Explicit messages – Rockwell Automation Ethernet Design Considerations Reference Manual User Manual
Page 72
72
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-RM002C-EN-P - May 2013
Chapter 4
EtherNet/IP Protocol
Explicit Messages
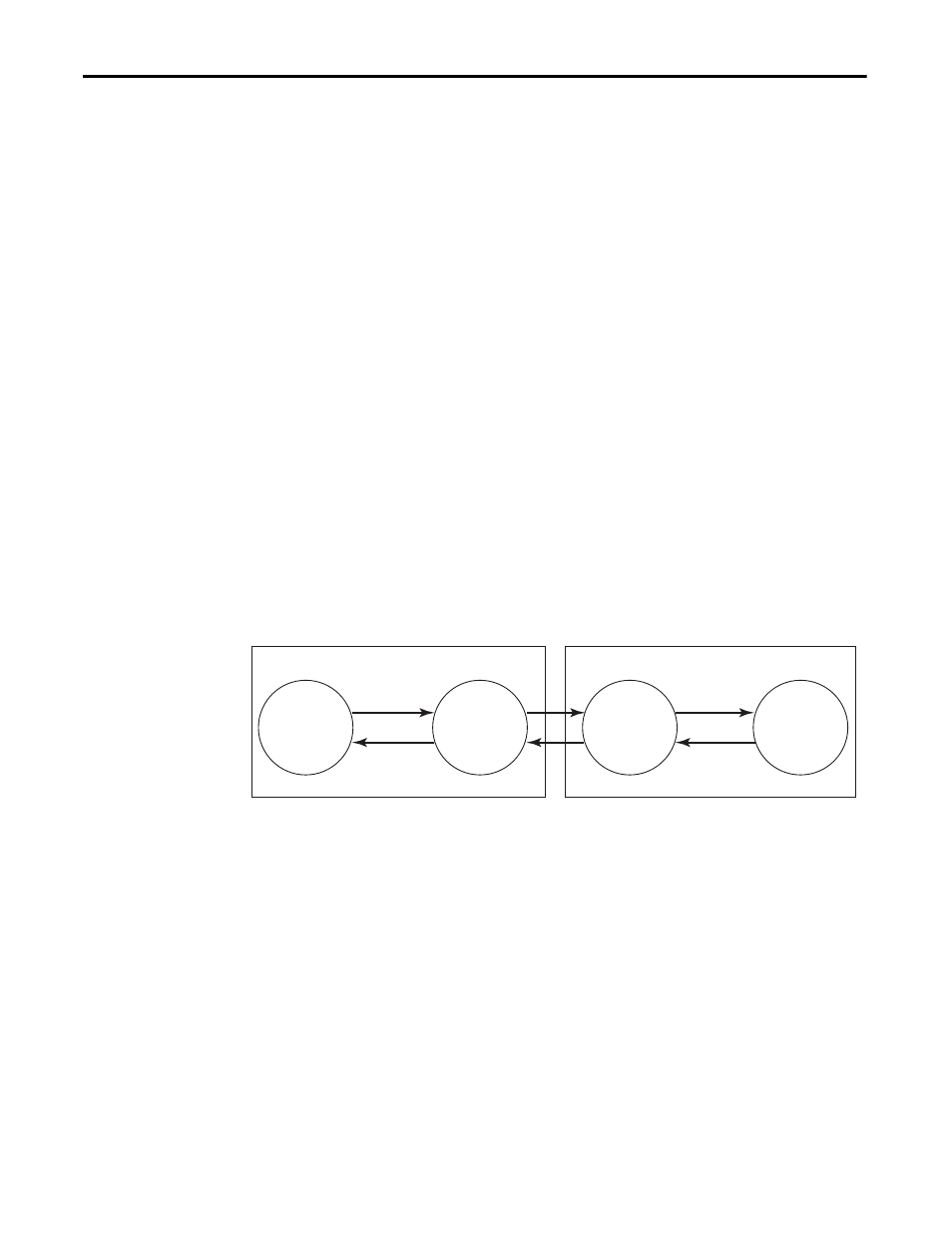
Explicit connections are non-time critical and are request/reply in nature.
Executing a MSG instruction or executing a program upload are examples of
explicit connections. Explicit refers to basic information (such as source address,
data type, or destination address) that is included in every message. Each request
is typically directed at a different data item. Examples of explicit applications
include the following:
•
HMI
•
RSLinx connections
•
Message (MSG) instructions
•
Program upload/download
Explicit messages use Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). Explicit messages
are used for point-to-point, client-server transactions that use transport class 3
(Class 3):
•
The server side is bound to the Message Router object and has access to all
internal resources.
•
The client side is bound to a client application object and must generate
requests to the server.
•
Explicit messages use an explicit messaging protocol in the data portion of
the message packet.
•
Explicit messages can be connected or unconnected.
An explicit message times out in 30 seconds. This is user-changeable in the
Message (MSG) instruction structure.
Application
Object
Explicit
Messaging
Connection
Request
Response
Application
Object
Explicit
Messaging
Connection
Request
Response
Device #1
Device #2
