Casio FX-9750GII User Manual
Page 113
5-7
S To store a parametric function
Example
To store the following expressions in memory areas Xt3 and Yt3:
x
= 3 sinT
y
= 3 cosT
(TYPE)(Parm) (Specifies parametric expression.)
BQTU(Inputs and stores
x
expression.)
BATU(Inputs and stores
y
expression.)
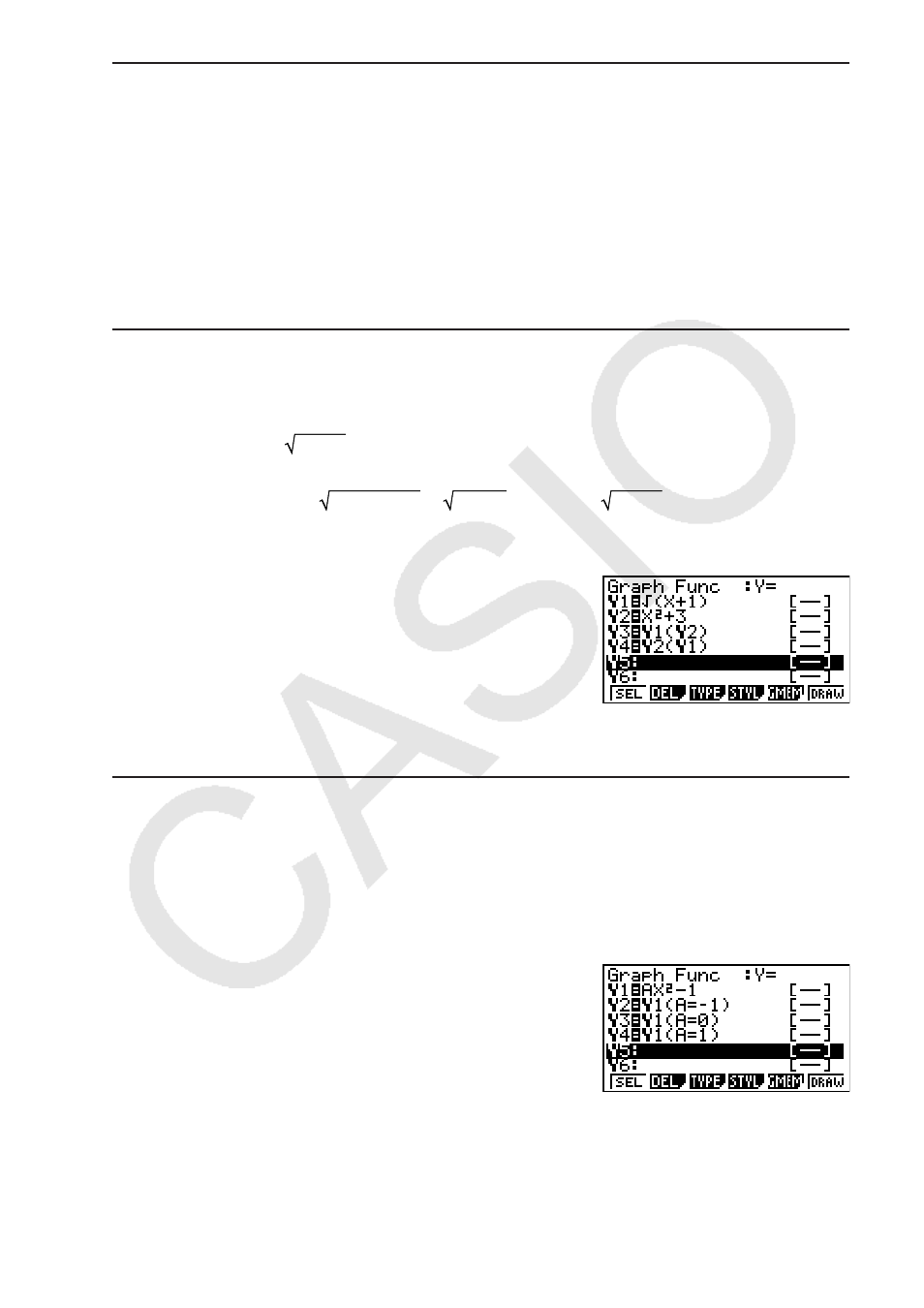
S To create a composite function
Example
To use relations in Y1 and Y2 to create composite functions for Y3
and Y4
Y1 = (X + 1), Y2 = X
2
+ 3
Assign Y1°Y2 to Y3, and Y2°Y1 to Y4.
(Y1°Y2 = ((x
2
+ 3) +1) = (x
2
+ 4) Y2°Y1 = ( (X + 1))
2
+ 3 = X + 4 (X
−1))
Input relations into Y3 and Y4.
(TYPE)(Y=))(GRPH)
(Y)@(Y)AU
)(GRPH)(Y)A
(Y)@U
• A composite function can consist of up to five functions.
S To assign values to the coefficients and variables of a graph function
Example
To assign the values −1, 0, and 1 to variable A in Y = AX
2
−1, and draw a
graph for each value
(TYPE)(Y=)
?T(A)TV@U
)(GRPH)(Y)@?T(A)
)(GRPH)(Y)@?T(A)
)(GRPH)(Y)@?T(A)
DDDD(SEL)
(DRAW)
