6 creating an environment, Creating an environment – Sun Microsystems 5.1.1 User Manual
Page 78
Chapter 6
Section 6.5
Implementing the HTTPS eWay BPEL Sample Projects
Building and Deploying the prjHTTPClient_BPEL Sample Project
HTTPS eWay Adapter User’s Guide
78
Sun Microsystems, Inc.
6.5.6
Creating an Environment
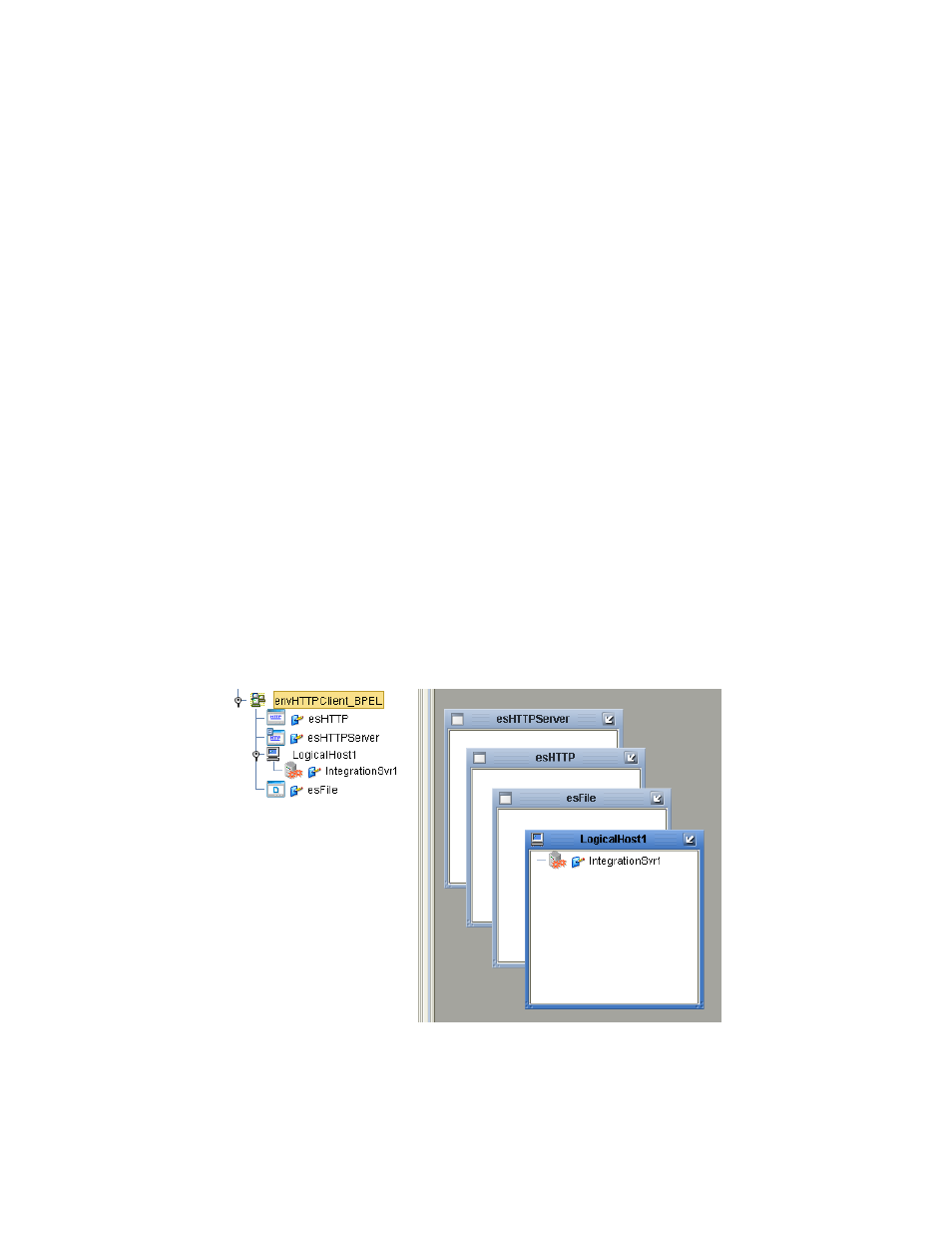
Environments include the external systems, Logical Hosts, Integration Servers, and
message servers used by a Project and contain the configuration information for these
components. Environments are created using the Enterprise Designer’s Environment
Editor.
1
From the Enterprise Designer’s Enterprise Explorer, click the Environment
Explorer
tab.
2
Right-click the Repository and select New Environment. A new Environment is
added to the Environment Explorer tree.
3
Rename the new Environment to envHTTPClient_BPEL.
4
Right-click envHTTPClient_BPEL and select New > File External System. Name
the External System esFile and click OK. esFile is added to the Environment Editor.
5
Right-click envHTTPClient_BPEL and select New > HTTP External System. Name
the External System esHTTP and click OK. esHTTP is added to the Environment
Editor.
6
Right-click envHTTPClient_BPEL and select New > Logical Host. LogicalHost1 is
added to the Environment Editor.
7
From the Environment Explorer tree, right-click LogicalHost1 and select New >
Sun SeeBeyond Integration Server
. A new Integration Server (IntegrationSvr1) is
added to the Environment Explorer tree under LogicalHost1.
8
Save changes to the repository. The Environment Explorer and Environment Editor
now appear as displayed in Figure 33.
Figure 33 Environment Editor - envHTTPClient_BPEL
9
Save your current changes to the Repository.
