7 insulation of flue gas ducts, 2 cladding of flue gas ducts – Roxul Industrial Insulation Process User Manual
Page 81
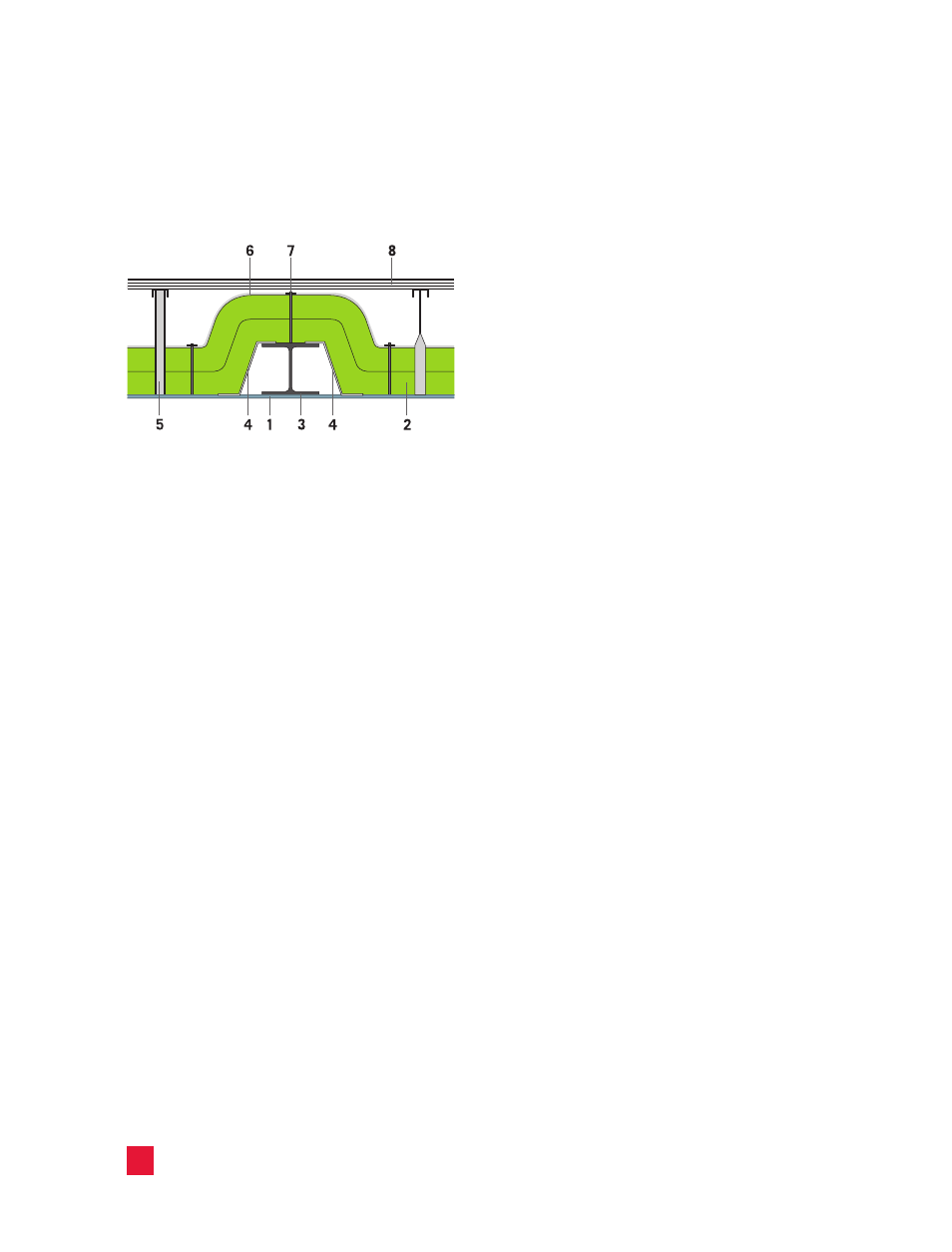
1.7 Insulation of flue gas ducts
1.7.1 Installation of the insulation systems for flue gas ducts
In the case of profiles measuring above 10"
(240 mm) in height, a covering sheet should also
be installed. The heat transfer from the duct wall
to the external flange is therefore not impeded
and the cavities do not need to be insulated.
The profile insulation described leads to increased
heat losses through convection in the case of
vertical steel girders. As a result, barriers – for
example in the form of sheets welded into the
reinforcement elements – must be fitted at
intervals of approximately 10 to 16 feet (3 to 5 m)
to reduce convection.
1.7.2 Cladding of flue gas ducts
Due to their size and the associated high demands
placed upon the flexural rigidity of cladding, flue
gas ducts are encased with profiled sheets such
as trapezoidal sheets. Flat sheets, which are
generally cambered, can also be used. The
claddings are secured to the flue gas duct using
substructures.
With ducts located outdoors with flue gas
temperatures of < 250 °F (120 °C), an air space of
at least 9/16" (15 mm) should be left between the
cladding and insulation. On clear nights,
especially, there is a risk that thermal radiation in
space (the small surface of the “flue gas duct”
radiates on an endlessly large surface “space”),
will cause the surface temperature of the cladding
to fall below the dew point temperature of the
ambient air. The atmospheric humidity from the
ambient air can then condense on the inside of the
cladding. Therefore, the insulation and cladding
must not be allowed to touch. To drain the water,
drill drainage or ventilation holes at the lowest
point on the underside.
With round flue gas ducts constructed using
ProRox
®
insulation without a spacer then
corrugated straps or bubble wrap are inserted
between the insulation and sheet cladding as a
spacer.
If the duct is located outside, the upper surface
of the cladding should have a gap of ≥ 3 %.
The following pages show two examples for the
cladding of a flue gas duct with a pent or gabled
roof.
1. Duct wall - 2. ProRox
®
insulation - 3. Reinforcing
element - 4. Covering sheet - 5. Support construction
and spacer - 6. Aluminum foil (optional) -
7. Welding pins/clips - 8. Metal cladding: corrugated
sheet
Insulation of reinforcing element with cavity and
covering sheet
78
