Pair volumes, Journal volumes, Journals – HP XP7 Storage User Manual
Page 11: Data path, Pair volumes journal volumes journals data path
Pair volumes
Original data is stored in the P-VOL and the remote copy is stored in the S-VOL. The pair can be
paired, split, resynchronized, and released. When synchronized, the volumes are paired; when
split, new or changed data sent to the P-VOL is not copied to the S-VOL. When re-synchronized,
changed data is copied to the S-VOL. If a disaster occurs, production operations can be transferred
to the S-VOL. When the local site is functional again, operations can be transferred and data can
be copied back to the P-VOL.
The P-VOL remains available to the host for read and write I/O operations. The secondary system
rejects write I/Os for the S-VOL, unless the write-enable option is specified. Then, write I/O is
allowed to the S-VOL while the pair is split. In this instance, S-VOL and P-VOL track maps keep
track of differential data and use it to re-synchronize the pair.
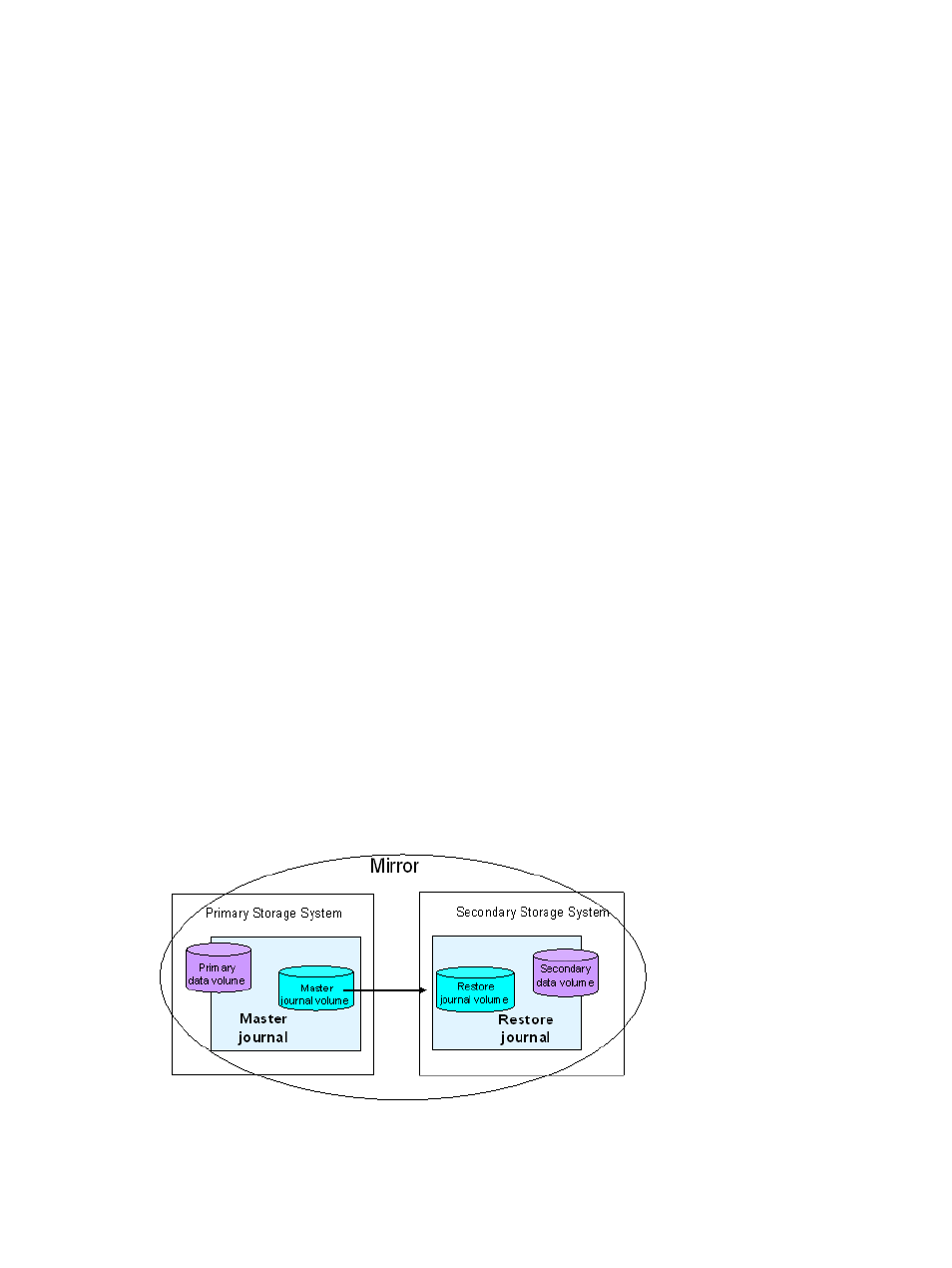
Journal volumes
For Continuous Access Journal operations, journal volumes are required on the primary and
secondary systems.
•
Updates to the P-VOL are copied to the master journal volume in the primary system. See the
illustration in
.
•
Master journal data is copied to the restore journal volume on the secondary system.
•
Journal volumes can have different volume sizes and different RAID configurations.
For information on planning journal volumes, see
“Sizing journal volumes ” (page 21)
.
Journals
Journals help you manage data consistency between multiple P-VOLs and S-VOLs. A journal is a
group of one or more data volumes and the related journal volume. Like consistency groups, you
can use journals to create multiple pairs, and to split, resynchronize, and release multiple pairs.
Journals are required on the primary and secondary systems.
Each data volume and its associated journal volume reside in the same journal.
•
The master journal contains master journal volumes and is associated with the P-VOL.
•
The restore journal contains restore journal volumes and is associated with the S-VOL
Each pair relationship between journals is called a "mirror". A mirror ID identifies a pair relationship
between journals. When the pair is created, it is assigned a mirror ID.
Figure 3 Journals
Data path
The physical transmission link between the primary and secondary systems is called the data path.
Continuous Access Journal commands and data are transmitted through the fibre-channel data
Hardware and software components
11
