Protocols and standards, Tunneling configuration task list – H3C Technologies H3C S12500-X Series Switches User Manual
Page 150
139
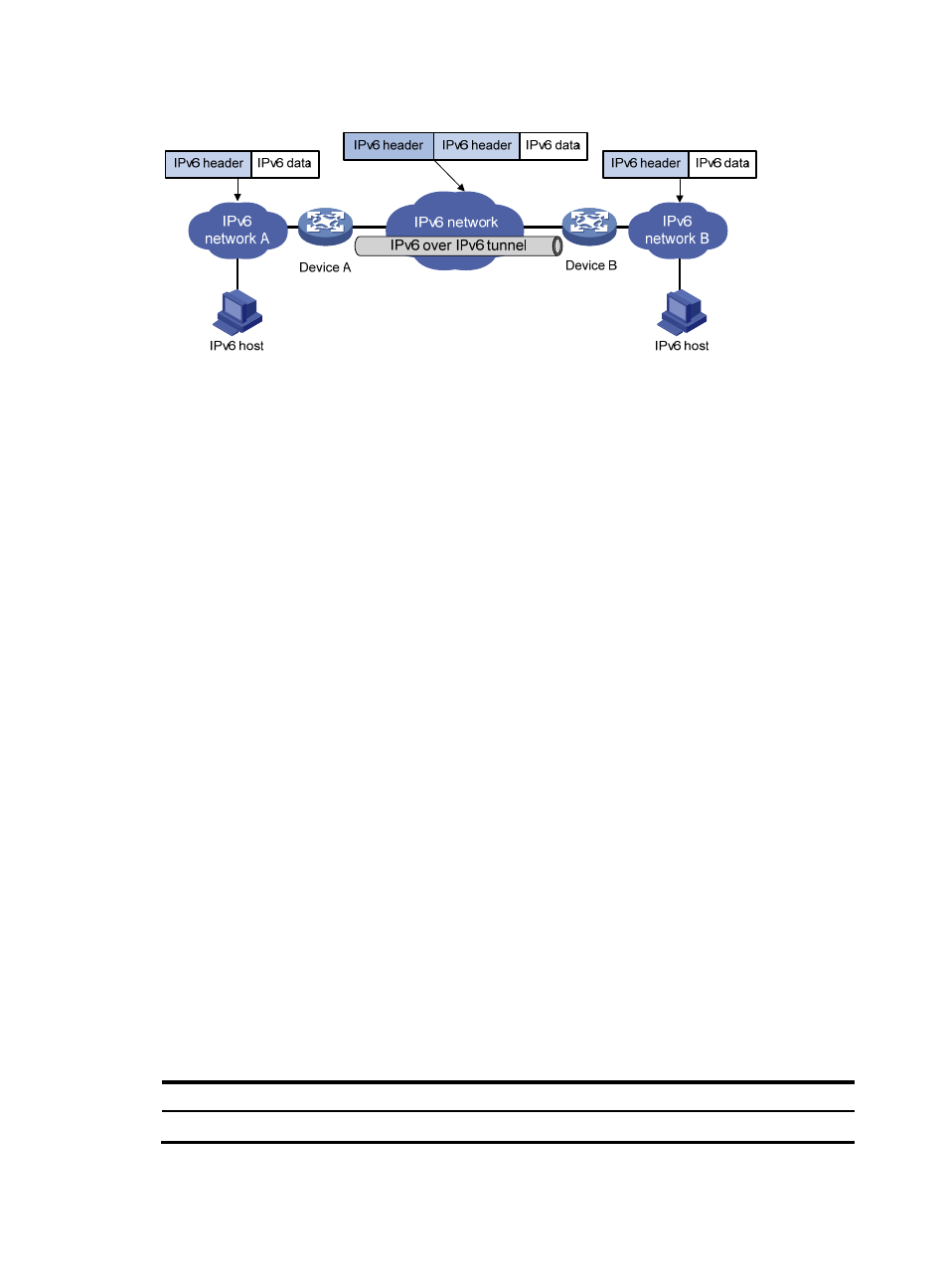
Figure 54 Principle of IPv6 over IPv6 tunneling
shows the encapsulation and de-encapsulation processes.
•
Encapsulation:
a.
After receiving an IPv6 packet, Device A submits it to the IPv6 protocol stack.
b.
The IPv6 protocol stack uses the destination IPv6 address of the packet to find the egress
interface. If the egress interface is the tunnel interface, the stack delivers it to the tunnel
interface.
c.
After receiving the packet, the tunnel interface adds an IPv6 header to it and submits it to the
IPv6 protocol stack.
d.
The IPv6 protocol stack forwards the packet according to its destination IPv6 address.
•
De-encapsulation:
a.
Upon receiving the IPv6 packet, Device B delivers it to the IPv6 protocol stack.
b.
The IPv6 protocol stack checks the protocol type of the data portion encapsulated in the IPv6
packet. If the encapsulation protocol is IPv6, the stack delivers the packet to the tunnel module.
c.
The tunnel module de-encapsulates the packet and sends it back to the IPv6 protocol stack.
d.
The IPv6 protocol stack forwards the IPv6 packet.
Protocols and standards
•
RFC 1853, IP in IP Tunneling
•
RFC 2473, Generic Packet Tunneling in IPv6 Specification
•
RFC 2893, Transition Mechanisms for IPv6 Hosts and Routers
•
RFC 3056, Connection of IPv6 Domains via IPv4 Clouds
•
RFC 4214, Intra-Site Automatic Tunnel Addressing Protocol (ISATAP)
•
RFC 6333, Dual-Stack Lite Broadband Deployments Following IPv4 Exhaustion
Tunneling configuration task list
Tasks at a glance
Configuring a tunnel interface
