Hoefer SP-2001 Vision Life Spectrophotometer User Manual
Page 28
Version 1.0
Page 28
Use of Background Correction
• Background correction at a wavelength totally separate from the nucleic acid and protein peaks at 260 and 280
nm, respectively, is sometimes used to compensate for the effects of background absorbance. The
wavelength used is 320 nm and it can allow for the effects of turbidity, high absorbance buffer solution and the
use of reduced aperture cells. The instrument can use background correction.
• If it is used, there will be different results from those when unused, because Abs320 is subtracted from Abs260
and Abs280 prior to use in equations:
Concentration = (Abs 260 - Abs 320) * Factor
Abs ratio = (Abs 260 - Abs 320) / (Abs 280 - Abs 320)
Abs ratio = (Abs 260 - Abs 320) / (Abs 230 - Abs 320)
• If your laboratory has not used background correction before, set this option to NO.
• The use of background correction can remove variability due to handling effects of low volume disposable cells.
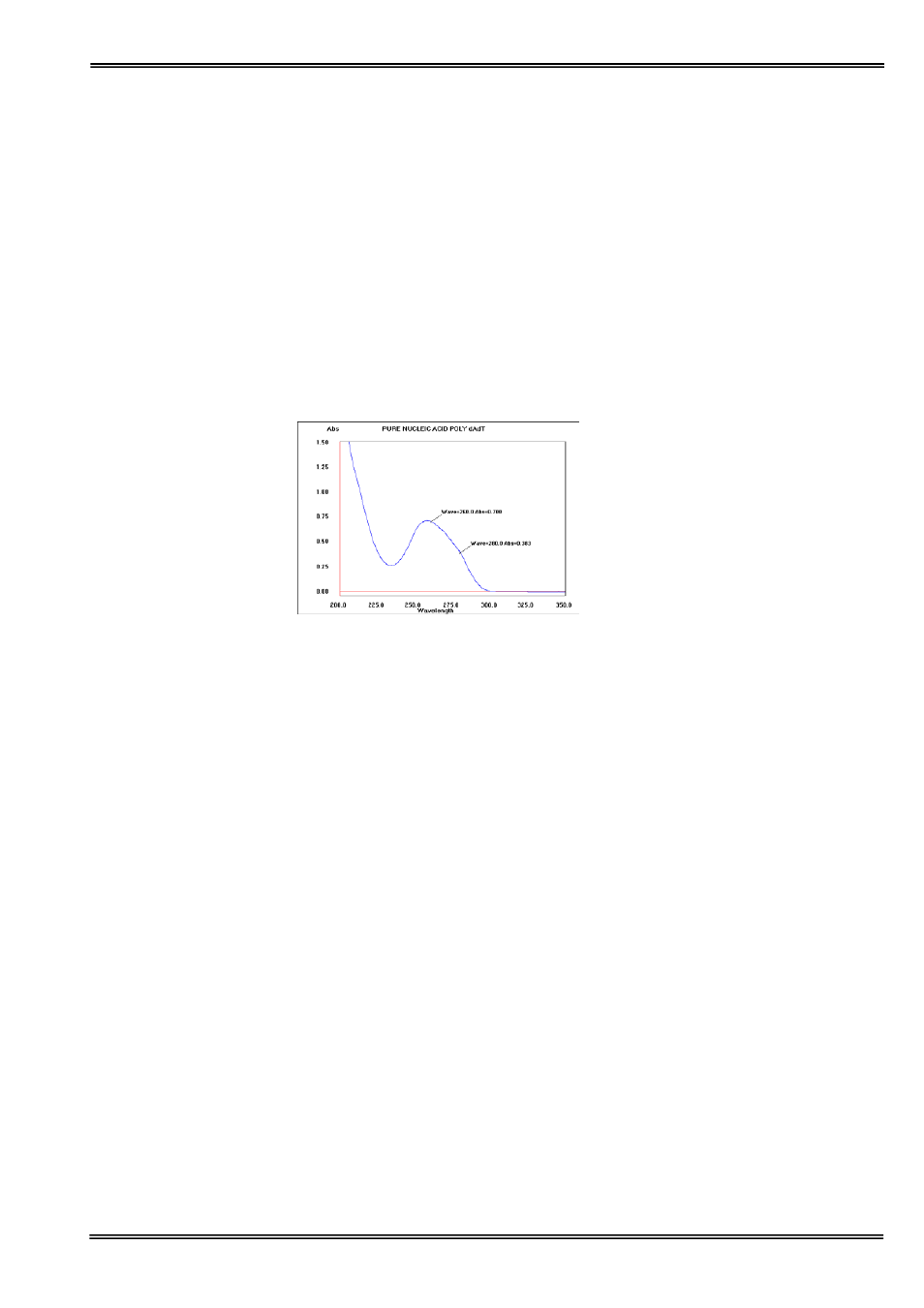
Spectral scan of nucleic acid
Note:
• absorbance maximum near 260 nm and absorbance minimum near 230 nm
• flat peak near 260 nm and steep slope at 280 nm
• very little absorbance at 320 nm
