Architectural overview, Attiny28l/v – Rainbow Electronics ATtiny28L User Manual
Page 6
6
ATtiny28L/V
1062E–10/01
Architectural
Overview
The fast-access register file concept contains 32 x 8-bit general-purpose working regis-
ters with a single clock cycle access time. This means that during one single clock cycle,
one ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit) operation is executed. Two operands are output from
the register file, the operation is executed, and the result is stored back in the register
file – in one clock cycle.
Two of the 32 registers can be used as a 16-bit pointer for indirect memory access. This
pointer is called the Z-pointer and can address the register file and the Flash program
memory.
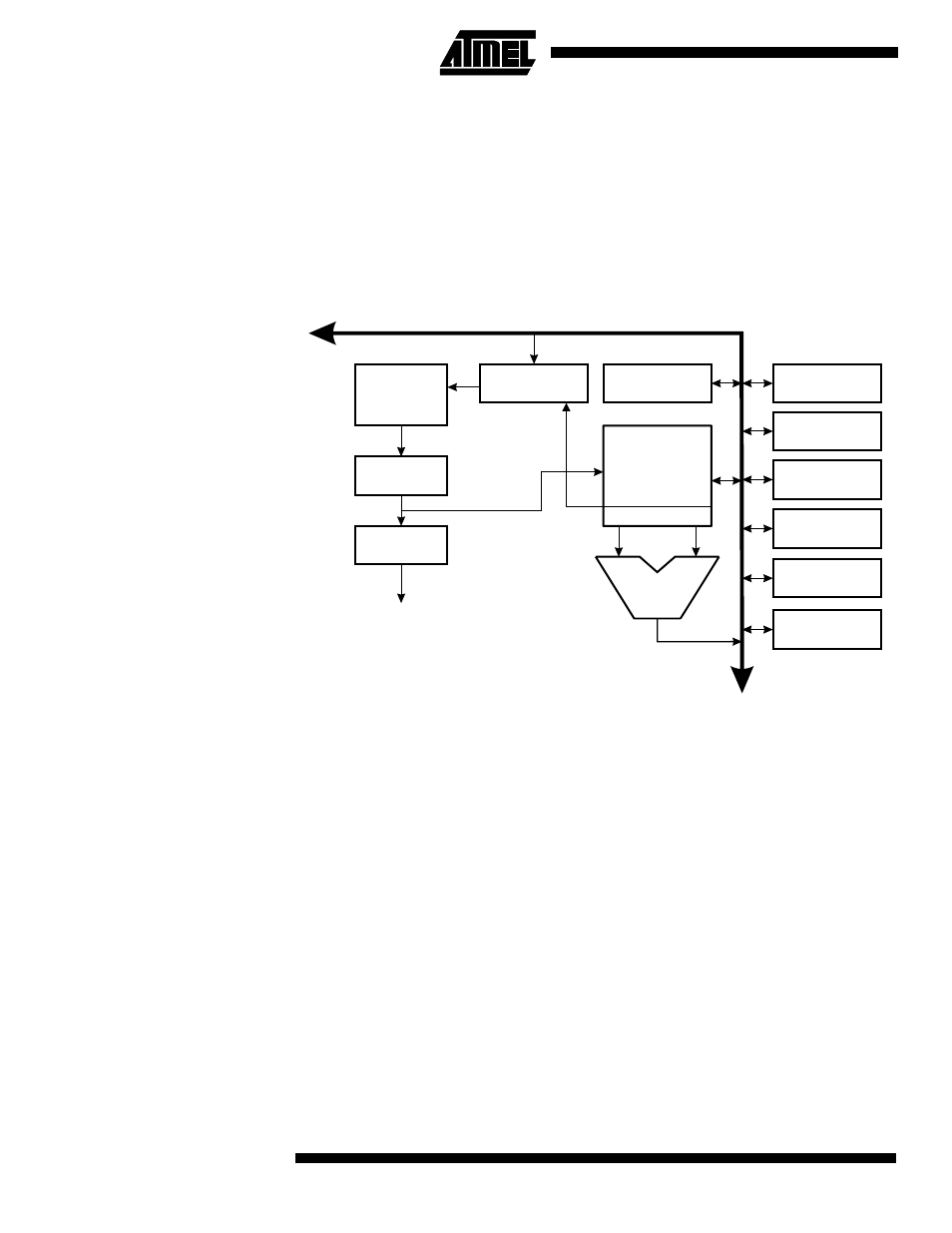
Figure 5. The ATtiny28 AVR RISC Architecture
The ALU supports arithmetic and logic functions between registers or between a con-
stant and a register. Single register operations are also executed in the ALU. Figure 5
shows the ATtiny28 AVR RISC microcontroller architecture. The AVR uses a Harvard
architecture concept – with separate memories and buses for program and data memo-
ries. The program memory is accessed with a two-stage pipeline. While one instruction
is being executed, the next instruction is pre-fetched from the program memory. This
concept enables instructions to be executed every clock cycle. The program memory is
reprogrammable Flash memory.
With the relative jump and relative call instructions, the whole 1K address space is
directly accessed. All AVR instructions have a single 16-bit word format, meaning that
every program memory address contains a single 16-bit instruction.
During interrupts and subroutine calls, the return address program counter (PC) is
stored on the stack. The stack is a 3-level-deep hardware stack dedicated for subrou-
tines and interrupts.
The I/O memory space contains 64 addresses for CPU peripheral functions such as
Control Registers, Timer/Counters and other I/O functions. The memory spaces in the
AVR architecture are all linear and regular memory maps.
A flexible interrupt module has its control registers in the I/O space with an additional
global interrupt enable bit in the status register. All the different interrupts have a sepa-
Control Lines
ALU
Data Bus 8-bit
1K x 16
Program
Flash
Instruction
Register
Instruction
Decoder
Program
Counter
Status
and Test
32 x 8
General
Purpose
Registrers
Z
Control
Registrers
Interrupts
Unit
8-bit
Timer/Counter
Watchdog
Timer
Analog
Comparator
20
I/O Lines
