Figure 3 update copy operation, Cascade function, Pairsplit operation – HP XP Business Copy Software User Manual
Page 18: 3 update copy operation, Figure 3, Illu
18
Business Copy XP (BC) for the XP128/XP1024
•
If shared memory is lost (for example, offline micro exchange or volatile PS on), the differential bitmap
is also lost. In this case, the disk array treats the entire BC P-VOL (S-VOL for COPY(RS) pairs) as
difference data and recopies all data to the S-VOL (P-VOL for COPY(RS) pairs) to ensure proper pair
resynchronization. For pairs with COPY(SP) or PSUS(SP) status, the disk array changes the status to
PSUE due to the loss of the differential bitmap, also ensuring proper resynchronization of these pairs. If
shared memory is lost, allow extra time for BC operations.
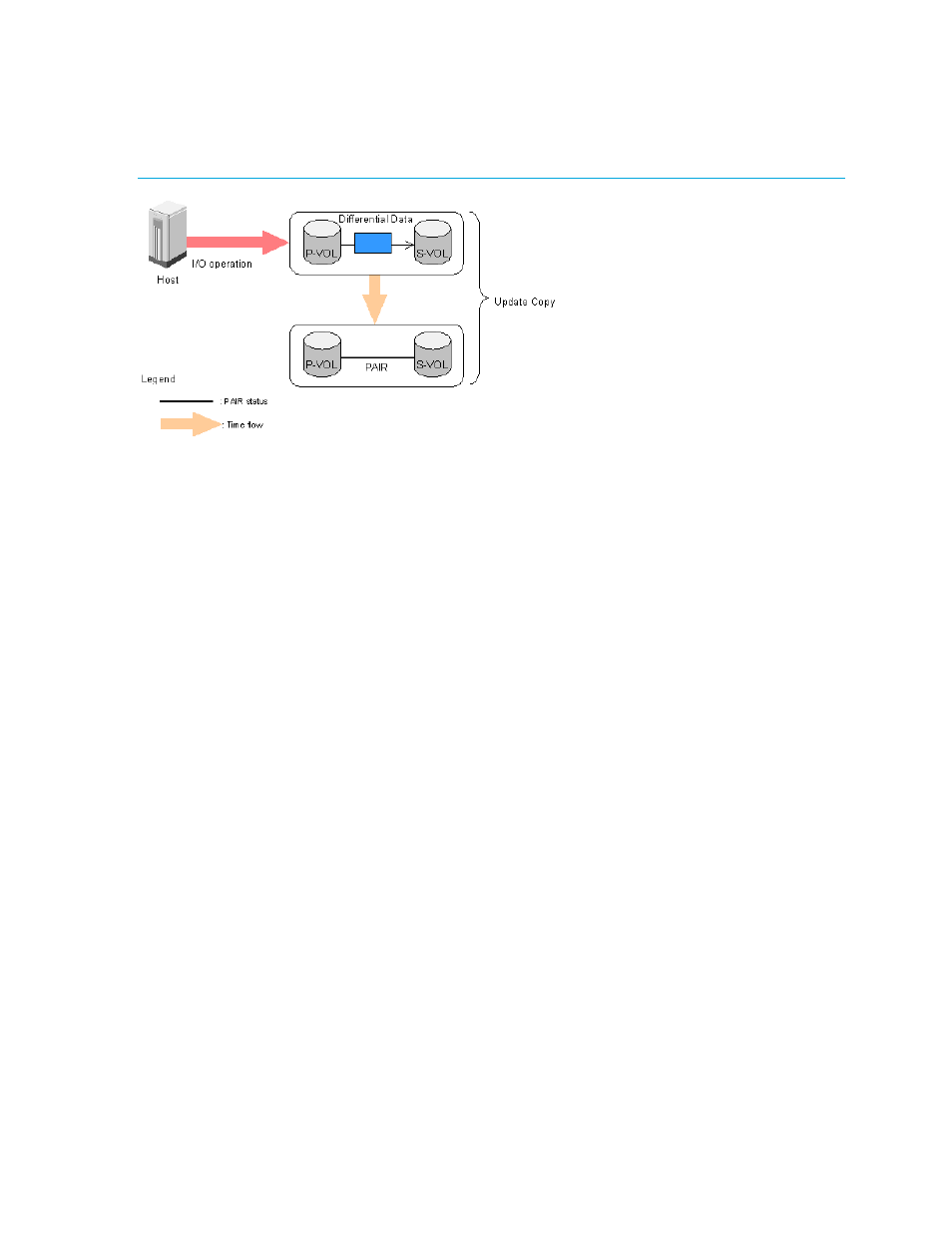
Figure 3
Update copy operation
Cascade function
This function creates a second layer of BC volume pairs (L2) underneath the first layer of BC pairs (L1).
Cascade pairs are created by clicking Cascade instead of Set in the Paircreate window (see ”
” on page 45). This cascade layering scheme creates up to nine copies of one BC P-VOL.
See ”
” on page 25 for further information on cascade pairs and the cascade function.
Pairsplit operation
The BC split capability provides point-in-time backup of data, and facilitates real data testing by making
the BC copies (S-VOLs) available for host access. The BC pairsplit operation performs all pending S-VOL
updates (those issued prior to the split command and recorded in the P-VOL track map) to make the S-VOL
identical to the state of the P-VOL when the split command was issued, and then provides full read/write
access to the split S-VOL. You can split existing pairs as needed. You can also use the pairsplit operation to
create and split pairs in one step.
Use the Pairsplit window (see ”
Splitting BC pairs (Pairsplit)
” on page 48) to split existing BC pairs or to
add and split new BC pairs in one step. When the split operation is complete, the pair status changes to
PSUS, and you have full read/write access to the split S-VOL (even though it is still reserved). While the
pair is split, the disk array establishes a track map for the split P-VOL and S-VOL, and records all updates
to both volumes. The P-VOL remains fully accessible during the pairsplit operation. Pairsplit operations
cannot be performed on suspended (PSUE) pairs.
•
When splitting pairs, you can select the pace for the pending update copy operation: Slower, Medium,
and Faster. The slower pace minimizes the impact of BC operations on disk array I/O performance,
while the faster pace splits the pairs as quickly as possible.
•
When splitting pairs, you can also select the split type: Quick Split or Steady Split.
• When quick split operations start, the pair status changes to PSUS(SP), and the S-VOL is available
immediately for read and write I/Os (even though it is still reserved). The disk array performs all
pending update copy operations to the S-VOL in the background. When the quick split is complete,
the pair status changes to PSUS.
• When steady split operations start, the pair status changes to COPY(SP), and the disk array
performs all pending update copy operations to the S-VOL. When the Steady Split operation is
complete, the pair status changes to PSUS, and you have full read/write access to the split S-VOL
(even though it is still reserved).
