Yokogawa ISC450 4-Wire Analyzer for Inductive Conductivity User Manual
Page 57
49
IM 12D06D05-01E
A
APPENDICES
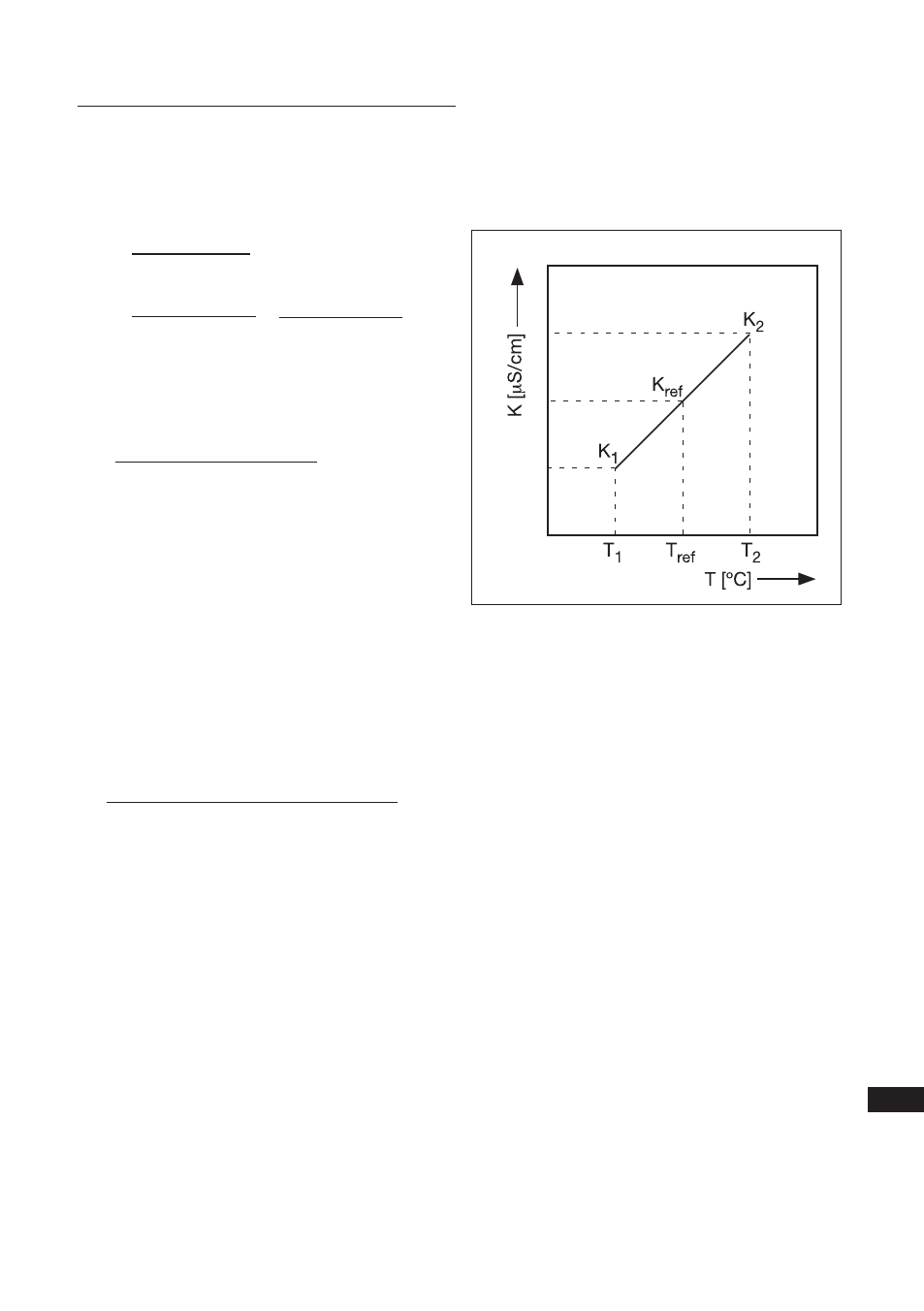
B. Calculation of temperature coefficient factor
(with two known conductivity values at different temperatures)
Measure the conductivity of the liquid at two temperatures, one below the reference and above
the reference temperature with the temperature coefficient set to 0,00%/°C and use the following
equation to calculate a temperature coefficient (α).
K
T
K
ref
=
1+α ( T - T
ref
)
K
2
- K
1
α = K
1
( T
2
- T
ref
) - K
2
( T
1
- T
ref
)
K
1
K
2
K
ref
=
=
1+α ( T
1
- T
ref
)
1+α ( T
2
- T
ref
)
K
1
(1 + α ( T
2
- T
ref
)) = K
2
(1 + α ( T
1
- T
ref
))
K
1
+ α ( T
2
- T
ref
) - K
2
+ α ( T
1
- T
ref
) = K
2
- K
1
Where T
1
, T
2
: liquid temperature (°C)
K
1
: conductivity at T
1
(°C)
K
2
: conductivity at T
2
(°C)
Figure 11-1. Conductivity
Calculation example
Calculate the temperature co-efficient of a liquid from the following data.
Conductivity 124.5 µS/cm at a liquid temperature of 18.0 °C and a
conductivity 147.6 µS/cm at a liquid temperature of 31.0 °C.
Substituting the data in the above formula gives the following result.
147.6 - 124.5
x 100= 1.298 %/C
α
=
124.5(31.0 - 25) - 147.6(18.0 - 25)
Set the temperature coefficient in the ISC450G converter.
