA C68SE (B) User Manual
Page 23
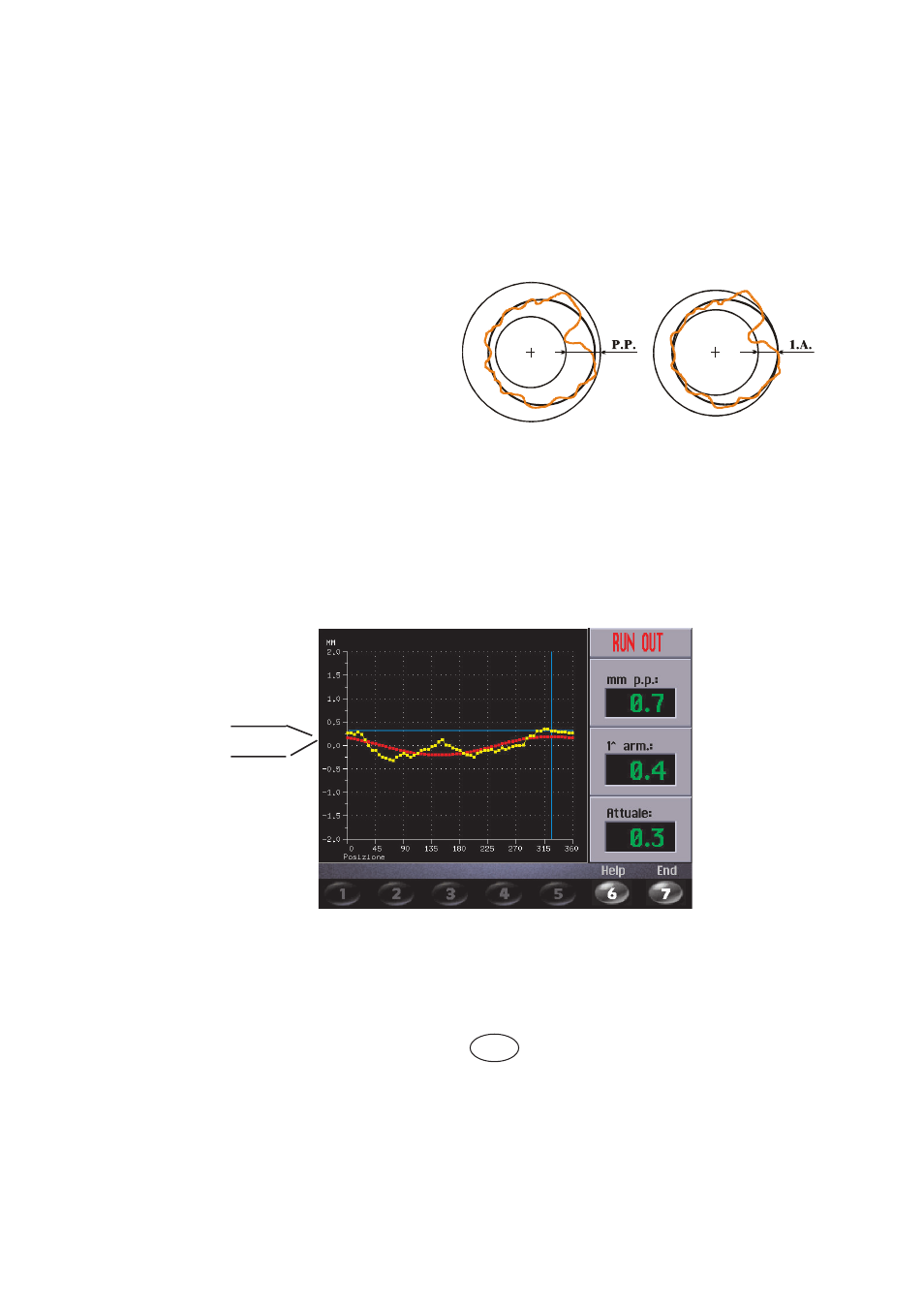
Fig.
A
Fig.
B
I 0201 GB- 23
5.9 - ECCENTRICITY MEASUREMENT (OPTIONAL)
The much enlarged fi gures show the outer tyre surface and axis of wheel rotation.
Fig. A shows measurement of the total Peak-to-Peak eccentricity defi ned as maximum radial deviation
of the tyre surface.
GRAPH 1 : represents the actual Peak-to-Peak eccentricity.
GRAPH 2 : represents the eccentricity of the 1st harmonic. For a wheel in optimum conditions, such
graph should approach a straight line.
While rotating the wheel, the screen cursor indicates the current value, with the stage referred to the
eccentricity measurement sensor. Press pushbutton
6
to access a panel where important informa-
tion about eccentricity is displayed, such as the imbalance effect which the fi rst eccentricity harmonic
measured may exert at an average speed of 120 km/h.
Fig. B shows measurement of the eccentricity
of the 1st harmonic, i.e. the eccentricity of that
circle which “recopies” the tyre shape, by avera-
ging the local deviations of the tyre from the
round shape.
Obviously the P.P. measurement is normally
greater than that of the 1st harmonic. Tyre
manufacturers normally supply two different
tolerances for the two eccentricities.
At the end of the balancing spin it is possible to automatically measure the eccentricity of the tyre
through the SONAR sensor installed on the guard. The sensor should be positioned by hand in front
of the tyre tread.
GRAPH 1 - (yellow)
GRAPH 2 - (red)
