Configuring nat, Overview – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 107
93
Configuring NAT
You cannot configure NAT after you configure local PBR or interface PBR. For more information about
PBR, see Layer 3—IP Routing Configuration Guide.
Overview
Network Address Translation (NAT) provides a way of translating the IP address in an IP packet header
to another IP address. In practice, NAT is primarily used to allow users using private IP addresses to
access public networks. With NAT, a smaller number of public IP addresses are used to enable a larger
number of internal hosts to access the Internet. Thus, NAT effectively alleviates the depletion of IP
addresses.
A private or internal IP address is used only in an internal network, whereas a public or external IP
address is used on the Internet and is globally unique.
According to RFC 1918, three blocks of IP addresses are reserved for private networks:
•
In Class A, 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255.
•
In Class B, 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255.
•
In Class C, 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255.
No host with an IP address in the three ranges exists on the Internet. You can use those IP addresses in
an enterprise network freely without requesting them from an ISP or a registration center.
In addition to translating private addresses to public addresses, NAT can also perform address
translation between any two networks. In this document, the two networks refer to an internal network
and an external network. Generally, a private network is an internal network, and a public network is an
external network.
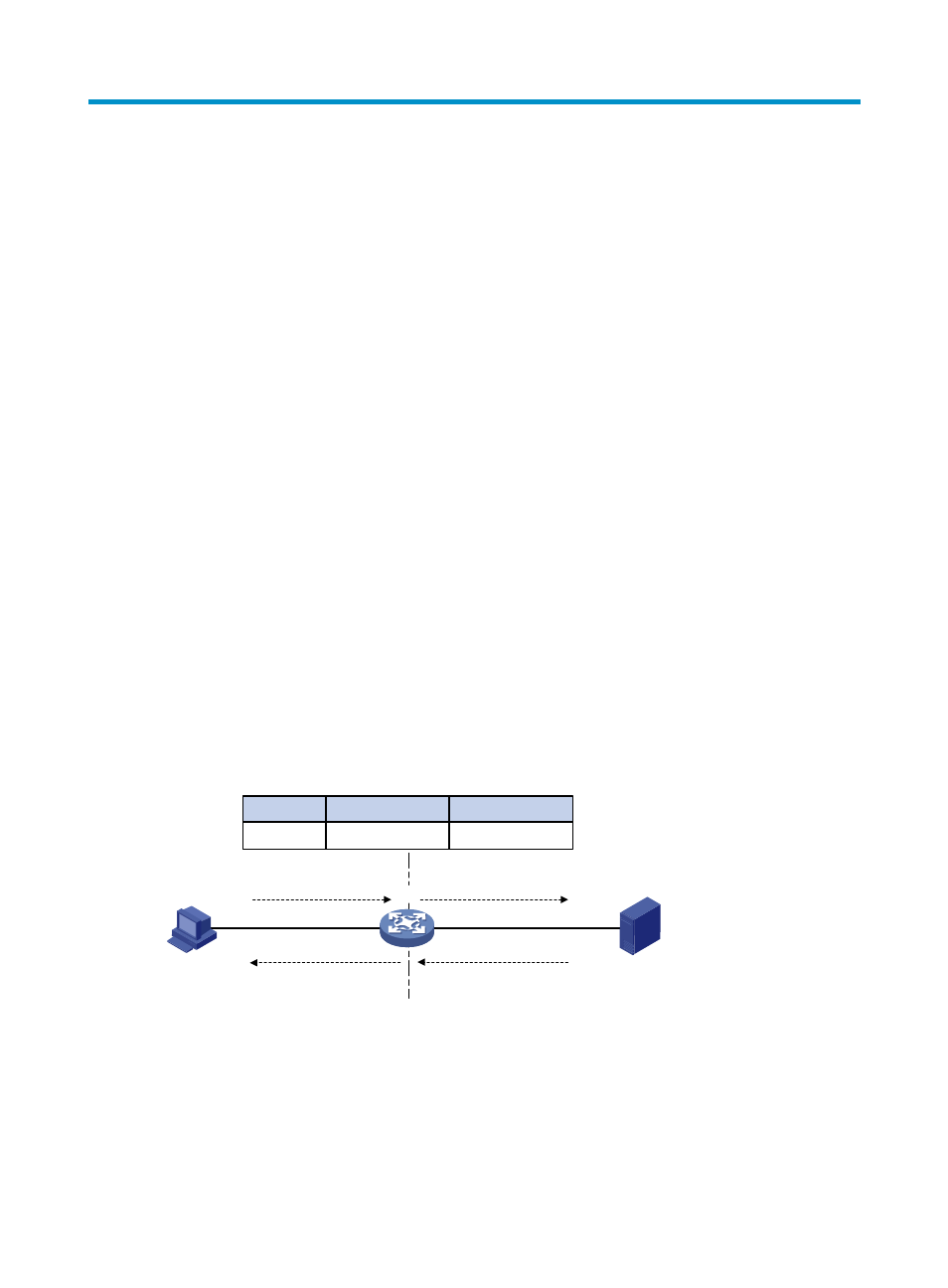
Figure 44 NAT operation
1.
The internal host with an IP address of 192.168.1.3 sends an IP packet to the external server with
an IP address of 1.1.1.2 through the NAT device.
2.
Upon receiving the packet, the NAT device checks the IP header and finds that it is destined to the
external network. Then it translates the private address 192.168.1.3 to the globally unique public
address 20.1.1.1 and then forwards the packet to the server on the external network. Meanwhile,
the NAT device adds the mapping of the two addresses into its NAT table.
192.168.1.3
Src : 192.168.1.3
Dst : 1.1.1.2
Src : 20.1.1.1
Dst : 1.1.1.2
192.168.1.1
20.1.1.1
Src : 1.1.1.2
Dst : 20.1.1.1
Src : 1.1.1.2
Dst : 192.168.1.3
1.1.1.2
Server
Host
NAT
Intranet
Internet
Before NAT
192.168.1.3
After NAT
20.1.1.1
Direction
Outbound
