NOVUS N2020 Controller User Manual
Page 2
N2020 Controller
NOVUS AUTOMATION
2/7
OUT3 -
Relay SPST-NA
Available at terminals 15 and 16 of controller
OUT4 -
Analog output:
Electrical current, 0-20 mA or 4-20 mA
Electrical voltage pulse, 10 Vdc / 20 mA
Available at 29 and 30 terminals of controller
CONTROL OUTPUT
It is the output channel which effectively actuates on the process.
Main exit.
ALARM OUTPUT
Output channels which actuates on the protection and signalization
of process condition.
RUN FUNCTION
RUN parameter (rvn) works as a main key of output channels of
controller. It enables channels defined as control output and channels
defined as alarm output. With YES in this parameter, the control and
alarm outputs are able to operate, turning on / off, according to the
controller’s determinations. With NO, all outputs remain off, regardless
of the process requirements. In this condition, the controller’s display
starts to show the STOP message, alternately with the measured
temperature value (PV).
This function can also be obtained by the F key when configured to
operate in such mode.
AUTOMATIC CONTROL MODE
The controller may act in two different modes of operation: Automatic
mode or Manual mode.
In automatic mode, the controller determines the control output
behavior in order to lead the process up to the defined value in SP. It
determines the duration the control output remains on and off,
balancing the energy quantity applied to the process. In a technical
language: it determines the MV value (Manipulated Variable). This is
the normal mode of the controller operation.
The parameter “(trl” defines the control mode to be adopted:
Avto for automatic control.
Man for manual control.
This exchange functionality between automatic and manual mode
can also be obtained by the key, when configured to operate in
such mode.
The period (PWM cycle period) is defined in Cycle time parameter
((t). In it, a time interval (seconds), is defined and considered as a
reference for the determination of MV.
For instance: For a 10 seconds interval ((t = 10), 20 % MV means
output on for 2 seconds and off for 8 seconds, balancing the energy
quantity applied to the process.
MANUAL CONTROL MODE
In the manual mode, is the user who determines the control output
behavior. It defines the MV value, this value will not be interfered by
the controller.
By exchanging the automatic mode to manual mode, the value
adopted for MV will be the last value defined automatically by the
controller. It is known as “bumpless transfer”.
ON-OFF CONTROL / PID CONTROL
In the automatic mode, it acts with ON-OFF adjustable hysteresis
control and also with the PID control with the automatic tuning
resource.
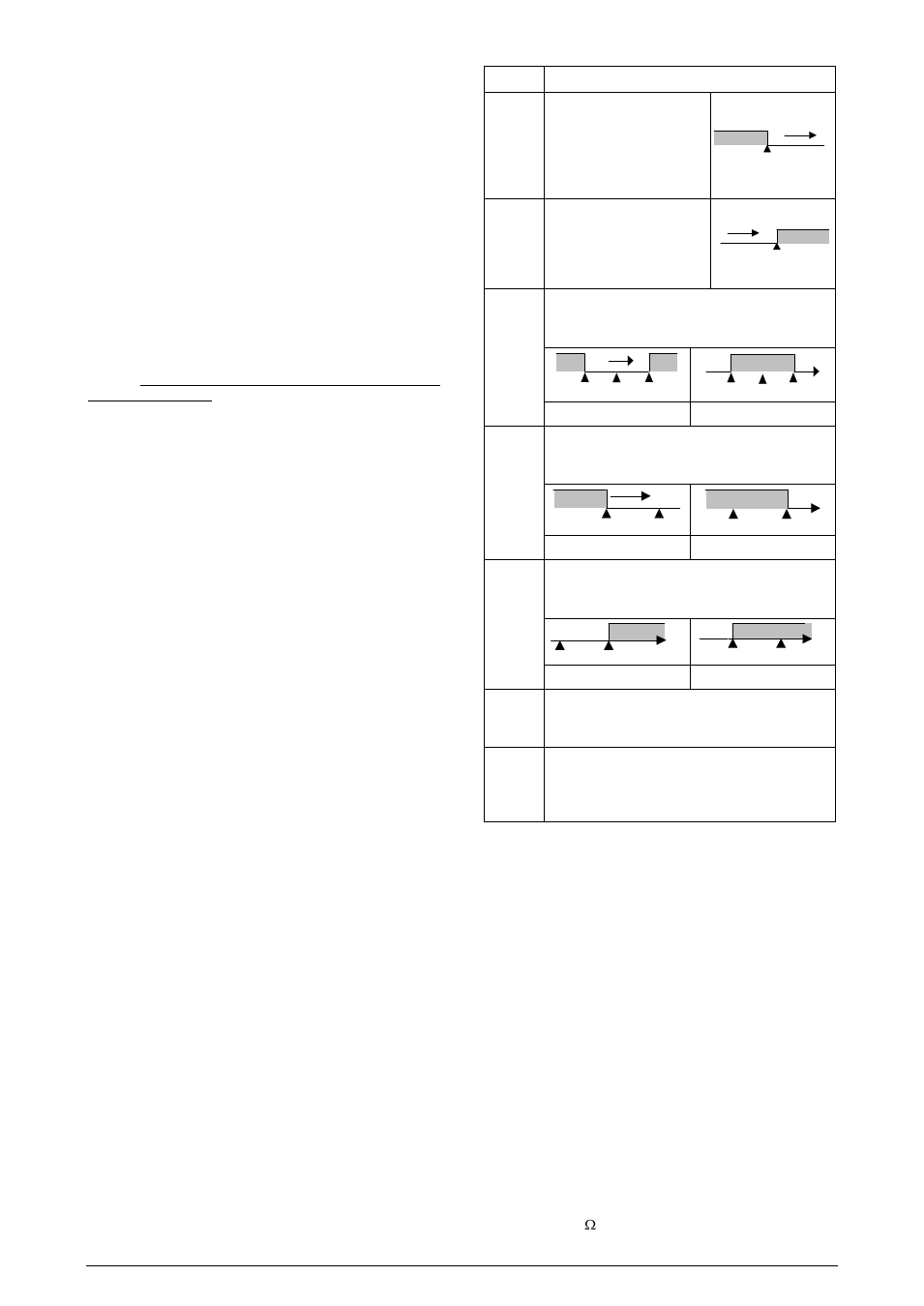
ALARM OUTPUT
The controller has two alarms which may be directed for any of the
output channels. These alarms can be configured to operate the
different functions described on Table 02.
off
Alarms turned off.
lo
Alarm of Absolute Minimum
Value. Triggers when the
value of measured PV is
below the value defined for
alarm Setpoint (SPA1 or
SPA2).
SPA1
PV
ki
Alarm of Valor Absolute
Maximum Value. Triggers
when the value of measured
PV is above the value
defined for alarm Setpoint.
SPA1
PV
dif
Alarm of Differential Value. In this function the
parameters SPA1 and SPA2 represent the deviation of
PV in relation to the SP of CONTROL.
SP
PV
SP + SPA1
SP
– SPA1
SP
PV
SV
– SPA1
alarme
SV + SPA1
alarme
SPA1 positive
SPA1 negative
difl
Alarm of Minimum Differential Value. It triggers when
the value of PV is below the defined point by (using
the Alarm 1 as example):
SP
PV
SP
– SPA1
SP
PV
SP
– SPA1
SPA1 positive
SPA1 negative
difk
Alarm of Valor Maximum Differential Value. Triggers
when the value of PV is above the defined point by
(using Alarm 1 as example):
SP
PV
SP + SPA1
SP
PV
SP + SPA1
SPA1 positive
SPA1 negative
ierr
Sensor Break Alarm. Activated when the input signal of
PV is interrupted, out of the range limits or Pt100 in short-
circuit.
Rs
Program Segment Alarms. It acts when a certain
segment of the ramps and soaks programs is
reached. The respective segment is defined on the
creation of ramps and soaks programs.
Table 02 – Alarme functions
Note: Alarm functions on Table 02 are also valid for Alarm 2 (SPA2).
INITIAL BLOCKING OF ALARM
The initial blocking option inhibits the alarm from being recognized
if an alarm condition is present when the controller is first energized
(or after a transition from run YES or NO). The alarm will be enabled
only after the occurrence of a non-alarm condition followed by a new
occurrence for the alarm.
The initial blocking is useful, for instance, when one of the alarms is
configured as a minimum value alarm, causing the activation of the
alarm soon upon the process start-up, an occurrence that may be
undesirable.
The first lock out is not valid for ierr function (Open Sensor).
PV AND SP ANALOGICAL RETRANSMISSION
The analogical output, OUT4, when available, may perform the
retransmission of PV or SP values, with 0-20 mA or 4-20 mA signs.
The analogical retransmission is scalable, i.e., it has minimum and
maximum limits, which define the output range, defined in rtLL and
rtkL
parameters.
To obtain a retransmission in voltage, the user should install one
shunt resistor (500 max.) on the analogical output terminals. The
value of this resistor depends on the voltage tension desired.
