Rockwell Automation Ethernet Design Considerations Reference Manual User Manual
Page 23
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-RM002C-EN-P - May 2013
23
Ethernet Infrastructure Components
Chapter 2
The EtherNet/IP embedded switch technology offers alternative network
topologies by embedding switches into the end devices themselves.
Table 5 - Topologies with Embedded Switch Technology
Topology
Description
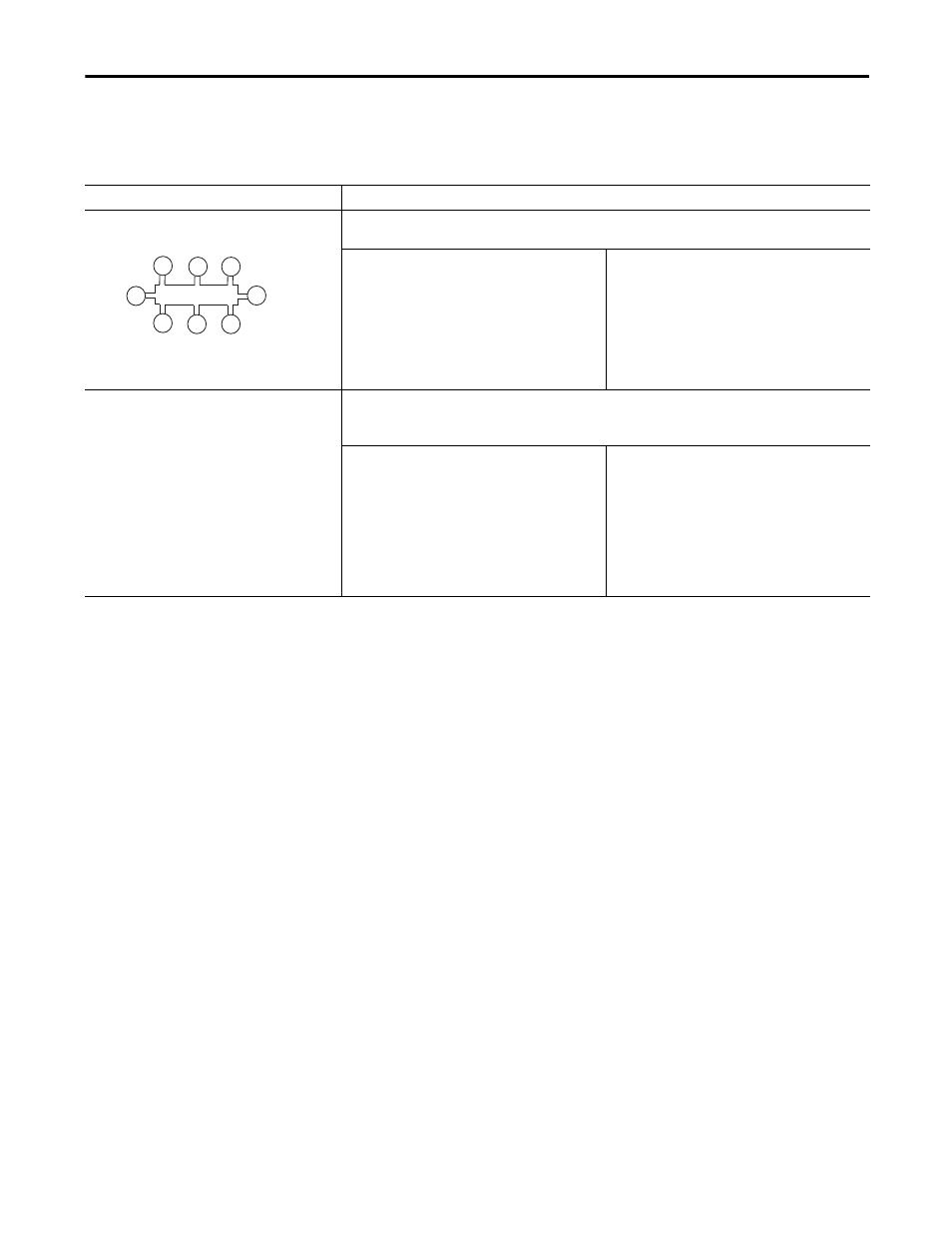
Device-level ring (DLR)—embedded switch
A DLR network is a single-fault tolerant ring network intended for the interconnection of automation devices. This
topology is also implemented at the device level. No additional switches are required.
Advantages
• Ability to survive a single point of failure or a device
being powered down on the ring.
• Simplified cabling
• Ability to cover long distances with 100 m between
each copper segment
• Very fast network convergence
Disadvantages
• Supervisor-node configuration required
• Additional configuration complexity
• Variable number of hops can make performance
difficult to predict
Linear—embedded switch
A linear network is a collection of devices that are daisy-chained together. The EtherNet/IP embedded switch technology
enables this topology to be implemented at the device level. No additional switches are required.
A linear topology works best for a limited number of nodes.
Advantages
• Easy to design, configure, and implement
• Least amount of cabling
• Minimal amount of cable needed
• Ability to cover long distances with 100 m between
each link
Disadvantages
• Loss of network service in case of connection failure (no
resiliency)
• Creates the potential for bottlenecks
• Variable number of hops can make performance
difficult to predict
• Powering down a device or the failure of a device in the
center of the network affects connectivity between any
of the devices on either side
• Each link in the chain represents network delay
D
D
D
D
D
D
D
D
