2 suspensions with mud and sand, 3 particle-shape effects, Suspensions with mud and sand – Campbell Scientific OBS500 Smart Turbidity Meter with ClearSensor Technology User Manual
Page 44: Particle-shape effects, Methods
OBS500 Smart Turbidity Meter with ClearSensor™ Technology
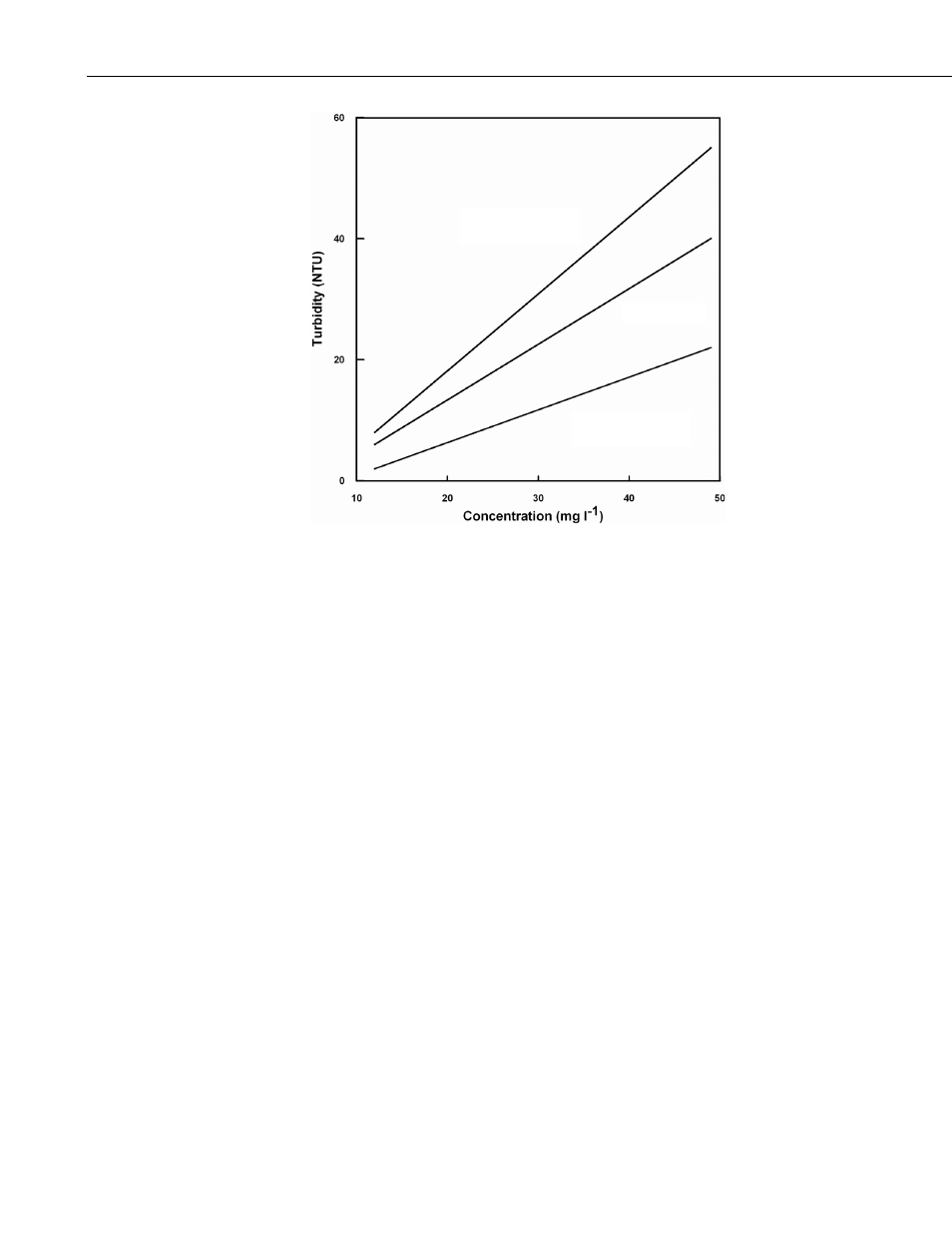
FIGURE 8-2. The apparent change in turbidity resulting from
disaggregation methods
8.2 Suspensions with Mud and Sand
As mentioned in Section 8.1, Particle Size, light scattering from particles is
inversely related to particle size on a mass concentration basis. This can lead
to serious difficulties in flow regimes where particle size varies with time. For
example, when sandy mud goes through a cycle of suspension and deposition
during a storm, the ratio of sand to mud in suspension will change. A turbidity
sensor calibrated for a fixed ratio of sand to mud will, therefore, indicate the
correct concentration only part of the time. There are no simple remedies for
this problem. One solution is to take a lot of water samples and analyze them
in the laboratory. This is not always practical during storms when the errors
are likely to be largest. Do not rely solely on turbidity sensors to monitor
suspended sediments when particle size or composition is expected to change
with time at a monitoring site.
8.3 Particle-Shape Effects
In addition to size and flocculation/aggregation, particle shape has a significant
effect on the scattering intensity from a sample and calibration slope of a
turbidity sensor. As the graph in FIGURE 8-3 shows, plate-shaped particle
(clay-mineral particles, for example) backscatter light about ten times more
efficiently than spherical particles, and angular shapes have intermediate
scattering efficiency. Turbidity sensors are very sensitive to shape effects and
this makes it very important to calibrate with material from the monitoring site.
It is also essential that particle shape remains constant during the monitoring
period.
Sonic Probe
(Most Aggressive)
Hand Shaking
(Least Aggressive)
Sonic Bath
34
