Virtual lans and segmentation – Rockwell Automation Ethernet Design Considerations Reference Manual User Manual
Page 42
42
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-RM002C-EN-P - May 2013
Chapter 3
Ethernet Infrastructure Features
Virtual LANs and
Segmentation
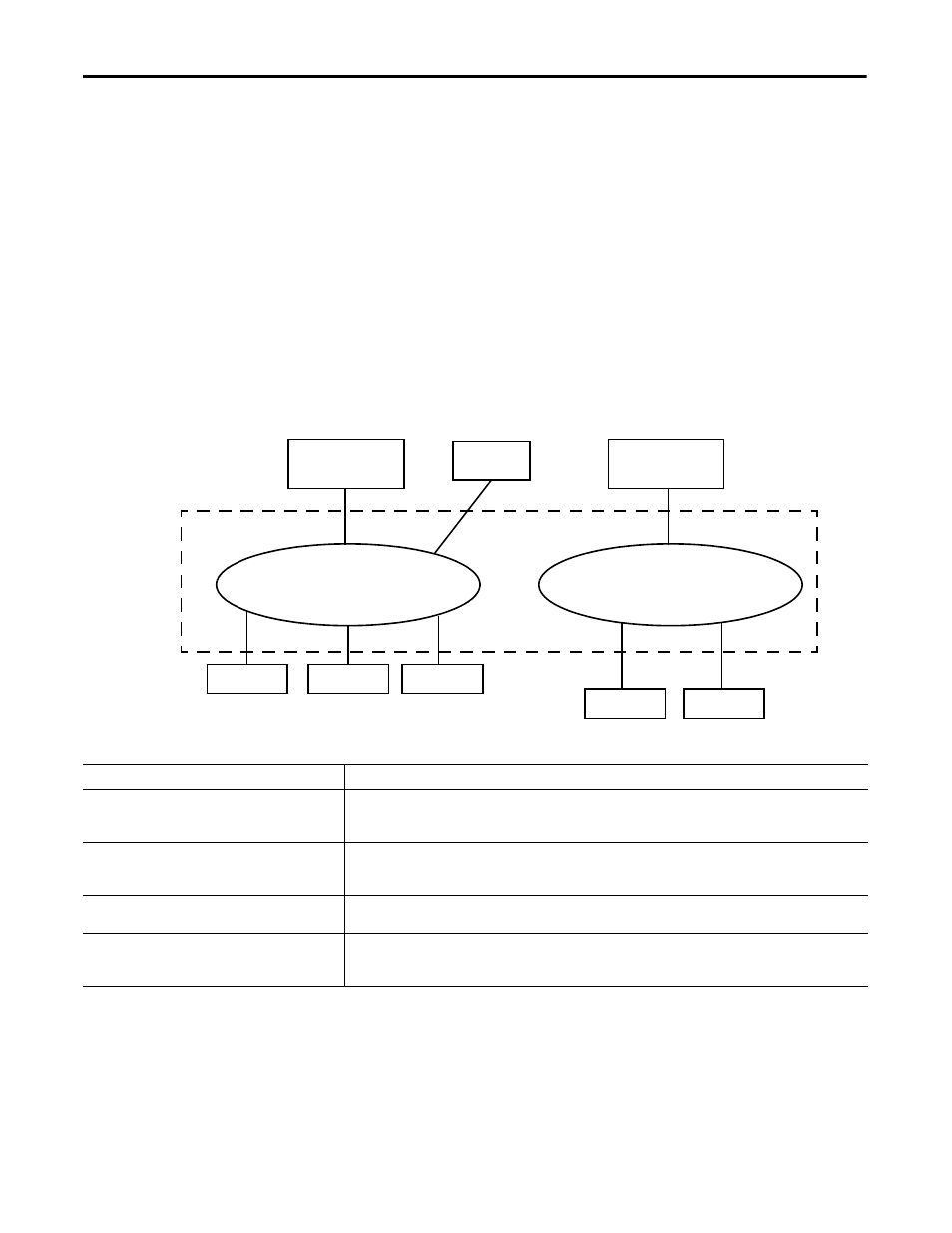
A virtual LAN (VLAN) is a switched network segmented on a functional
application or organizational basis rather than a physical or geographical basis.
Switches filter destination MAC addresses and forward VLAN frames to ports
that serve the VLAN only to which the traffic belongs. A VLAN consists of
several end systems. These systems are either hosts or network equipment, such as
switches and routers, that are members of a single logical broadcast domain. A
VLAN does not have physical proximity constraints for the broadcast domain.
With VLANs, you can configure a switch to share two isolated networks without
the traffic from one network burdening the other. IP multicast traffic from
VLAN 1 does not reach VLAN 2. A VLAN blocks broadcast traffic and adds a
measure of security between networks.
A VLAN also gives you the ability to control access and security to a group of
devices independent of their physical location.
Segmentation is the process of outlining which endpoints need to be in the same
LAN. Segmentation is a key consideration for a cell or area network.
Segmentation is important to help manage the real-time communication
properties of the network, and yet support the requirements as defined by the
network traffic flows. Security is also an important consideration in making
segmentation decisions.
Table 6 - VLAN Features
Feature
Description
Broadcast control
Just as switches isolate collision domains for attached hosts and forward appropriate traffic out a particular port, VLANs
refine this concept and provide complete isolation between VLANs. A VLAN is a bridging domain, and all broadcast and
multicast traffic is contained within it.
Security
High-security users can be grouped into a VLAN, possibly on the same physical segment, and no users outside of that
VLAN can communicate with them. VLANs can also assist in securing plant-floor systems by limiting access of production
floor personnel, such as a vendor or contractor, to certain functional areas of the production floor.
Performance
The logical grouping of devices prevents traffic on one VLAN from burdening other network resources. Performance
within the VLAN is also improved because the VLAN acts as a dedicated LAN.
Network management
You can logically move a device from one VLAN to another by configuring a port into a VLAN. The device does not have to
be physically disconnected from one network and reconnected to another, which can result in expensive,
time-consuming recabling.
Switch
Controller 1
PC
I/O
Controller 2
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
VLAN 1
VLAN 2
