Rc connections overview, Using the rc channels – Pololu Simple User Manual
Page 38
RC Connections Overview
The RC connection block consists of two channels oriented as columns and a battery elimination circuit (BEC)
column for supplying power to the RC receiver. Each channel has a ground pin (outlined in black in the above
diagrams), a power pin (outlined in red in the above diagrams), and a signal pin (outlined in yellow in the above
diagrams). The RC signal pins can read standard hobby servo RC pulses with peaks anywhere from 2 to 5 V. The
included
can be used to supply the power pin row with either 3.3 V
or 5 V, which in turn can be used to power an RC receiver.
Note: If you want to connect servos directly to your RC receiver, you must power it separately as
the Simple Motor Controller’s regulators cannot supply enough current to power a servo. If your RC
receiver is powered separately, you must leave the BEC jumper off to avoid shorting the motor controller’s
regulated voltage to your RC receiver’s power source. Your receiver and Simple Motor controller must
always have a common ground, even if you power the RC receiver separately.
The channel pins have a 0.1" spacing, which means that a
can be used to connect an RC receiver directly to the board.
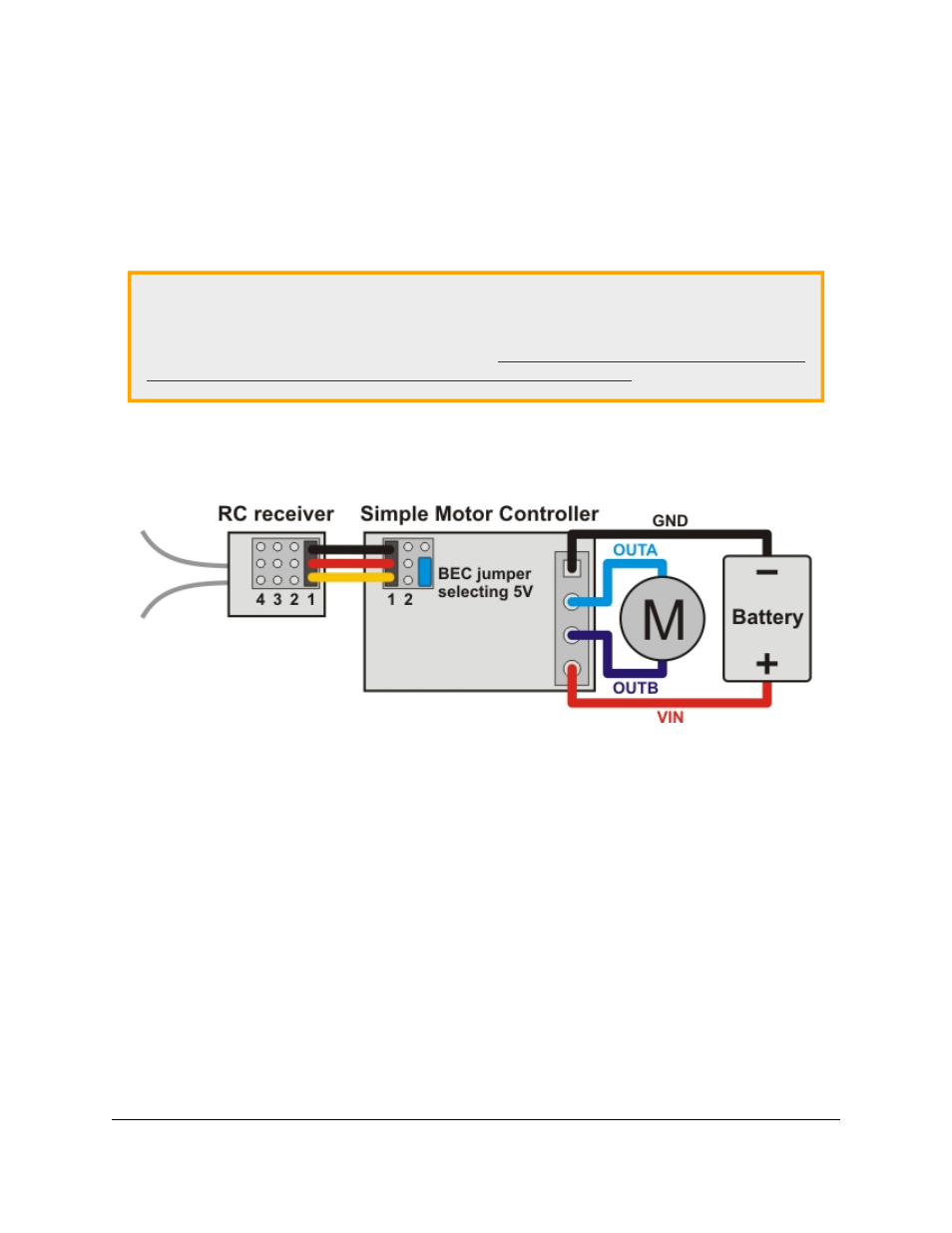
Simple Wiring Example: Connecting to an RC Receiver
Wiring diagram for connecting an RC receiver to a Simple Motor Controller.
Using the RC Channels
The Simple Motor Controller is constantly reading the two RC channels and making the measured pulse widths
available via the USB and serial interfaces, even when the controller is not in RC mode. For example, you can use the
serial interface to read the RC channel values while the motor controller is in analog mode. The RC channels are read
with 0.25 µs resolution, and RC pulse frequencies from 10 Hz to 333 Hz are permitted. A number of settings exist for
adjusting what constitutes a valid RC signal.
Driving a Motor
In RC mode, the channel values are mapped to motor speed based on the channel calibration values and the mixing
mode. We recommend your first step after connecting your RC receiver be to use the Quick Input Setup wizard in the
Simple Motor Control Center. The wizard instructs you to move your transmitter control sticks to their extremes and
maps stick full forward/right to the maximum forward motor speed, the neutral stick to speed zero, and the stick full
back/left to maximum reverse speed. Calibration can have a significant impact on performance.
If mixing mode is disabled, only channel 1 affects motor speed. If mixing mode is set to “right” or “left”, channel 1
is considered the “throttle” input and channel 2 is considered the “steering” input. Left mixing mode obtains motor
Pololu Simple Motor Controller User's Guide
© 2001–2014 Pololu Corporation
4. Connecting Your Motor Controller
Page 38 of 101
