Configuring ip addressing, Overview, Ip address classes – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 34
20
Configuring IP addressing
Overview
IP addressing uses a 32-bit address to identify each host on a network. To make addresses easier to read,
they are written in dotted decimal notation, each address being four octets in length. For example,
address 00001010000000010000000100000001 in binary is written as 10.1.1.1.
IP address classes
Each IP address breaks down into the following parts:
•
Net ID—Identifies a network. The first several bits of a net ID, known as the class field or class bits,
identify the class of the IP address.
•
Host ID—Identifies a host on a network.
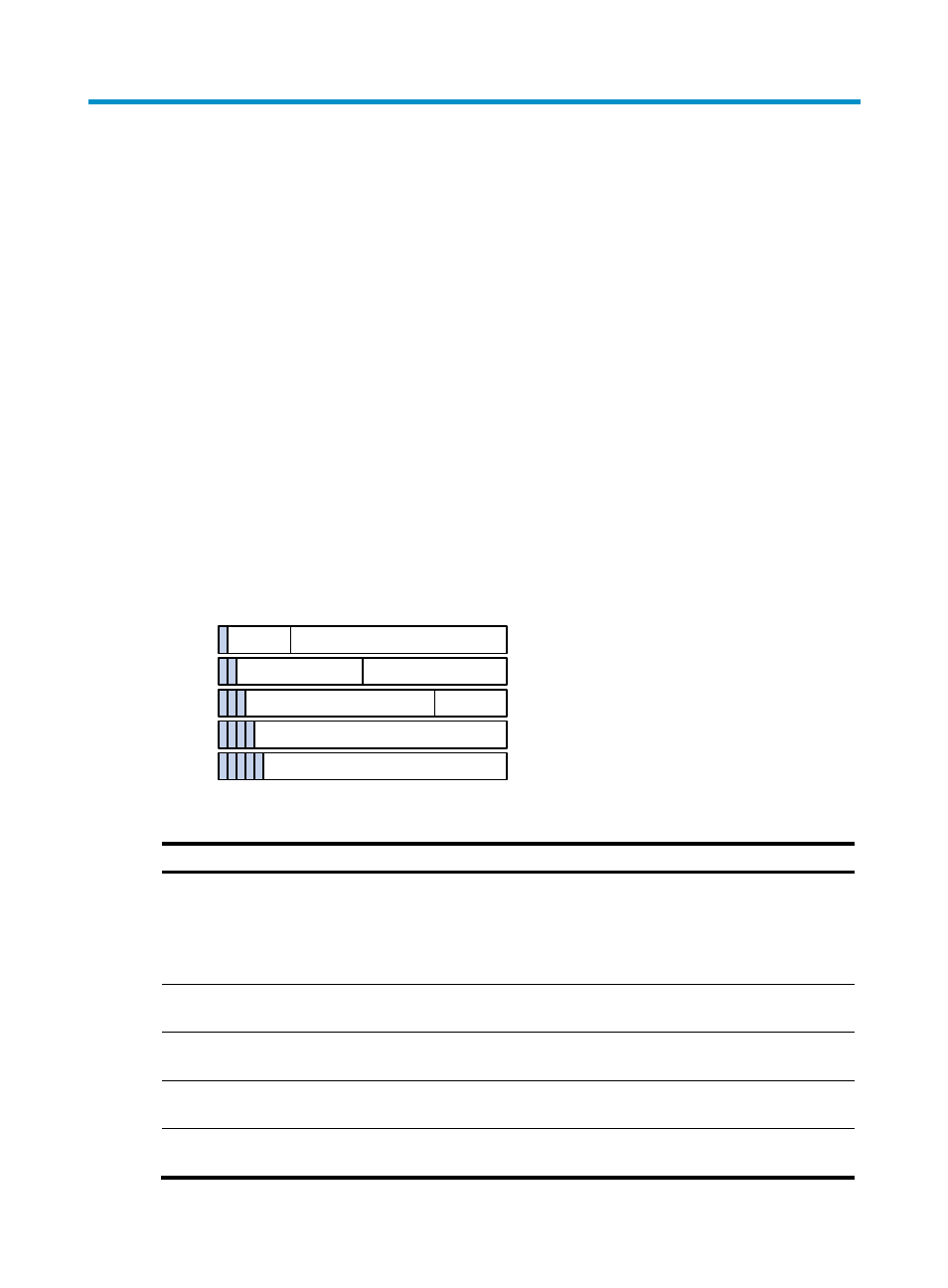
IP addresses are divided into five classes, as shown in
. The shade areas represent the address
class. The first three classes are widely used.
Figure 10 IP address classes
Table 1 IP address classes and ranges
Class Address
range Description
A
0.0.0.0 to
127.255.255.255
The IP address 0.0.0.0 is used by a host at startup for temporary
communication. This address is never a valid destination address.
Addresses starting with 127 are reserved for loopback test.
Packets destined to these addresses are processed locally as input
packets rather than sent to the link.
B
128.0.0.0 to
191.255.255.255
N/A
C
192.0.0.0 to
223.255.255.255
N/A
D
224.0.0.0 to
239.255.255.255
Multicast addresses.
E
240.0.0.0 to
255.255.255.255
Reserved for future use except for the broadcast address
255.255.255.255.
0
Net ID
Host ID
1
Net ID
Host ID
0
1
Net ID
Host ID
0
1
1
Multicast address
0
1
1
1
Reserved
1
1
1
Class A
Class B
Class C
Class D
Class E
0
7
15
23
31
0
