Casio FX-9750GII User Manual
Page 138
5-32
• You can calculate the point of intersection for rectangular coordinate graphs (Y=
f
(
x
) type)
and inequality graphs (Y
f
(
x
), Y
f
(
x
), Y
P
f
(
x
) or Y
O
f
(
x
)) only.
• Either of the following can cause poor accuracy or even make it impossible to obtain
solutions.
- When a solution is a point of tangency between two graphs
- When a solution is an inflection point
I Determining the Coordinates for Given Points
The following procedure describes how to determine the
y
-coordinate for a given
x
, and the
x
-coordinate for a given
y
.
1. Draw the graph.
2. Select the function you want to perform. When there are multiple graphs, the selection
cursor (
I) appears at the lowest numbered graph.
y
-coordinate for given
x
(E)(X-CAL) ...
x
-coordinate for given
y
3. Use
DA to move the cursor (I) to the graph you want, and then press U to select it.
4. Input the given
x
-coordinate value or
y
-coordinate value.
Press
U to calculate the corresponding
y
-coordinate value or
x
-coordinate value.
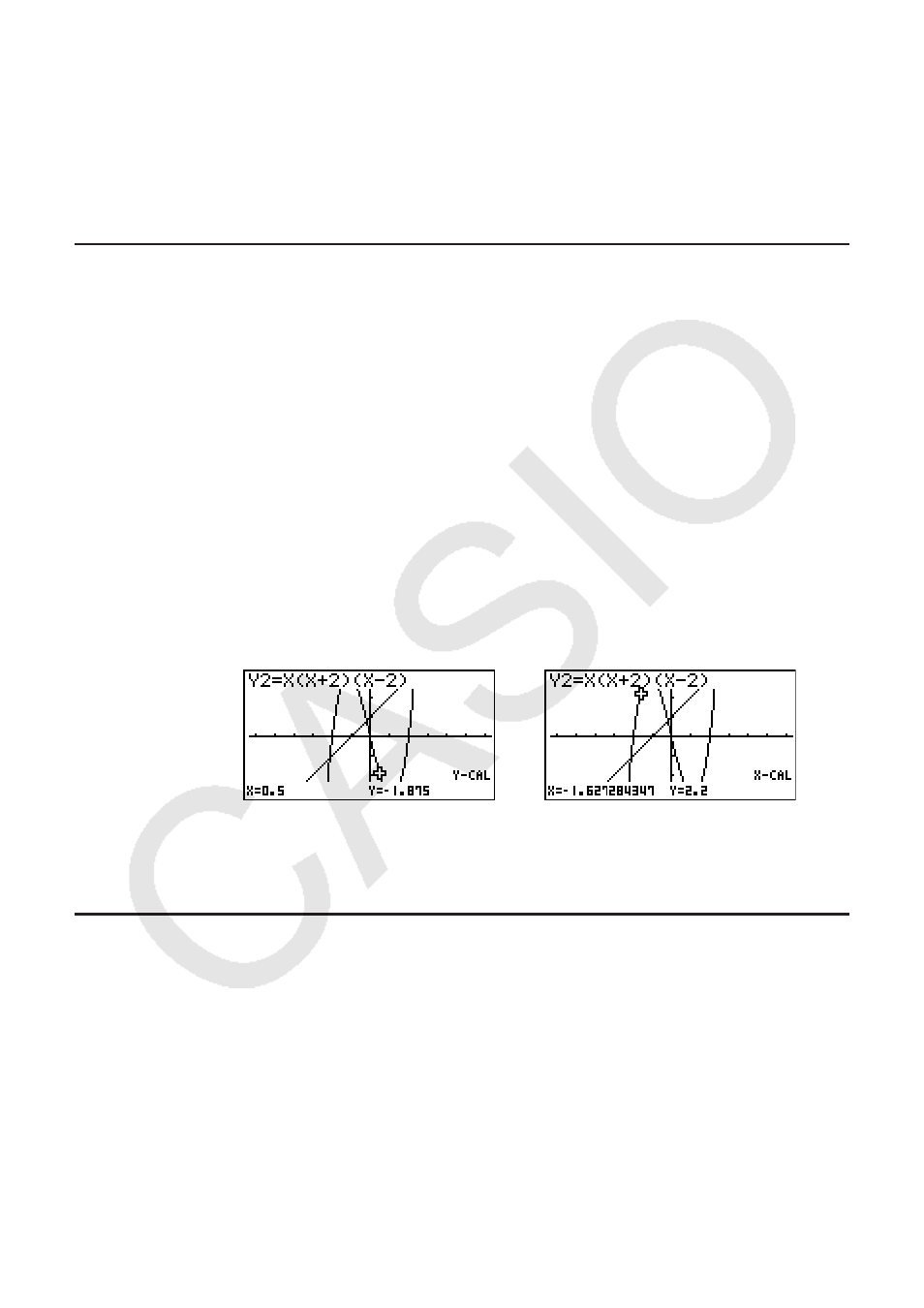
Example
Graph the two functions shown below and then determine the
y
-
coordinate for
x
= 0.5 and the
x
-coordinate for
y
= 2.2 on graph Y2.
Y1 =
x
+ 1, Y2 =
x
(
x
+ 2)(
x
– 2)
• When there are multiple results for the above procedure, press
C to calculate the next
value. Pressing
B returns to the previous value.
• The X-CAL value cannot be obtained for a parametric function graph.
I Calculating the lntegral Value for a Given Range
Use the following procedure to obtain integration values for a given range.
1. Draw the graph.
2. Press
dx
). When there are multiple graphs, this causes the
selection cursor (
I) to appear at the lowest numbered graph.
3. Use
DA to move the cursor (I) to the graph you want, and then press U to select it.
4. Use
BC to move the lower limit pointer to the location you want, and then press U.
5. Use
C to move the upper limit pointer to the location you want.
6. Press
U to calculate the integral value.
