2 calibration “cal – Yokogawa Low Concentration (ppm) Zirconia Oxygen Analyzer OX400 User Manual
Page 47
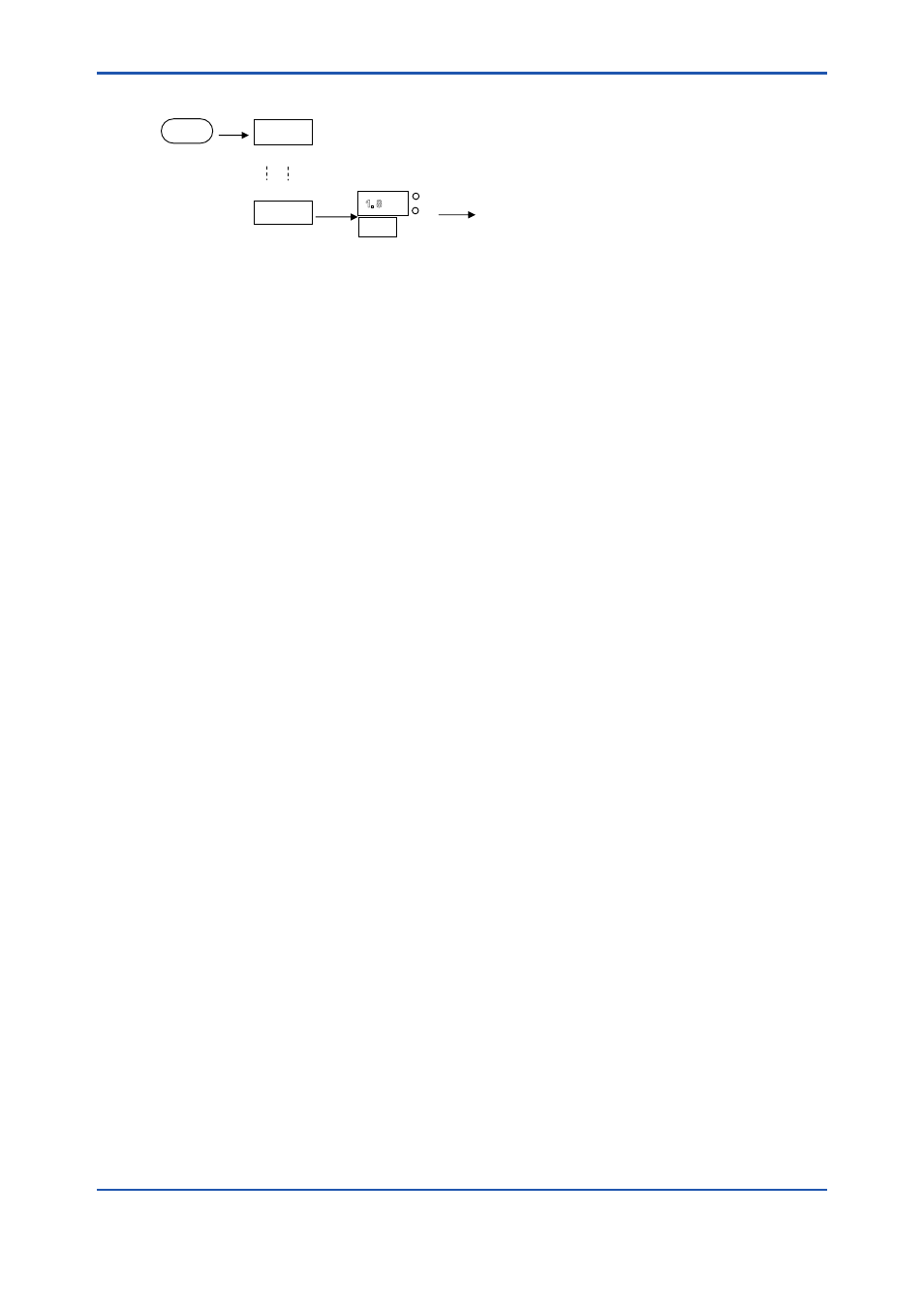
<6. Operation and Parameters>
6-10
IM 11M10B01-01E
rEV
▼↓↑▲
MODE
CAL
▼↓↑▲
▼↓↑▲
[ENT] 1. 8
rEV
PPM
[ENT]
▼↓↑▲
%
To “rEV”
Hold down
for 2 seconds.
Return to “rEV.”
Figure 6.13
Display Software Revision “rEV”
6.2 Calibration “CAL”
Be sure to perform calibration in the measurement mode after the warm-up operation ends.
Calibration cannot be performed during the warm-up operation. If an error occurs during calibration,
that calibration will be invalid, and keys other than the [MODE] key become invalid. Hold down the
[MODE] key for 2 seconds to return to the beginning of the calibration “CAL” and press the [MODE]
key again to return to the measurement state.
With respect to the calibration methods of the OX400, there are four types of method.
1) 3-point (All) calibration “ALL”
By performing calibration at the three points of 10 ppm, 1000 ppm, and Air, the linearity for the
entire zone between 0-10 ppm and 100% O
2
is guaranteed. Gas used for calibration is restricted
to the ranges of O
2
concentration as follows.
(1) 8 ppm ≤10 ppm gas ≤ 20 ppm
(2) 800 ppm ≤1000 ppm gas ≤ 2000 ppm
(3) O
2
concentration in Air: 20.6% (Normal air is within this range)
NOTE: Be sure to use gas that meets conditions (1), (2), and (3) for calibration.
2) 2-point calibration “2Pnt”
Select zero and span calibration points in the measurement range you will use to perform
calibration. However, gas used for calibration is restricted to the ranges of O
2
concentration as
follows.
(1) Zero gas is 8%FS or more.
(2) Span gas is less than 120%FS.
(3) Between zero and span of the smallest range must be more than 20%FS of the MANUAL
range.
Example 1: Two points of 1 ppm and 3 ppm in the 10 ppm range
Example 2: Two points of 20 ppm and 40 ppm in the 100 ppm range
< When the range is more than 1000 ppm.>
(1) Zero gas is 800 ppm or more.
(2) Span gas is 100%FS or less.
(3) Between zero and span of the smallest range must be more than 2000 ppm.
Example 3: Two points of 0.6% and 0.8% in the 1% range
Example 4: Two points of 20.6% and 90% in the 100% range
3) 1-point calibration “1Pnt”
Principally, 1-point calibration allows obtaining an accurate concentration in an area near the
calibration point, but the error may become greater as the distance from the calibration point
increases. This is a useful calibration method when it is used in some limited areas. Select
one point in an area as close to the concentration you want to measure as possible to perform
