2power supplies, 1 migrating from nexys4 – Digilent 410-292P-KIT User Manual
Page 3
Nexys4 DDR™ FPGA Board Reference Manual
Copyright Digilent, Inc. All rights reserved.
Other product and company names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 3 of 29
1.1 Migrating from Nexys4
The Nexys4 DDR is an incremental update to the Nexys4 board. The major improvement is the replacement of the
16 MiB CellularRAM with a 128 MiB DDR2 SDRAM memory. Digilent will provide a VHDL reference module that
wraps the complexity of a DDR2 controller and is backwards compatible with the asynchronous SRAM interface of
the CellularRAM, with certain limitations. See the Nexys4 DDR page a
or updates.
Furthermore, to accommodate the new memory, the pin-out of the FPGA banks has changed as well. The
constraints file of existing projects will need to be updated.
The audio output (AUD_PWM) needs to be driven open-drain as opposed to push-pull on the Nexys4.
2
Power Supplies
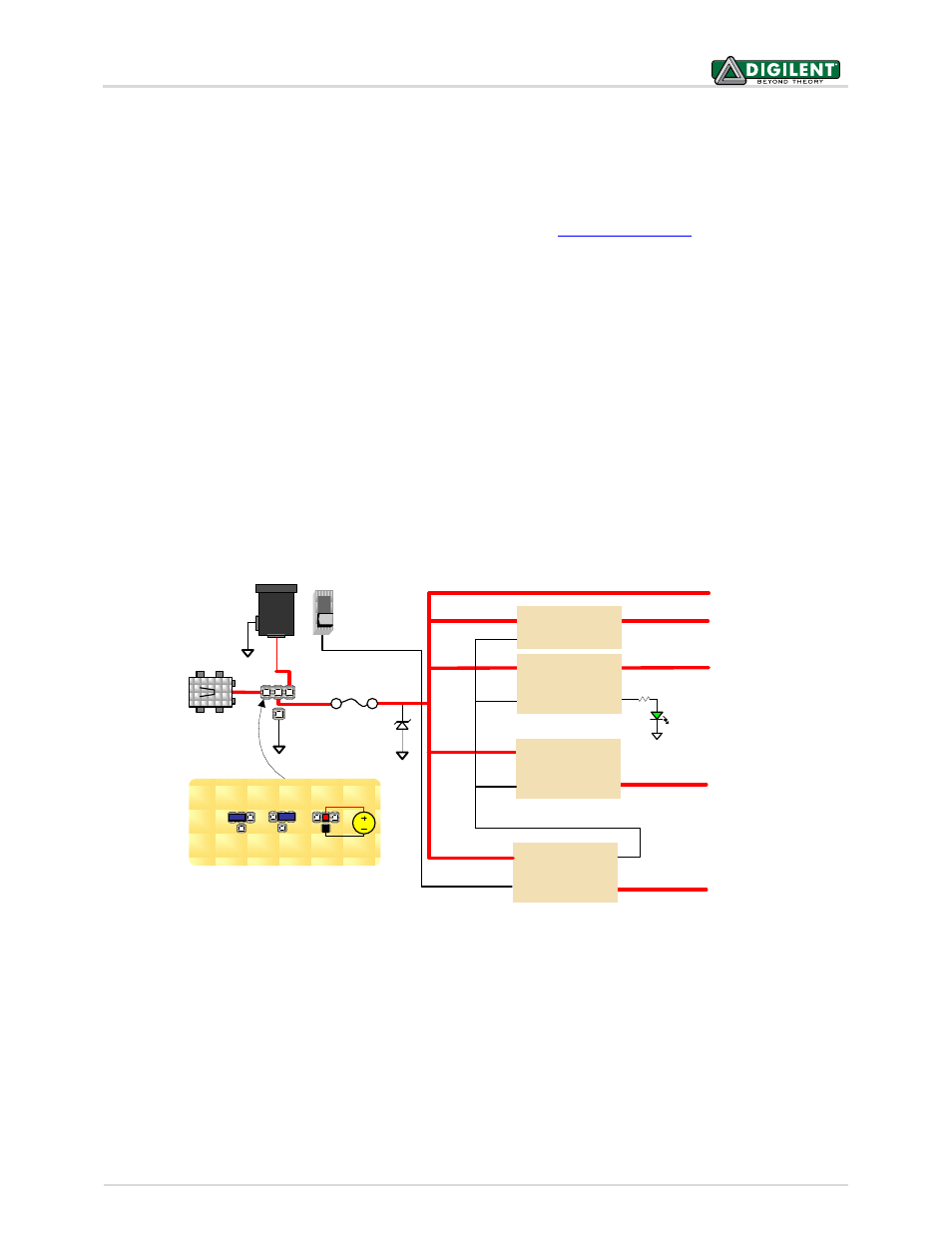
The Nexys4 DDR board can receive power from the Digilent USB-JTAG port (J6) or from an external power supply.
Jumper JP3 (near the power jack) determines which source is used.
All Nexys4 DDR power supplies can be turned on and off by a single logic-level power switch (SW16). A power-good
LED (LD22), driven by the “power good” output of the ADP2118 supply, indicates that the supplies are turned on
and operating normally. An overview of the Nexys4 DDR power circuit is shown in Figure 2.
Power
Jack
(J13)
3.3V
IC17: ADP2118
Power
Switch
(SW16)
Power On
LED (LD22)
Micro-USB
Port (J6)
VU5V0
J12
IC23: ADP2138
EN
800 mA
VIN
IC22: ADP2118
EN
PGOOD
3A
VIN
1.8V
1.0V
Power Source Select
JP3
J12
USB
WALL
BATTERY
EN
PGOOD
3A
VIN
JP3
Audio
3.3V
EN
150mA
VIN
R287
D16
Figure 2. Nexys4 DDR power circuit.
The USB port can deliver enough power for the vast majority of designs. Our out-of-box demo draws ~400mA of
current from the 5V input rail. A few demanding applications, including any that drive multiple peripheral boards,
might require more power than the USB port can provide. Also, some applications may need to run without being
connected to a PC’s USB port. In these instances, an external power supply or battery pack can be used.
An external power supply can be used by plugging into to the power jack (JP3) and setting jumper J13 to “wall”.
The supply must use a coax, center-positive 2.1mm internal-diameter plug, and deliver 4.5VDC to 5.5VDC and at
