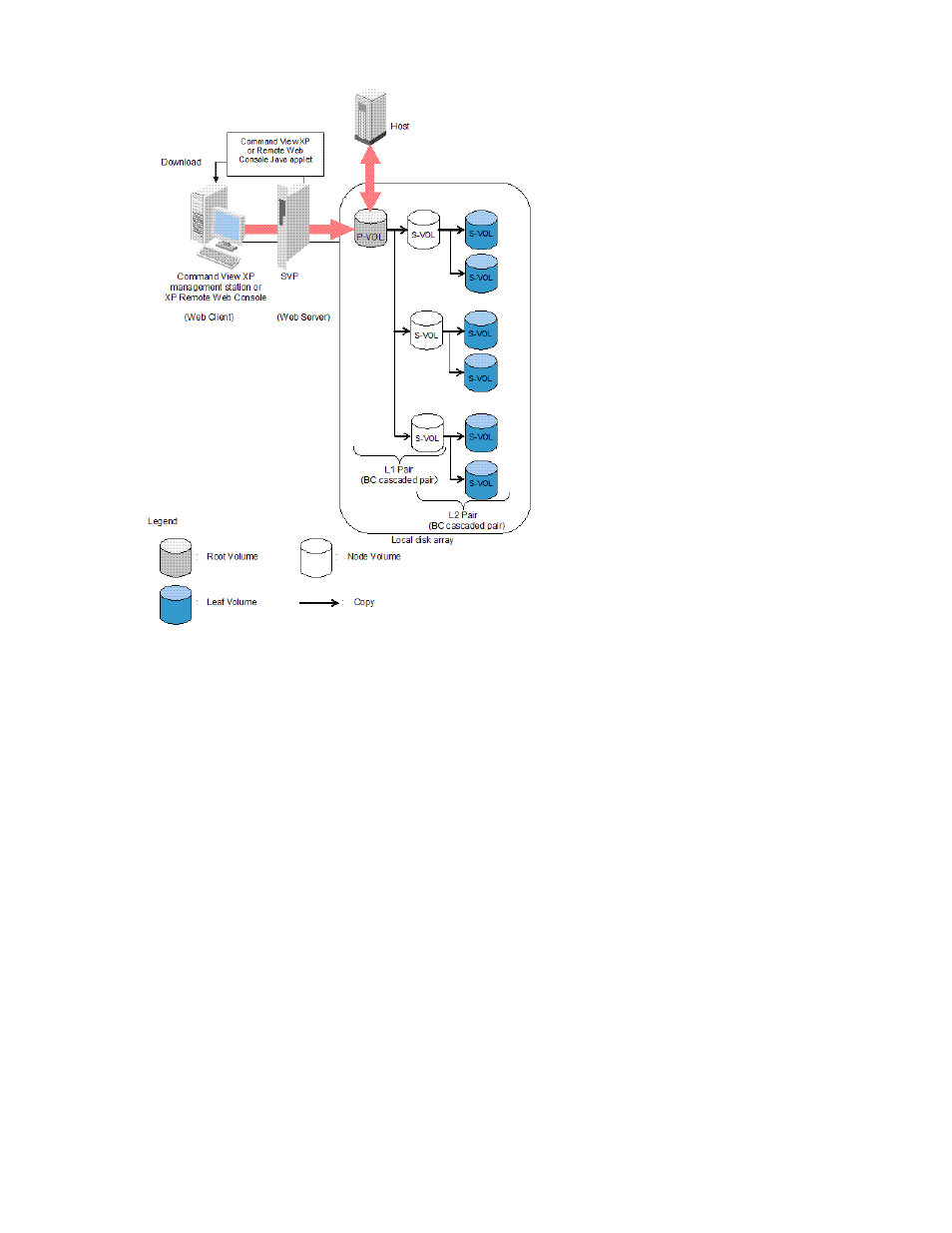
Figure 1 bc overview, Bc volume pairs (p-vols and s-vols), 1 bc overview – HP XP Business Copy Software User Manual
Page 12: Figure 1
12
Business Copy XP (BC) for the XP128/XP1024
•
BC software on the Command View XP management station or XP Remote Web Console
Figure 1
BC overview
Use BC from the Command View XP management station or XP Remote Web Console to copy volumes in
the local disk array. The volume that has original data is called a P-VOL (primary volume), and a volume to
which data is copied is called an S-VOL (secondary volume). Pairs of P-VOLs and S-VOLs made by BC are
called BC pairs. You can specify an S-VOL as a P-VOL to make another two BC pairs. As a result, you can
use BC to make a total of nine S-VOLs. Use the cascade style to make BC pairs by specifying S-VOLs as
P-VOLs. In cascade style, pairs in the first cascade layer are called L1 pairs and pairs in the second
cascade layer are called L2 pairs.
BC volume pairs (P-VOLs and S-VOLs)
Disk arrays contain and manage original and copied BC data. The XP128/XP1024 disk arrays support a
maximum of 8,190 BC volumes: 4,095 pairs and the RAID Manager command device. When BC pairs
include size-expanded LUs, the maximum number of pairs decreases. When pairs include more than one
S-VOL, the maximum number of P-VOLs decreases.
BC performs internal copy operations for logical volume pairs that you establish. Each BC pair consists of
one primary volume (P-VOL) and up to three secondary volumes (S-VOLs) located in the same disk array.
BC P-VOLs are primary volumes containing original data. BC S-VOLs are secondary or mirrored volumes
containing backup data. Each S-VOL must be paired with only one P-VOL. During BC operations, P-VOLs
remain available to all hosts for read and write I/O operations (except during reverse resync and quick
restore). S-VOLs become available for host access only after the pair is split.
When a BC volume pair is created, data on the P-VOL is copied to the S-VOL to synchronize the volumes.
During this initial copy operation and after the pair is synchronized, all write operations to the S-VOL are
prohibited. To access an S-VOL, you can “split” the pair to make the S-VOL accessible (the P-VOL is
accessible except during reverse resync). While a BC pair is split, the disk array keeps track of all changes
to the P-VOL and S-VOL. When you “resync” the pair, the differential data in the P-VOL (due to P-VOL and
S-VOL updates) is copied to the S-VOL, so the S-VOL is again identical to the P-VOL. For reverse resync, the
