I drawing a normal probability distribution graph, I calculations using the distribution function – Casio FX-9750GII User Manual
Page 160
6-20
4. Press
K, select the RUN • MAT (or RUN) mode, press *(E)(PROB)
(
(PROB) on the fx-7400G
II
) to recall the probability calculation (PROB) menu.
(PROB)*(E)(
t
()
@E? DU
* fx-7400G
II
:
(PROB)
(Normalized variate
t
for 160.5 cm)
Result: –1.633855948
( –1.634)
(
t
()
@FD DU
(Normalized variate
t
for 175.5 cm)
Result: 0.4963343361
( 0.496)
(P()? CHE
(P()@ EBCU
(Percentage of total)
Result:
0.638921
(63.9% of total)
(R()? CHEU
(Percentile)
Result:
0.30995
(31.0 percentile)
I Drawing a Normal Probability Distribution Graph
You can draw a normal probability distribution graph using manual graphing with the
RUN • MAT (or RUN) mode.
1. From the Main Menu, enter the RUN • MAT (or RUN) mode.
2. Input the commands to draw a rectangular coordinate graph.
3. Input the probability value.
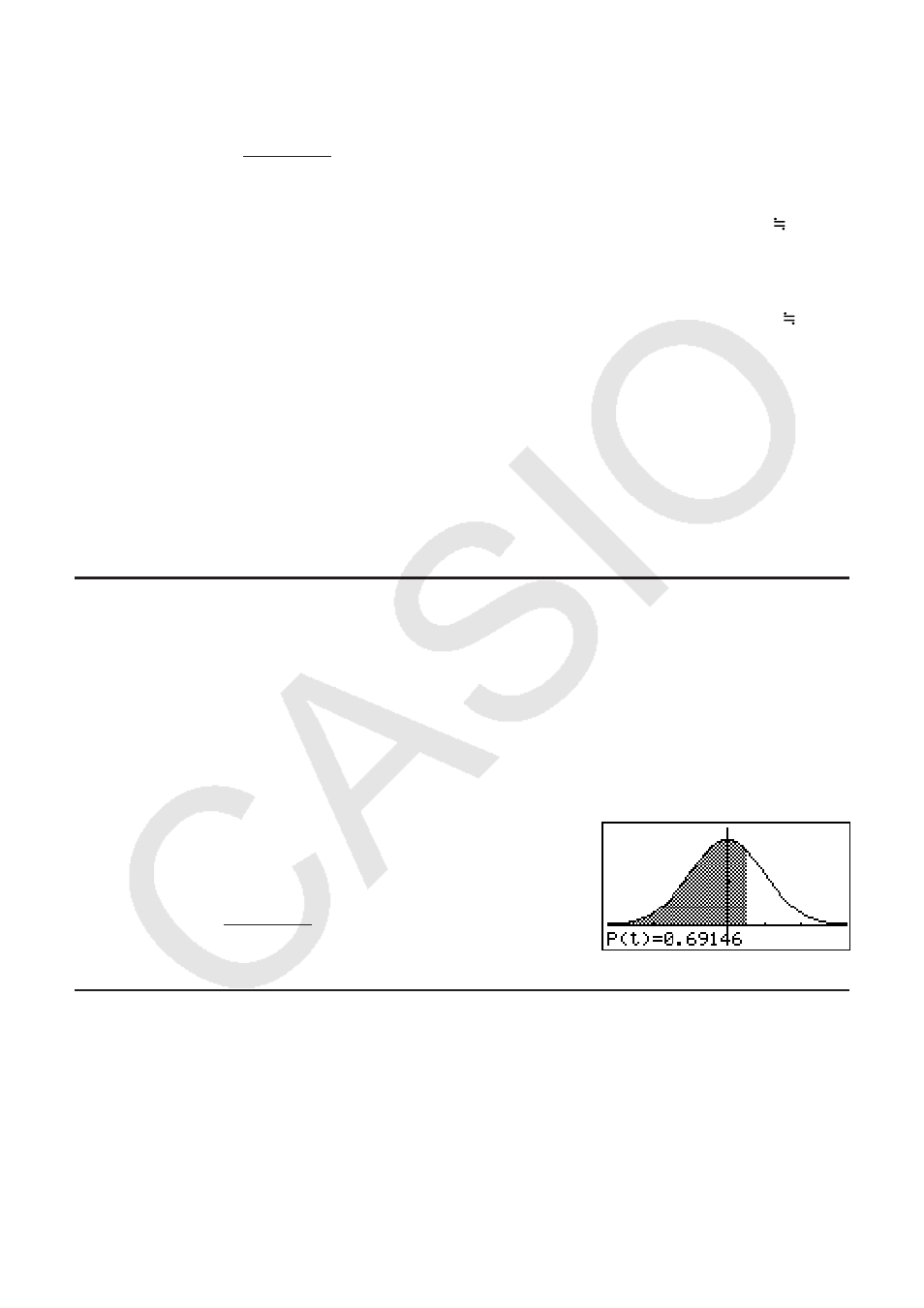
Example To draw a normal probability P (0.5) graph.
K RUN • MAT (or RUN)
(GRPH)(Y=)
*(E)(PROB)*(E)(P()? DU
* fx-7400G
II
:
(PROB)
I Calculations Using the Distribution Function
Important!
• The following operations cannot be performed on the fx-7400G
II
.
You can use special functions in the RUN • MAT mode or PRGM mode to perform calculations
that are the same as the STAT mode distribution function calculation (page 6-38).
Example To calculate normal probability distribution in the RUN • MAT mode for
the data {1, 2, 3}, when the population standard deviation is
S = 1.5 and
the population mean is
ƫ
= 2.
