Block and parity striping (raid 5) – Promise Technology FastTrak SX Series Version 4.4 User Manual
Page 92
Promise Array Management
88
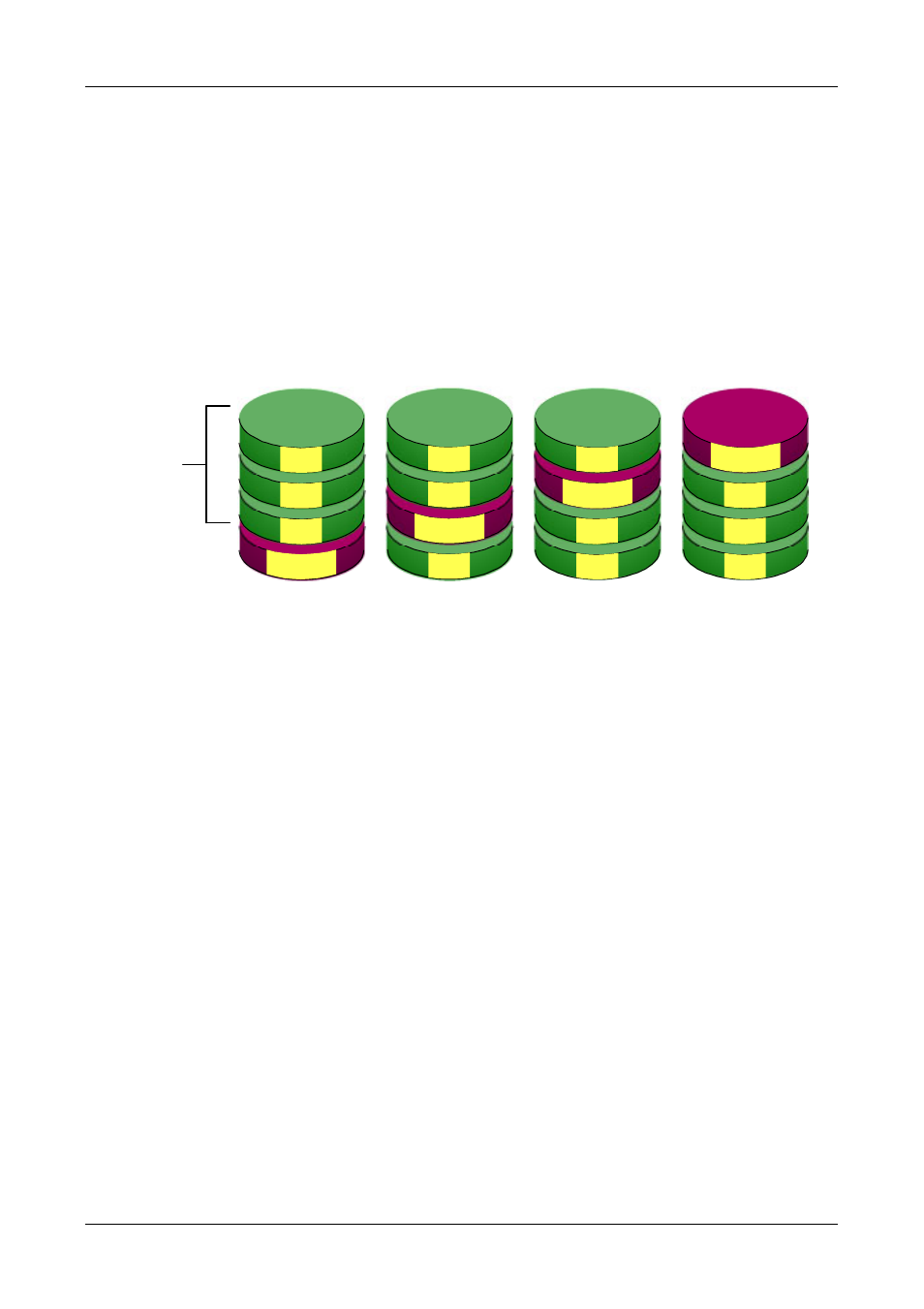
Block and Parity Striping (RAID 5)
RAID 5 calculates parity in order to achieve redundancy rather than writing a
second copy of the data, like RAID 1. Parity is distributed across the physical
drives along with the data blocks. In each case, the parity data is stored on a
different disk than its corresponding data block.
RAID 5 makes efficient use of hard drives and is the most versatile RAID Level.
It works well for file, database, application and web servers.
4b
4c
4d
a parity
3a
3c
3d
b parity
2a
2b
2d
c parity
1a
1b
1c
d parity
Disk Drives
Distributed Parity
Data
Blocks
Figure 86. RAID 5 Stripes all Drives with Data and Parity Information
The capacity of a RAID 5 array is the smallest drive size multiplied by the
number of drives, less one. Hence, a RAID 5 array with four 100 GB hard drives
will have a capacity of 300 GB. An array with two 120 GB hard drives and one
100 GB hard drive will have a capacity of 200 GB.
