4 device description – Eppendorf Multiporator User Manual
Page 16
58
4.7 Electroporation
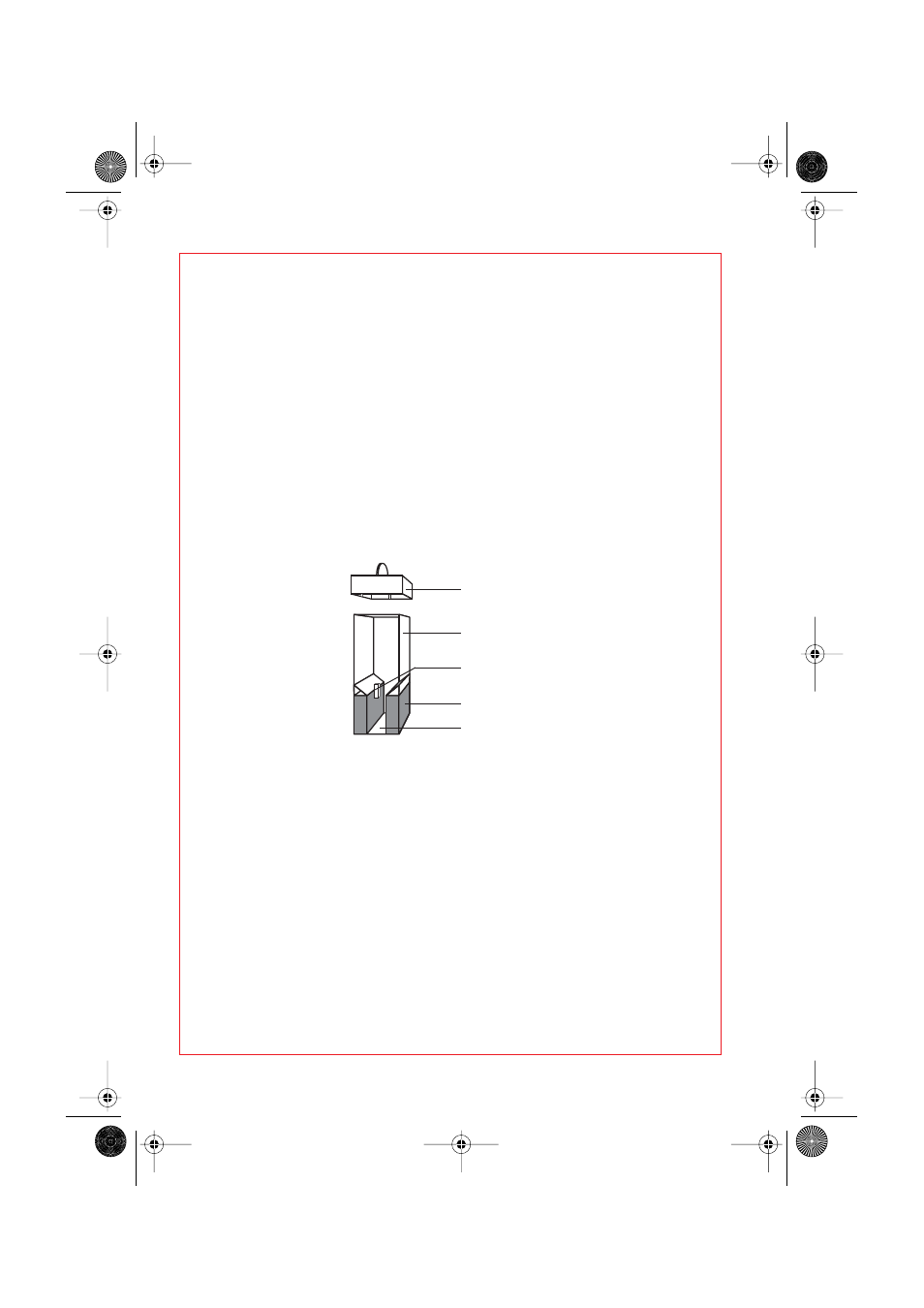
4.7.1 Cuvettes and cuvette insert
The electroporation of eukaryotic cells, bacteria or yeasts is carried out in
disposable cuvettes. The biological material is placed in the gap between
the electrodes of the cuvette, whereby the prescribed liquid volumes of
the relevant cuvette are to be maintained. Although a supernatant above
the electrode does not drastically affect the experiment, however it
reduces the general efficiency.
A matt window allows the cuvette to be inscribed.
The plastic nose on the cuvette ensures that the cuvette is inserted
correctly into the cuvette insert. The lid seals the cuvette. However, to
safeguard against excess pressure, the cuvette is not hermetically sealed
by the lid. A filled cuvette should therefore be transported in an upright
position only in order to ensure that biological material does not leak out.
Fig. 4: Schematic diagram of electroporation cuvette
The cuvette insert is removed from the Multiporator
using the protruding
grip. No bubbles are present when the cuvette is filled.
When the cuvette is inserted into the inner recess of the cuvette insert,
care must be taken to ensure that the cuvette nose is positioned in the
long slit and that the cuvette is in contact with the base of the cuvette
insert. The cuvette insert, complete with cuvette, is then pushed into the
device up to the stop.
The cuvette insert may be stored in a cool place.
When transporting the device, please note that the cuvette insert may slip
out of the device if no cuvette has been inserted (see chap. 4.3).
Lid
Plastic cuvette
Plastic nose
Electrodes
Gap
4 Device description
Multiporator_Text_en.fm Seite 58 Freitag, 9. Juni 2006 8:05 08
