Protocols and standards – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 216
202
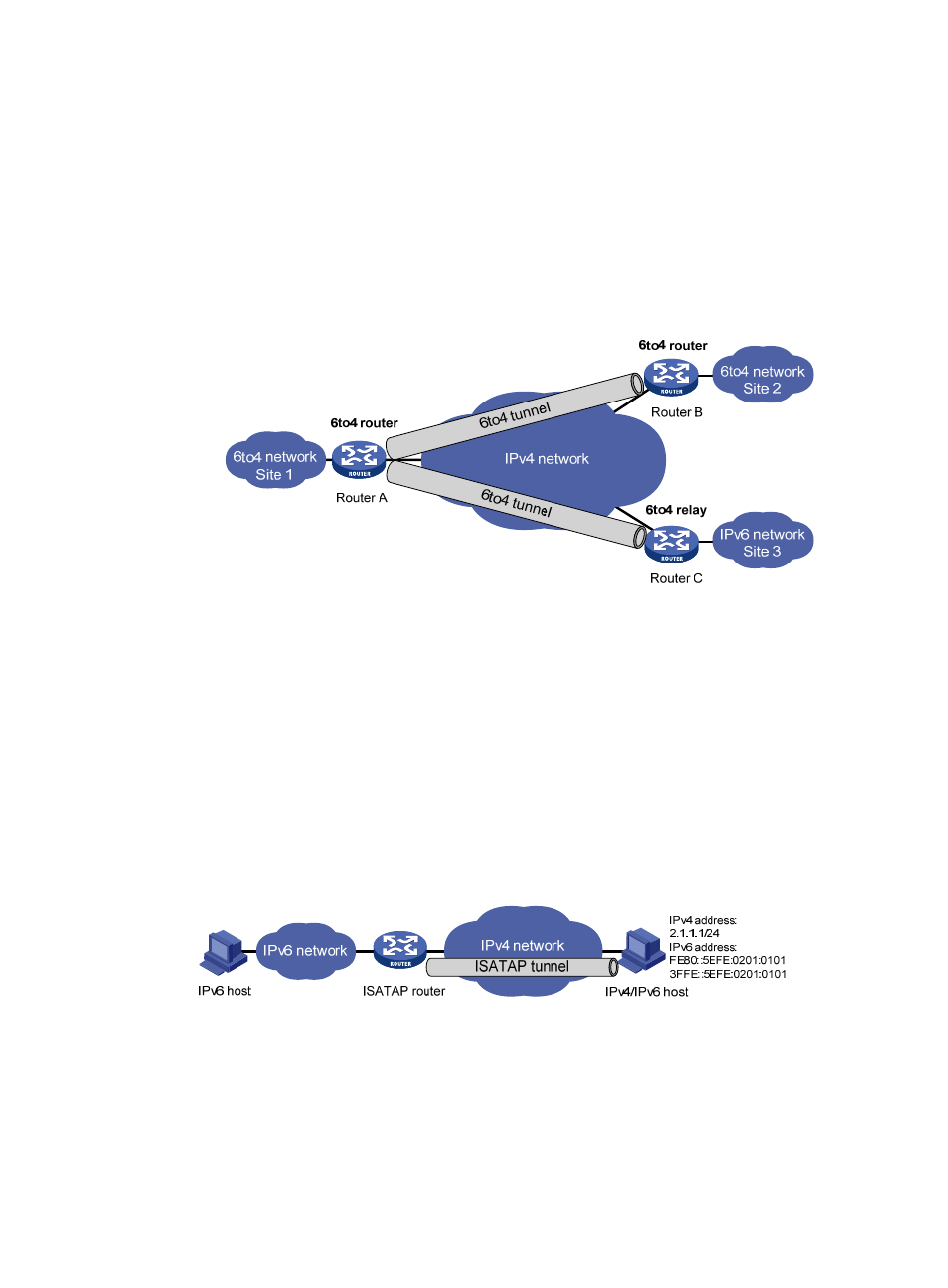
A 6to4 tunnel is only used to connect 6to4 networks, whose IP prefix must be 2002::/16.
However, IPv6 network addresses with the prefix such as 2001::/16 can also be used in IPv6
networks. To connect a 6to4 network to an IPv6 network, a 6to4 router must be used as a
gateway to forward packets to the IPv6 network. Such a router is called 6to4 relay router.
As shown in
, a static route must be configured on the border router in the 6to4
network and the next-hop address must be the 6to4 address of the 6to4 relay router. All
packets destined for the IPv6 network are forwarded to the 6to4 relay router, and then to the
IPv6 network. This provides interworking between the 6to4 network (with the address prefix
starting with 2002) and the IPv6 network.
Figure 86 Principle of 6to4 tunnel and 6to4 relay
5.
ISATAP tunnel
An ISATAP tunnel is a point-to-point automatic tunnel. The destination of a tunnel can automatically
be acquired from the embedded IPv4 address in the destination address of an IPv6 packet.
When an ISATAP tunnel is used, the destination address of an IPv6 packet and the IPv6 address
of a tunnel interface both adopt special ISATAP addresses. The ISATAP address format is
prefix(64bit):0:5EFE:ip-address. The 64-bit prefix is the prefix of a valid IPv6 unicast address,
while ip-address is a 32-bit source IPv4 address in the form of abcd:efgh (for example, 1.1.1.1 is
represented as 0101:0101 in hexadecimal), which need not be globally unique. Through the
embedded IPv4 address, an ISATAP tunnel can automatically be created to transfer IPv6 packets.
The ISATAP tunnel is mainly used for connection between IPv6 routers or between an IPv6 host and
an IPv6 router over an IPv4 network.
Figure 87 ISATAP tunnel
Protocols and standards
•
RFC 1853, IP in IP Tunneling
•
RFC 2473, Generic Packet Tunneling in IPv6 Specification
•
RFC 2893, Transition Mechanisms for IPv6 Hosts and Routers
