Casio FX-9750GII User Manual
Page 224
8-13
Description: This command increments the value of a control variable by 1, and then tests
(checks) it. If the current value is non-zero, execution continues with the next statement. If the
current value is zero, execution jumps to the statement following the multi-statement command
(:), display command (
<), or carriage return (=).
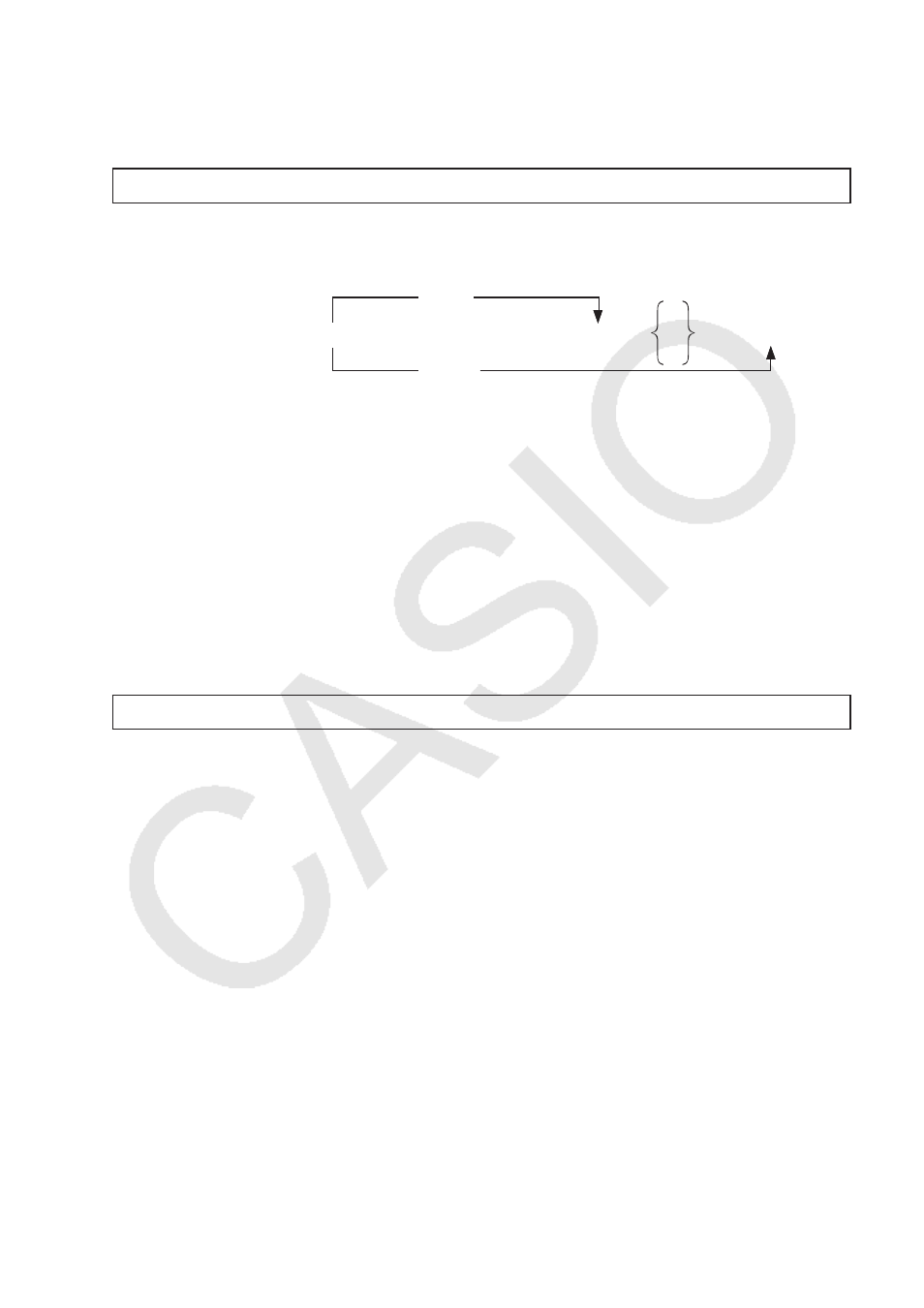
(Jump Code)
Function: This code is used to set up conditions for a conditional jump. The jump is executed
whenever the conditions are false.
Syntax:
True
_
:
^
False
Parameters:
• left side/right side: variable (A to Z,
r
,
Q), numeric constant, variable expression (such as:
A × 2)
• relational operator: =,
x, >, <, r, b (page 8-18)
Description:
• The conditional jump compares the contents of two variables or the results of two
expressions, and a decision is made whether or not to execute the jump based on the results
of the comparison.
• If the comparison returns a true result, execution continues with the statement following
the
command. If the comparison returns a false result, execution jumps to the statements
following the multi-statement command (:), display command (
<), or carriage return (=).
Menu
Function: Creates a branching menu in a program.
Syntax: Menu " n >", variable n > Parameters: value (0 to 9), variable (A to Z, r , Q) Description: • Each " n >" , n > part is a branch set, and the entire branch set must be included. • From two to nine branching sets can be included. An error occurs when there is only one or more than nine branching sets. • Selecting a branch on the menu while the program is running jumps to the same type of label (Lbl n ) as the one used in combination with the Goto command. Specifying “"OK", 3” for the “" n >", n >” part specifies a jump to Lbl 3. Example: Lbl 2 = Menu "IS IT DONE?", "OK", 1, "EXIT", 2 = Lbl 1 = "IT’S DONE !"
"
