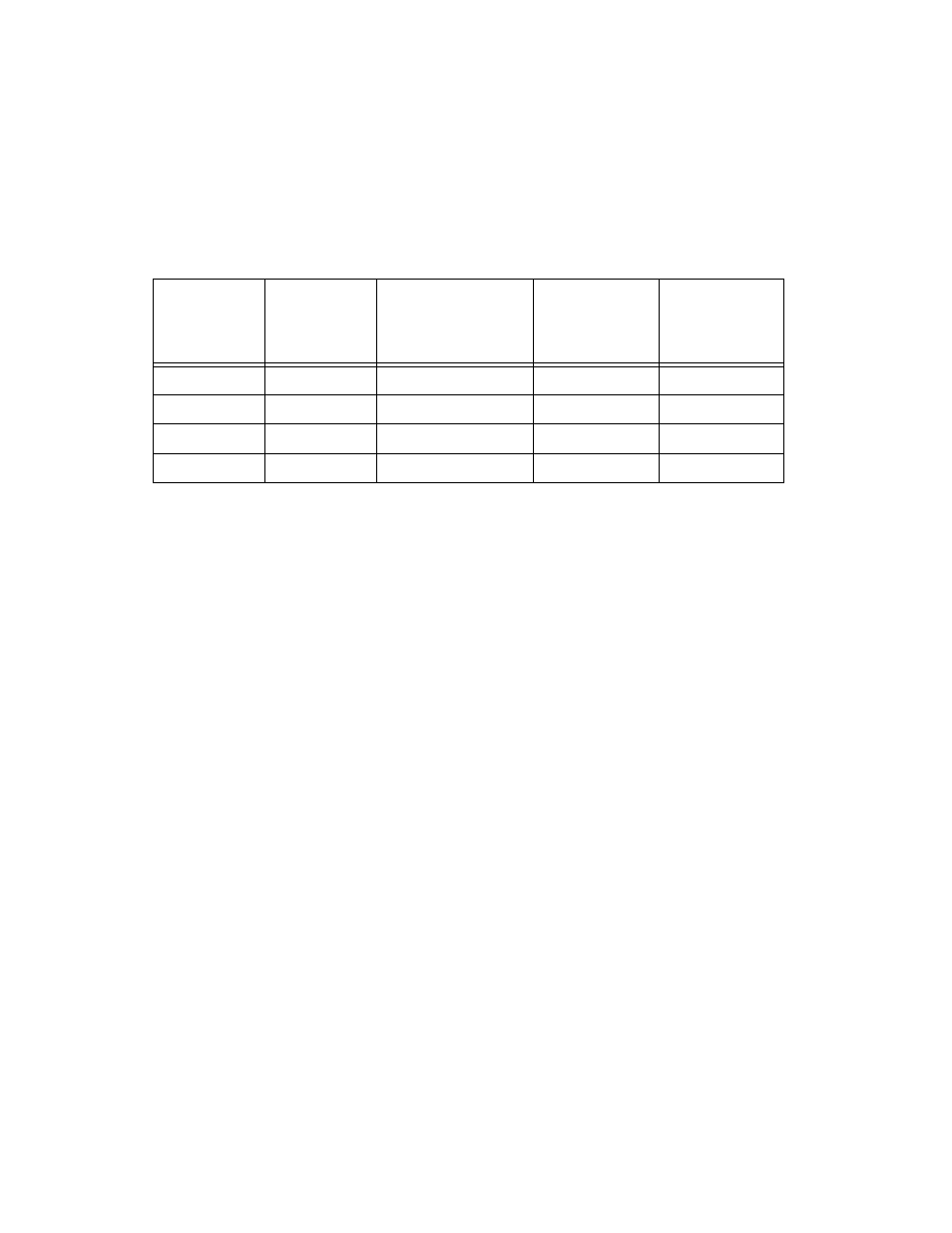
Table 7-2. frequency measurement method comparison, Position measurement, Measurements using quadrature encoders – National Instruments Network Device DAQ S User Manual
Page 86: Position measurement -14, Measurements using quadrature encoders -14
Chapter 7
Counters
7-14
ni.com
Table 7-2 summarizes some of the differences in methods of measuring
frequency.
For information about connecting counter signals, refer to the
section.
Position Measurement
You can use the counters to perform position measurements with
quadrature encoders or two-pulse encoders. You can measure angular
position with X1, X2, and X4 angular encoders. Linear position can be
measured with two-pulse encoders. You can choose to do either a single
point (on-demand) position measurement or a buffered (sample clock)
position measurement. You must arm a counter to begin position
measurements.
Measurements Using Quadrature Encoders
The counters can perform measurements of quadrature encoders that use
X1, X2, or X4 encoding. A quadrature encoder can have up to three
channels—channels A, B, and Z.
•
X1 Encoding—When channel A leads channel B in a quadrature
cycle, the counter increments. When channel B leads channel A in a
quadrature cycle, the counter decrements. The amount of increments
and decrements per cycle depends on the type of encoding—X1, X2,
or X4.
Table 7-2. Frequency Measurement Method Comparison
Method
Number of
Counters
Used
Number of
Measurements
Returned
Measures High
Frequency
Signals
Accurately
Measures Low
Frequency
Signals
Accurately
1
1
1
Poor
Good
1b
1
Many
Fair
Good
2
1 or 2
1
Good
Poor
3
2
1
Good
Good
