Ipv6 over ipv6 tunneling, Troubleshooting ipv4 dns configuration, Symptom – H3C Technologies H3C S12500-X Series Switches User Manual
Page 149: Solution, Troubleshooting ipv6 dns configuration
138
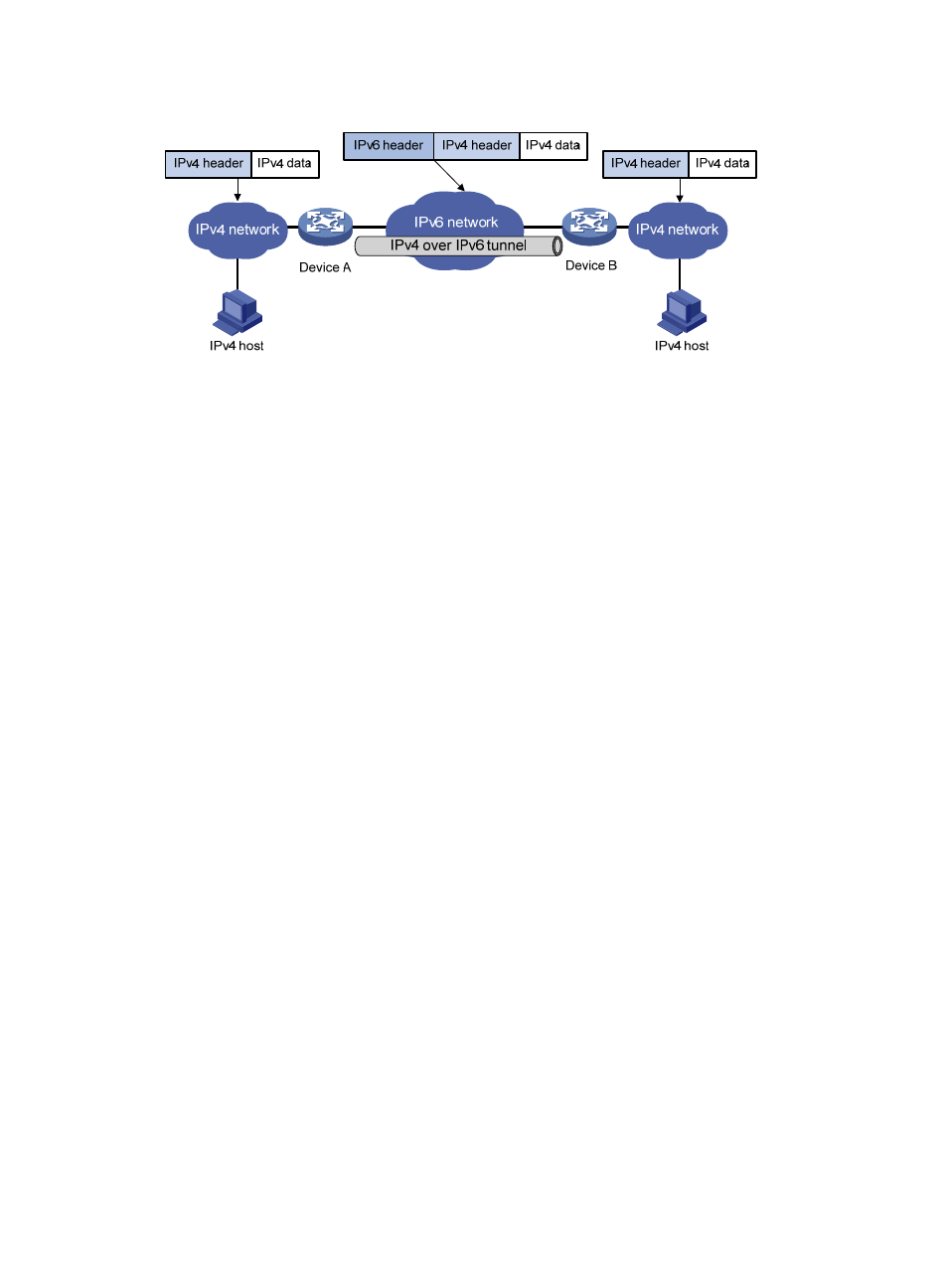
Figure 53 IPv4 over IPv6 tunnel
Packets traveling through a tunnel undergo encapsulation and de-encapsulation, as shown in
.
•
Encapsulation:
a.
Upon receiving an IPv4 packet, Device A delivers it to the IPv4 protocol stack.
b.
The IPv4 protocol stack uses the destination address of the packet to determine the egress
interface. If the egress interface is the tunnel interface, the IPv4 protocol stack delivers the
packet to the tunnel interface.
c.
The tunnel interface adds an IPv6 header to the original IPv4 packet and delivers the packet to
the IPv6 protocol stack.
d.
The IPv6 protocol stack uses the destination IPv6 address of the packet to look up the routing
table, and then sends it out.
•
De-encapsulation:
a.
Upon receiving the IPv6 packet from the attached IPv6 network, Device B delivers the packet
to the IPv6 protocol stack to examine the protocol type encapsulated in the data portion of the
packet.
b.
If the protocol type is IPv4, the IPv6 protocol stack delivers the packet to the tunneling module.
c.
The tunneling module removes the IPv6 header and delivers the remaining IPv4 packet to the
IPv4 protocol stack.
d.
The IPv4 protocol stack forwards the IPv4 packet.
IPv6 over IPv6 tunneling
IPv6 over IPv6 tunneling (RFC 2473) enables isolated IPv6 networks to communicate with each other
over another IPv6 network. For example, two isolated IPv6 networks that do not want to show their
addresses to the Internet can use an IPv6 over IPv6 tunnel to communicate with each other.
