Dns mapping, Easy ip – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 110
96
to the private IP address and port number of the internal server. When the NAT device receives a
response packet from the internal server, it translates the source private IP address and port number of the
packet into the public IP address and port number of the internal server.
Figure 46 Internal server operation
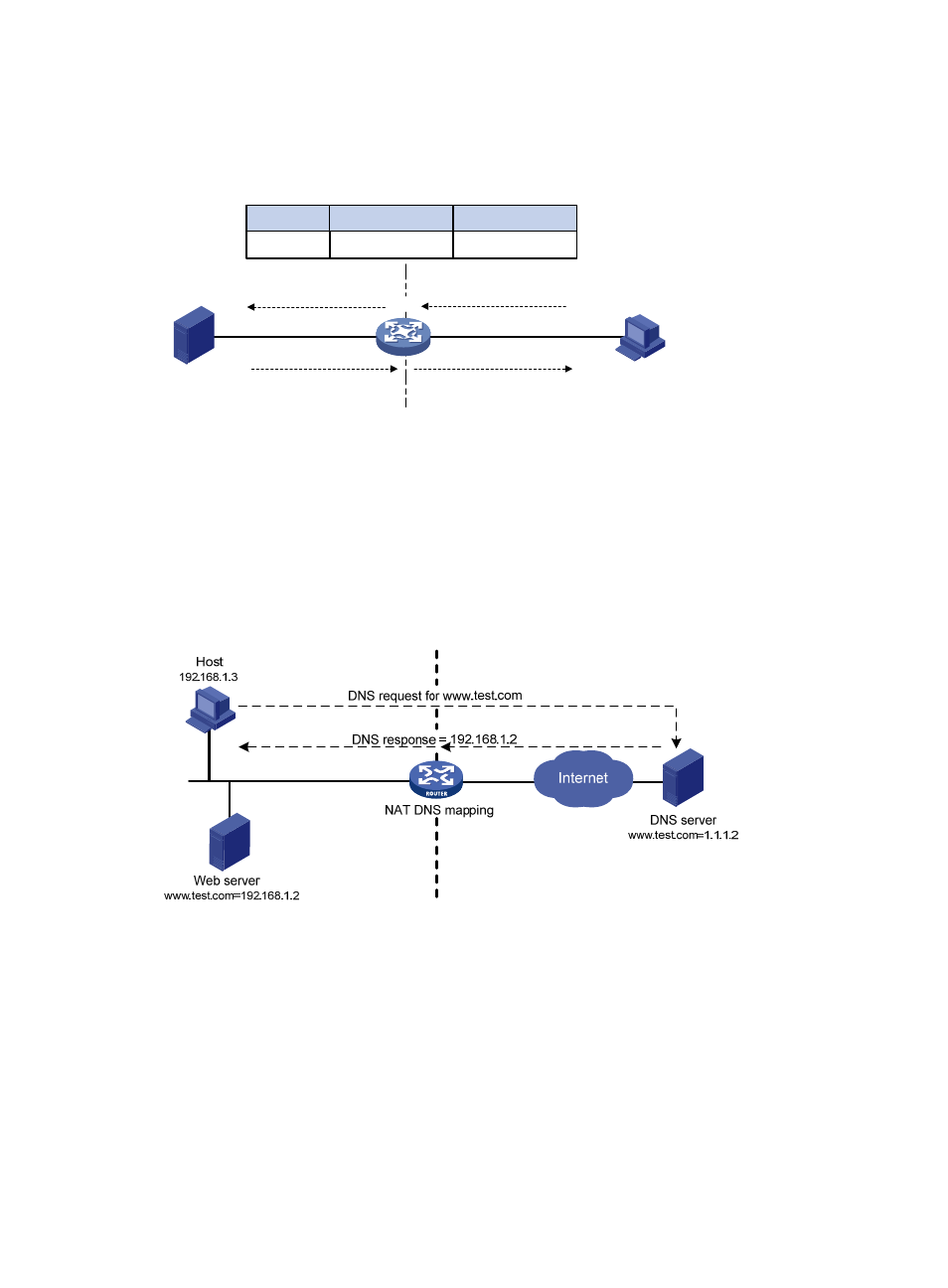
DNS mapping
Generally, the DNS server and users that need to access internal servers reside on the public network.
You can specify an external IP address and port number for an internal server on the public network
interface of a NAT device, so that external users can access the internal server using its domain name or
pubic IP address. In
, an internal host wants to access an internal web server by using its domain
name, and the DNS server is located on the public network. The DNS server replies with the public
address of the internal server to the host and the host cannot access the internal server. The DNS
mapping feature can solve the problem.
Figure 47 NAT DNS mapping operation
A DNS mapping entry records the domain name, public address, public port number, and protocol type
of an internal server. Upon receiving a DNS reply, the NAT-enabled interface matches the domain name
in the message against the DNS mapping entries. If a match is found, the private address of the internal
server is found and the interface replaces the public IP address in the reply with the private IP address.
Then, the host can use the private address to access the internal server.
Easy IP
Easy IP uses the public IP address of an interface on the switch as the translated source address to save
IP address resources, and uses ACLs to permit only certain internal IP addresses to be NATed.
192.168.1.3
192.168.1.1
20.1.1.1
1.1.1.2
NAT
Intranet
Internet
Host
Server
Dst : 20.1.1.1:8080
Dst : 192.168.1.3:8080
Src : 192.168.1.3:8080
Src : 20.1.1.1:8080
Before NAT
20.1.1.1:8080
After NAT
192.168.1.3:8080
Direction
Inbound
