Navman 11 User Manual
Page 9
9
MN002000A © 2004 Navman NZ Ltd. All rights reserved. Proprietary information and specifications subject to change without notice.
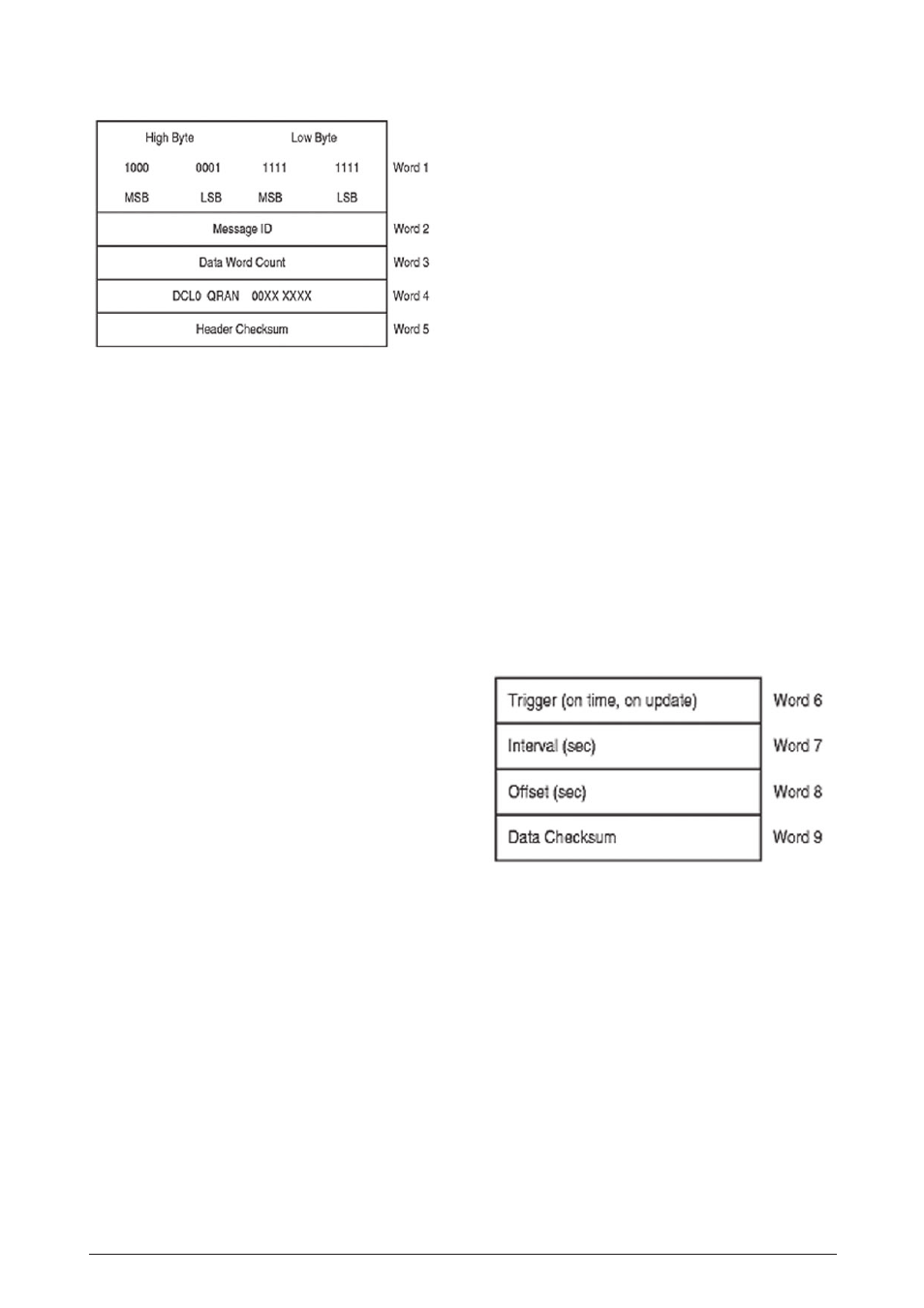
Figure 3-1 Binary message header format
3.2 Binary message header
The binary message header format has been
modified slightly from the NavCore V format to
accommodate message logging requests. The
format of the new message header is shown in
Figure 3-1.
3.2.1 Message header word 1
Each input/output message starts with a
synchronisation word of the form 0x81FF
HEX
with
DEL (255 decimal) occupying the first eight bits
followed by the Start Of Header (SOH) (129
decimal) occupying the second eight bits of the
synchronisation word.
3.2.2 Message header word 2
Word 2 contains the numeric message ID. For
example, word 2 for Message ID 1000 would be:
or 0x03E8
HEX
.
3.2.3 Message header word 3
Word 3 contains the word count for the data
portion of the message. The word count does not
include the data checksum word. A zero data word
count indicates a ‘header-only’ message.
3.2.4 Message header word 4
The fourth word of the message header is a 16-bit
field allocated to protocol and message related
flags. These flag bits extend control over ACK/
NAK requests and implement message logging
requests. The zero’s represented in the word 4
field shown in Figure 3-1 are reserved bits and
should be set to zero within this word.
The ACK/NAK control mechanism gives the user
the ability to request either ACK or NAK, or both,
independently for each message request. The user
sets the request (R) bit and either the acknowledge
(A) bit or negative acknowledge (N) bit, or both, to
select the proper acknowledge behaviour. With this
approach, the user can configure requests only
to be NAKed, alerting the user when a problem
arises without incurring the overhead necessary to
continuously process ACKs.
The lower six bits of the flags word can be used
as an additional input identifier. This identifier
is not explicitly processed by the receiver; it is
echoed back, in the same location, as part of
the header in ACK/NAK responses. This feature
allows the user to uniquely distinguish which input
message an acknowledgement corresponds to
when multiple input messages with the same
message ID were processed during a particular
period of time. The flags word now supports
message logging requests. The connect (C) and
disconnect (D) bits are used to enable and disable,
respectively, message outputs, and can be used
either independently or in conjunction with the log
request bits.
A ‘header-only’ message, with a message ID and
the connect bit set, enables the specified message
with existing timing characteristics. Likewise, a
header-only message, with message ID and the
disconnect bit set, disables the specified message.
Figure 3-2 Standard log request message
format (data portion)
A message with both connect and disconnect
bits is ignored. Note that enabling and disabling a
message does not modify its timing characteristics
(trigger, interval, or offset). A log request with the
connect bit set will set up the message’s timing
characteristics and then enable the message.
Similarly, for a combined log and disable request,
the message will be disabled after the timing
characteristics are set. To disable all messages,
set the message ID to FFFF
HEX
(all bits set) and set
the disconnect (D) bit.
Setting the query (Q) request bit will output the
message specified by the message ID one time
High Byte
Low Byte
0000
MSB
0011
LSB
1110
MSB
1000
LSB
