6 insulation of boilers, Barriers – Roxul Industrial Insulation Process User Manual
Page 75
1.6 Insulation of boilers
1.6.2 Supercritical steam generators
Convection in the insulation
With vertical insulation constructions in particular,
where cavities can form on the heated side
between the object and the insulation, there is an
increased risk of heat loss – caused by convection
in the insulation. This risk equally applies to
finned walls, as an insulation that follows the
contours of the object, in which the cavities in the
area of the bars are sealed, cannot always be
secured. Take the following measures to prevent
convection:
Construct vertical barriers at intervals of 16 to 26
feet (5 to 8 m).
Only use insulations with a longitudinal flow
resistance of ≥ 50 kPa s/m².
Fitting an aluminum foil between the individual
insulation layers and/or on the exterior is
recommended.
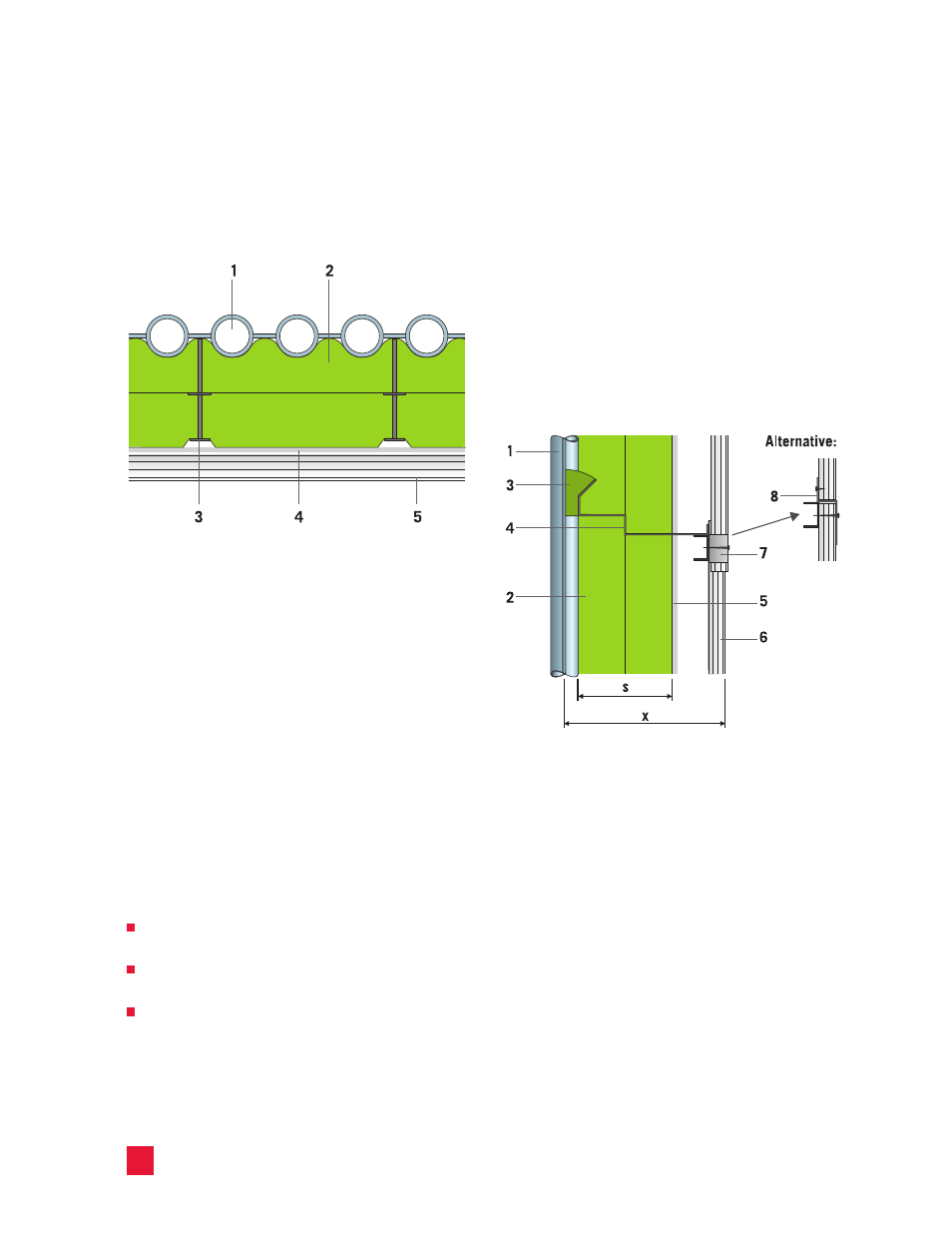
Barriers
The following diagrams show two designs for
vertical barriers. Depending on the temperature
or structural requirements, the barrier can be
manufactured from sheet metal [≥ 0.02" (0.5 mm)]
or aluminum foil [≥ 0.003" (80 μm)]. The barrier
must be fastened to the object on the heated side
and must reach to the cladding on the cold side.
Fill interstices with loose stone wool (mineral
wool). Where the insulation is constructed in
multiple layers, cascade the barriers.
Diagram of a boiler insulation system with no gap
between the insulation and sheet cladding
1. Tube wall - 2. ProRox
®
insulation – 3. spring plates -
4. Aluminum foil if required - 5. Cladding (e.g. profiled
sheet)
1. Boiler wall - 2. ProRox
®
insulation - 3. Fill with loose
rock wool - 4. Convection barrier sheet - 5. Aluminum
foil if required - 6. Metal cladding - 7. MF profile filling -
8. Z-profile separating sheet
72
