Support constructions and spacers, Cladding – Roxul Industrial Insulation Process User Manual
Page 54
Insulation of v
es
sels
Support constructions and spacers
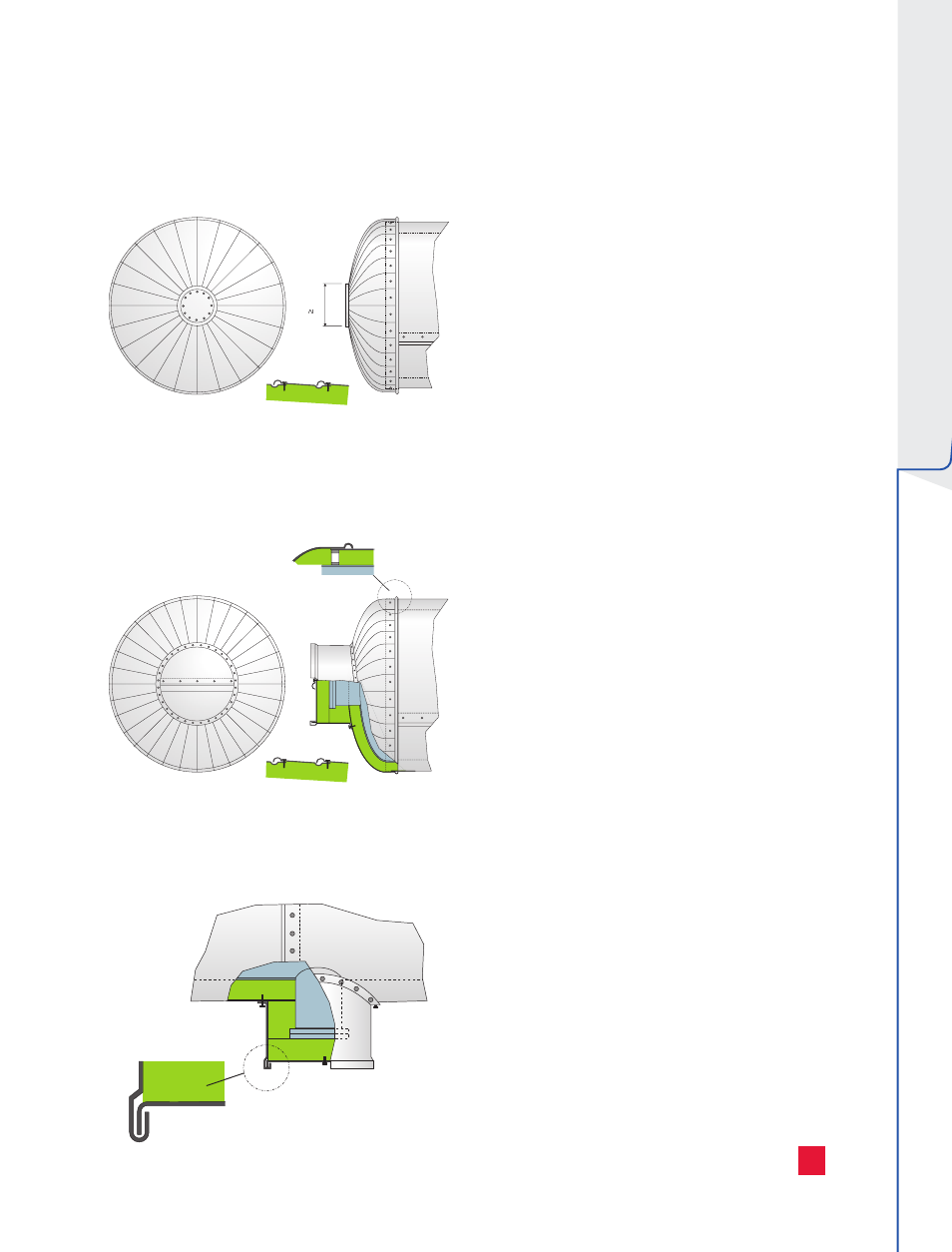
The application of support constructions and
spacers on vessels is essential. The objective of
support constructions is to bear the weight of the
insulation system and to bear the weight above
mounting supports on the object to be insulated.
The spacers keep the cladding of the insulation at
a predetermined distance. On vertical pipes, the
substructures often assume the function of the
support construction and spacer. The design
specifications are illustrated in Chapter 1.4.
The corresponding requirements for support
constructions and spacers can be found in MICA
National Insulation Standards and the AGI
guidelines Q153 and 154.
Before commencing the insulation works, fit
mounting supports to the vessels to which the
support constructions are fitted. The shape,
construction and measurements of mounting
supports for support constructions must enable
the insulation to be fitted during assembly. If
desired use the design loads specified in DIN
guidelines 1055-4 and 1055-5 to dimension the
mounting supports and the support constructions
and spacers.
Cladding
The cladding of vessels protects the insulation
against mechanical influences and the weather.
There is a wide range of different flat and profiled
sheets available. See Chapter 3.2 for an overview.
Flat sheets are primarily used to clad smaller
vessels. With large-scale insulation systems, flat
sheets can only bear small, static loads exerted by
the wind. It is therefore essential to reduce the
distance between the support structures.
The result will be a higher number of support
structures and thermal bridges. On large
surfaces, flat sheets are more likely to buckle or
dent, leading to optical damages, than profiled
sheets. To improve the stability and optical
characteristic, the sheets can be canted
diagonally (cambered).
8"
(200 mm)
Insulation of a conical head
Insulation of a conical head with a manhole
Insulation of vessel outlet
51
