Rainbow Electronics MAX9452 User Manual
Page 9
MAX9450/MAX9451/MAX9452
High-Precision Clock Generators
with Integrated VCXO
_______________________________________________________________________________________
9
10 GIGABIT ETHERNET
SONET
INPUT CLK: 50MHz
INPUT CLK: 19.44MHz
CRYSTAL
FREQUENCY
(MHz)
P
M
Ni
OUTPUT
FREQUENCY
(MHz)
CRYSTAL
FREQUENCY
(MHz)
P
M
Ni
OUTPUT
FREQUENCY
(MHz)
50
2
2
1
50
51.84
1
8
1
51.84
125
2
5
2
62.5
77.76
1
4
1
77.76
125
2
5
1
125
155.52
1
8
1
155.52
—
—
—
—
—
155.52
1
4
2
77.76
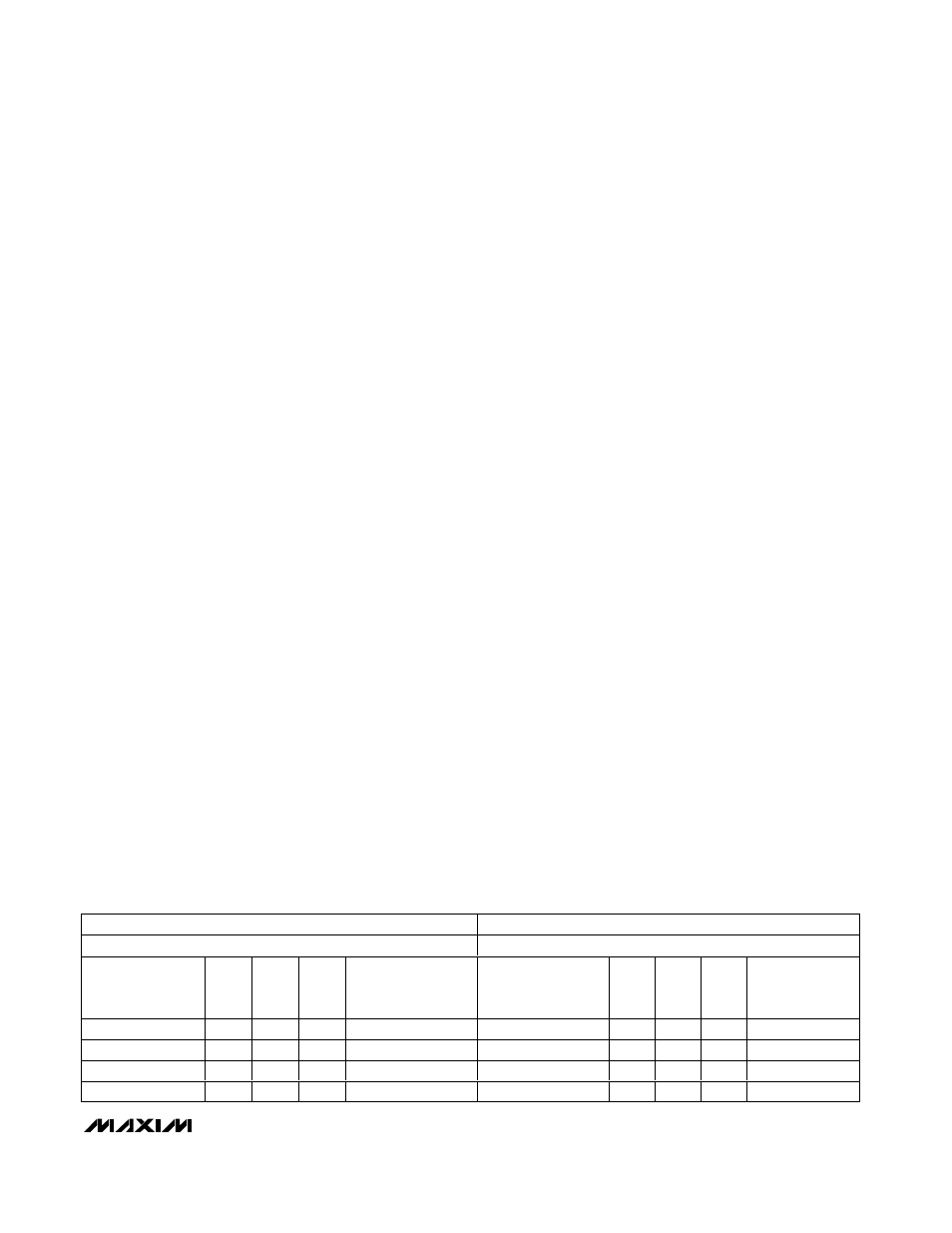
Table 1. Output Frequency Selection and Register Content Values
where f
CLKn
is the frequency at the CLKn output, f
REF
is the frequency of the reference clock, M (1 to 32,768)
is the dividing factor in the feedback loop, Ni (1, 2, 3, 4,
5, 6, 8, 16) are the dividing factors of the outputs, and P
(1 to 256) is the dividing factor to the input reference
clock. It is possible to set various frequencies at the
two differential CLK_ outputs with this configuration.
For example, in 10 Gigabit Ethernet or SONET applica-
tions, set the dividing factors to generate the required
frequencies, as shown in Table 1.
Input Clock Monitor
Failure Detection
The MAX9450/MAX9451/MAX9452 clock-failure-detec-
tion function monitors the two reference inputs simultane-
ously. If a reference input clock signal (IN_) does not
transition for two or more VCO cycles, the device reports
a failure by setting INT high and bit CR7[6] or CR7[5] to
1. See Table 9. After a reference clock failure, the moni-
tor switches to the other valid input reference. At the
same time, the clock monitor loads CR7 with the status of
the reference clocks and which input is selected. The
mapping of CR7 is given in Table 9. If one of the inputs is
disabled according to the bits in CR5[3:2], then the mon-
itor is disabled.
Revert Function
The response of the MAX9450/MAX9451/MAX9452 to a
detected input failure depends on the setting of the
revert function. If the failed input recovers from the
failure, INT and CR7[5:6] resets to 0 if revert is activat-
ed. If the recovered input is selected by CR5[4] as the
default input reference, the MAX9450/MAX9451/
MAX9452 reselect this input. If the revert function is not
activated, once an input failure is detected, the monitor
remains in the failure state with INT = 1 and CR7[5:6] =
1, until the MAX9450/MAX9451/MAX9452 are reset.
Activate the revert function using the bit CR5[1].
Failure-Detection Monitor Reset
Reset the fault by toggling
CMON from low to high,
toggling MR or CR6[4] from low to high, or by toggling
the bit CR5[0] from low to high. In revert mode, when
the monitor is reset, INT and CR7[5:6] reset to 0 and
the default input is the one indicated by CR5[4].
Holdover Function
The holdover function locks the output frequency to its
nominal value within ±20ppm. Activate this function by
setting CR6[7] to 1. The MAX9450/MAX9451/MAX9452
enter holdover when the devices detect a failure from
both input references. Setting CR6[6] to 1 forces the
device into the holdover state, while resetting CR6[6]
exits holdover.
Use a reset-to-exit holdover. If the revert function is
activated once an input is recovered from the failure,
the device also exits holdover and switches to the
recovered input reference. If both inputs recover simul-
taneously, the device switches to the default input.
VCXO frequency during holdover is the value of the
frequency right before the failure of inputs.
When CR6[5] goes from 0 to 1, the value of the VCXO
frequency is acquired and stored. The VCXO can be
switched to this acquired frequency by setting CR6[1]
to 1. Such a transition can happen in both the normal
mode of operation and the holdover mode.
PLL Lock Detect
The MAX9450/MAX9451/MAX9452 also feature PLL
lock detection. The MAX9450/MAX9451/MAX9452
compare the frequency of the phase detector input with
the output frequency of the loop frequency divider.
When these two frequencies deviate more than 20ppm,
the
LOCK output goes high. At power-up, LOCK is
high.
LOCK goes low when the PLL locks. PLL lock
time will also depend on the loop filter bandwidth.
