Gateway address – Rockwell Automation Ethernet Design Considerations Reference Manual User Manual
Page 17
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-RM002C-EN-P - May 2013
17
EtherNet/IP Overview
Chapter 1
Gateway Address
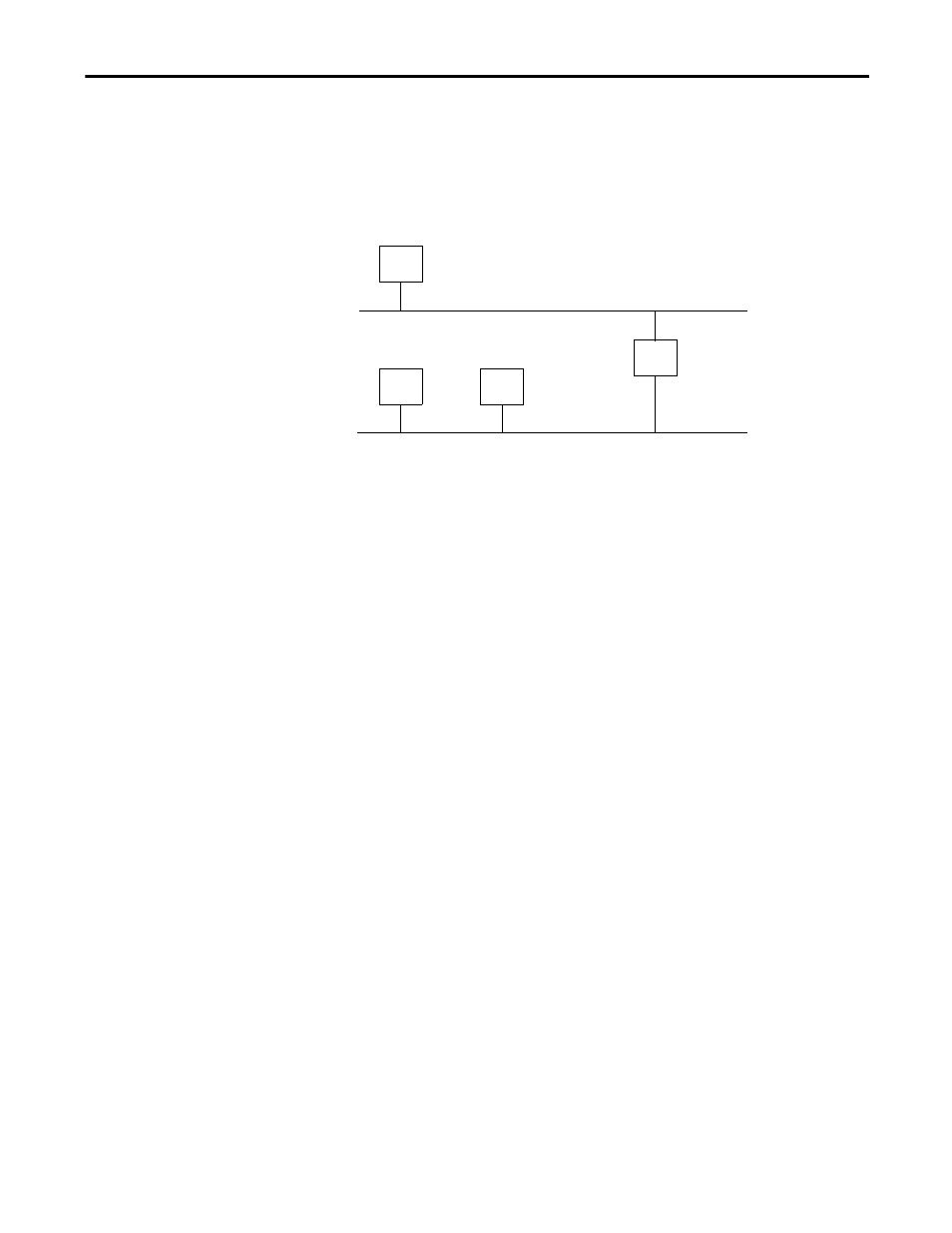
A gateway connects individual physical networks into a system of networks.
When a node needs to communicate with a node on another network, a gateway
transfers the data between the two networks. The following figure shows
gateway G connecting Network 1 with Network 2.
When host B with IP address 128.2.0.1 communicates with host C, it knows
from C’s IP address that C is on the same network. In an Ethernet environment,
B can then resolve C’s IP address to a MAC address and communicate with C
directly.
When host B communicates with host A, it knows from A’s IP address that A is
on another network because the network IDs differ. To send data to A, B must
have the IP address of the gateway connecting the two networks. In this example,
the gateway’s IP address on Network 2 is 128.2.0.3.
The gateway has two IP addresses (128.1.0.2 and 128.2.0.3). Network 1 hosts
must use the first IP address, and Network 2 hosts must use the second IP
address. To be usable, a host’s gateway IP address must match its own net ID.
Devices with IP address switches use the default gateway address of either
192.168.1.1 or 0.0.0.0. Check your product information to determine which
gateway address applies for your device.
Network 1
Network 2
A
B
C
G
128.1.0.2
128.2.0.3
128.2.0.2
128.2.0.1
128.1.0.1
