Nielsen-Kellerman ClearNav User Manual
Page 67
NK ClearNav Manual • Version 0.5 • July 3, 2008
Page 67 of 86
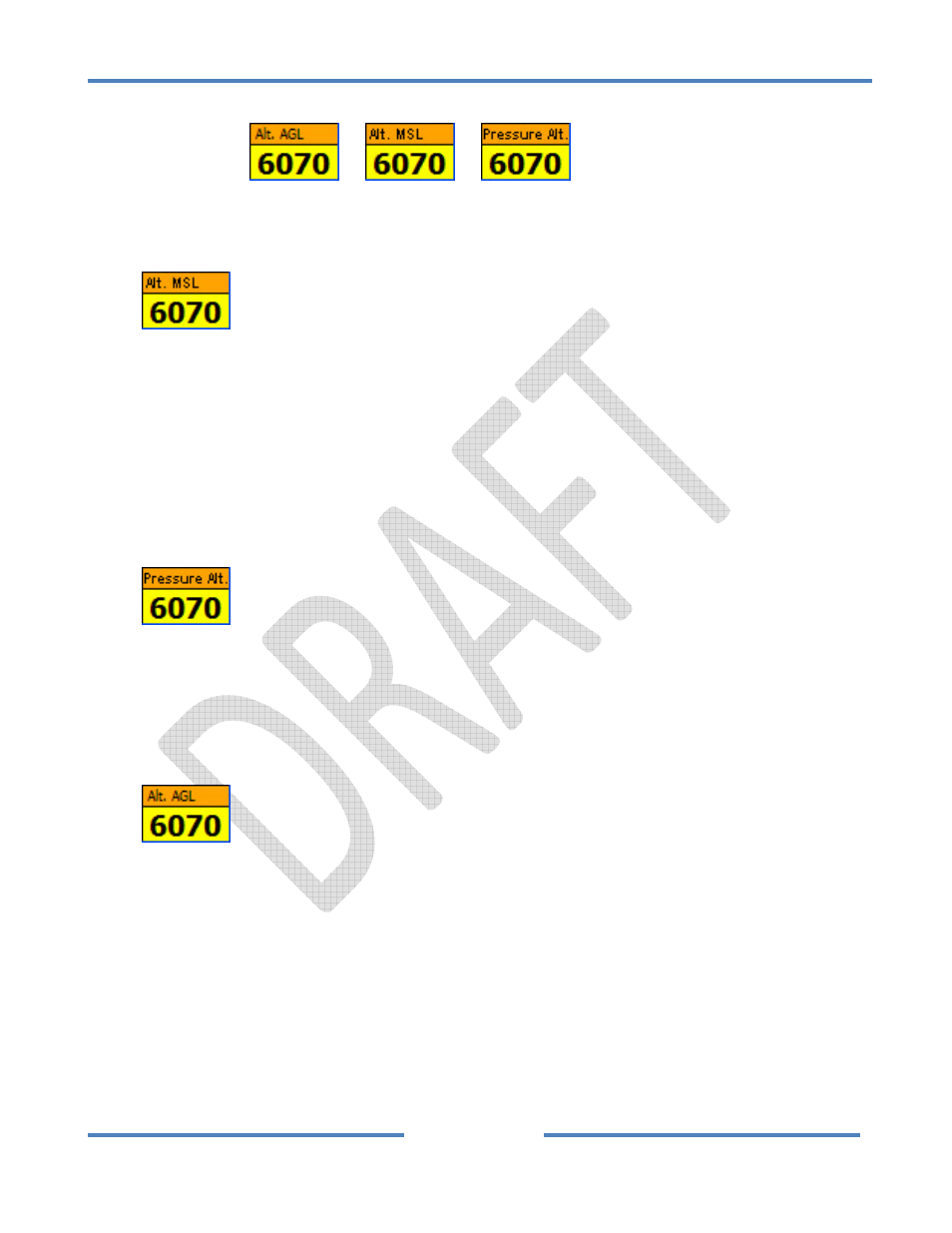
4.2.3.5 Altitude Window
The Altitude Window
or
or
is displayed in the lower right corner
of the screen. It can display several altitude numbers and can be used to access the Set MSL Tab.
Altitude Display Options
•
Altitude MSL (Mean Sea Level)
The Altitude MSL is the altitude that has been adjusted to compensate for changes from the
standard atmosphere. You can and should edit the Altitude MSL before takeoff every time you
fly by setting it to match the known airport elevation. This number is the one used for the final
glide calculations – so be sure to set it before takeoff. The Altitude AGL (below) is based on
the MSL Altitude so it will only display accurately if the MSL Altitude is set accurately. You can
easily use a local automated weather transmitter (AWOS) pressure setting to adjust the MSL
Altitude in flight.
•
Pressure Altitude
The Pressure Altitude is the raw altitude from the pressure transducer and shows the altitude in
a standard atmosphere. Since the local barometric pressure is not likely to match the standard
atmosphere this number will be different than the MSL Altitude. This number is used when
near special use airspace such as when near 18,000 feet in the USA.
•
Altitude AGL (Above Ground Level)
The Altitude AGL is the approximate altitude above ground level. This is a very powerful feature
because it makes it easy to know your approximate altitude above the terrain at a glance. You
will find the Altitude AGL especially useful when flying in mountainous areas. Of course, the
elevation model is not perfect, so don’t count on this number to warn you about local objects
that stand up above the general terrain elevation. The MSL Altitude is used to calculate the
Altitude AGL so it is important to set the Altitude MSL before takeoff. The Altitude AGL is
calculated by subtracting the ground elevation (from the built‐in ground elevation model) from
the Altitude MSL.
