Casio FX-9750GII User Manual
Page 157
6-17
• Linear Regression (
ax
+
b
).............
(
a
+
bx
).............
• Quadratic Regression.....................
• Cubic Regression ...........................
• Quartic Regression ........................
• Logarithmic Regression..................
• Exponential Repression (
a
·
e
bx
) .......
(
a
·
b
x
)........
• Power Regression ..........................
• Sin Regression ...............................
• Logistic Regression ........................
S Estimated Value Calculation for Regression Graphs
The STAT mode also includes a Y-CAL function that uses regression to calculate the estimated
y
-value for a particular
x
-value after graphing a paired-variable statistical
regression.
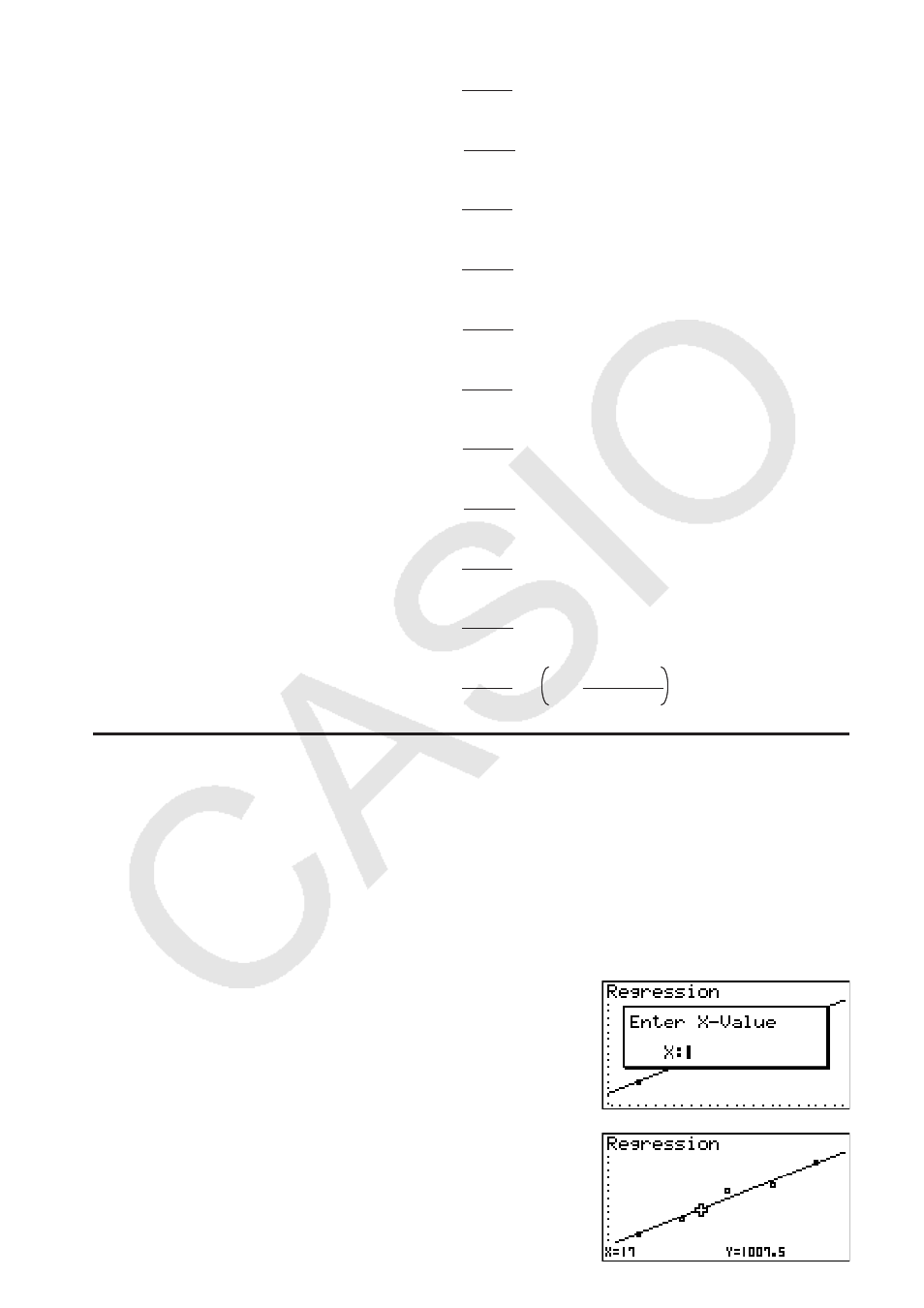
The following is the general procedure for using the Y-CAL function.
1. After drawing a regression graph, press
selection mode, and then press
U.
If there are multiple graphs on the display, use
D and A to select the graph you want,
and then press
U.
• This causes an
x
-value input dialog box to appear.
2. Input the value you want for
x
and then press
U.
• This causes the coordinates for
x
and
y
to appear at
the bottom of the display, and moves the pointer to the
corresponding point on the graph.
MSe
=
1
n
– 2
i
=1
n
(y
i
– (ax
i
+ b))
2
MSe
=
1
n
– 2
i
=1
n
(y
i
– (ax
i
+ b))
2
MSe
=
1
n
– 2
i
=1
n
(y
i
– (a + bx
i
))
2
MSe
=
1
n
– 2
i
=1
n
(y
i
– (a + bx
i
))
2
MSe
=
1
n
– 3
i
=1
n
(y
i
– (ax
i
+ bx
i
+ c))
2
2
MSe
=
1
n
– 3
i
=1
n
(y
i
– (ax
i
+ bx
i
+ c))
2
2
MSe
=
1
n
– 4
i
=1
n
(y
i
– (ax
i
3
+ bx
i
+ cx
i
+ d ))
2
2
MSe
=
1
n
– 4
i
=1
n
(y
i
– (ax
i
3
+ bx
i
+ cx
i
+ d ))
2
2
MSe
=
1
n
– 5
i
=1
n
(y
i
– (ax
i
4
+ bx
i
3
+ cx
i
+ dx
i
+ e))
2
2
MSe
=
1
n
– 5
i
=1
n
(y
i
– (ax
i
4
+ bx
i
3
+ cx
i
+ dx
i
+ e))
2
2
MSe
=
1
n
– 2
i
=1
n
(y
i
– (a + b ln x
i
))
2
MSe
=
1
n
– 2
i
=1
n
(y
i
– (a + b ln x
i
))
2
MSe
=
1
n
– 2
i
=1
n
(ln y
i
– (ln a + bx
i
))
2
MSe
=
1
n
– 2
i
=1
n
(ln y
i
– (ln a + bx
i
))
2
MSe
=
1
n
– 2
i
=1
n
(ln y
i
– (ln a + (ln b) · x
i
))
2
MSe
=
1
n
– 2
i
=1
n
(ln y
i
– (ln a + (ln b) · x
i
))
2
MSe
=
1
n
– 2
i
=1
n
(ln y
i
– (ln a + b ln x
i
))
2
MSe
=
1
n
– 2
i
=1
n
(ln y
i
– (ln a + b ln x
i
))
2
MSe
=
1
n
– 2
i
=1
n
(y
i
– (a sin (bx
i
+ c) + d ))
2
MSe
=
1
n
– 2
i
=1
n
(y
i
– (a sin (bx
i
+ c) + d ))
2
MSe
=
1
n
– 2
1 + ae
–bx
i
C
i
=1
n
y
i
–
2
MSe
=
1
n
– 2
1 + ae
–bx
i
C
i
=1
n
y
i
–
2
